| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Heterotrophic organisms ranging from E. coli to humans rely on the chemical energy found mainly in carbohydrate molecules. Many of these carbohydrates are produced by photosynthesis , the biochemical process by which phototrophic organisms convert solar energy (sunlight) into chemical energy. Although photosynthesis is most commonly associated with plants, microbial photosynthesis is also a significant supplier of chemical energy, fueling many diverse ecosystems. In this section, we will focus on microbial photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis takes place in two sequential stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions ( [link] ). In the light-dependent reaction s , energy from sunlight is absorbed by pigment molecules in photosynthetic membranes and converted into stored chemical energy. In the light-independent reaction s , the chemical energy produced by the light-dependent reactions is used to drive the assembly of sugar molecules using CO 2 ; however, these reactions are still light dependent because the products of the light-dependent reactions necessary for driving them are short-lived. The light-dependent reactions produce ATP and either NADPH or NADH to temporarily store energy. These energy carriers are used in the light-independent reactions to drive the energetically unfavorable process of “fixing” inorganic CO 2 in an organic form, sugar.
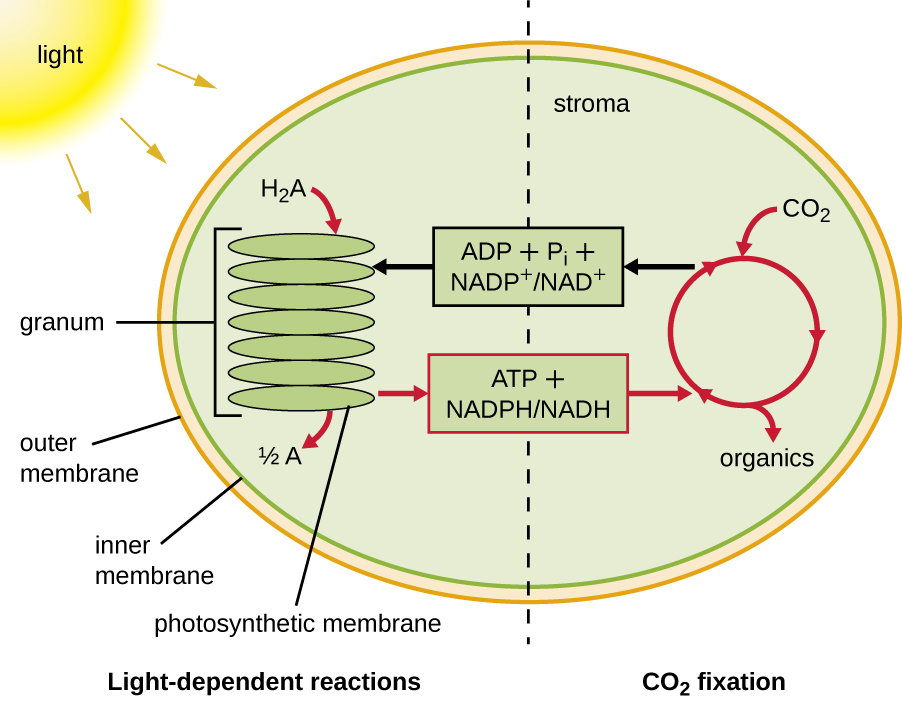
In all phototrophic eukaryotes , photosynthesis takes place inside a chloroplast , an organelle that arose in eukaryotes by endosymbiosis of a photosynthetic bacterium (see Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells ). These chloroplasts are enclosed by a double membrane with inner and outer layers. Within the chloroplast is a third membrane that forms stacked, disc-shaped photosynthetic structures called thylakoid s ( [link] ). A stack of thylakoids is called a granum , and the space surrounding the granum within the chloroplast is called stroma .
Photosynthetic membranes in prokaryotes, by contrast, are not organized into distinct membrane-enclosed organelles; rather, they are infolded regions of the plasma membrane. In cyanobacteria, for example, these infolded regions are also referred to as thylakoids. In either case, embedded within the thylakoid membranes or other photosynthetic bacterial membranes are photosynthetic pigment molecules organized into one or more photosystems, where light energy is actually converted into chemical energy.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?