| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The conflict over which policy tool to use can be frustrating to those who want to categorize economics as “liberal” or “conservative,” or who want to use economic models to argue against their political opponents. But the AD–AS model can be used both by advocates of smaller government, who seek to reduce taxes and government spending, and by advocates of bigger government, who seek to raise taxes and government spending. Economic studies of specific taxing and spending programs can help to inform decisions about whether taxes or spending should be changed, and in what ways. Ultimately, decisions about whether to use tax or spending mechanisms to implement macroeconomic policy is, in part, a political decision rather than a purely economic one.
Fiscal policy can also contribute to pushing aggregate demand beyond potential GDP in a way that leads to inflation. As shown in [link] , a very large budget deficit pushes up aggregate demand, so that the intersection of aggregate demand (AD 0 ) and aggregate supply (SRAS 0 ) occurs at equilibrium E 0 , which is an output level above potential GDP. This is sometimes known as an “overheating economy” where demand is so high that there is upward pressure on wages and prices, causing inflation. In this situation, contractionary fiscal policy involving federal spending cuts or tax increases can help to reduce the upward pressure on the price level by shifting aggregate demand to the left, to AD 1 , and causing the new equilibrium E 1 to be at potential GDP, where aggregate demand intersects the LRAS curve.
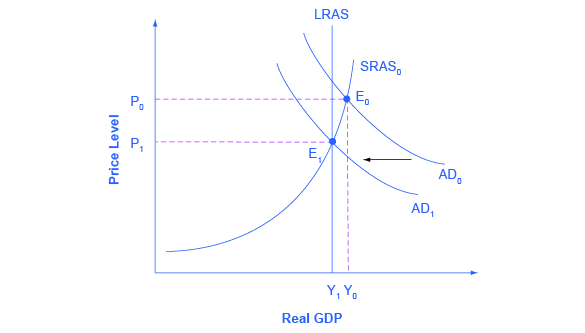
Again, the AD–AS model does not dictate how this contractionary fiscal policy is to be carried out. Some may prefer spending cuts; others may prefer tax increases; still others may say that it depends on the specific situation. The model only argues that, in this situation, aggregate demand needs to be reduced.
Expansionary fiscal policy increases the level of aggregate demand, either through increases in government spending or through reductions in taxes. Expansionary fiscal policy is most appropriate when an economy is in recession and producing below its potential GDP. Contractionary fiscal policy decreases the level of aggregate demand, either through cuts in government spending or increases in taxes. Contractionary fiscal policy is most appropriate when an economy is producing above its potential GDP.
Specify whether expansionary or contractionary fiscal policy would seem to be most appropriate in response to each of the situations below and sketch a diagram using aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves to illustrate your answer:
Alesina, Alberto, and Francesco Giavazzi. Fiscal Policy after the Financial Crisis (National Bureau of Economic Research Conference Report) . Chicago: University Of Chicago Press, 2013.
Martin, Fernando M. “Fiscal Policy in the Great Recession and Lessons from the Past.” Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis: Economic Synopses . no. 1 (2012). http://research.stlouisfed.org/publications/es/12/ES_2012-01-06.pdf.
Bivens, Josh, Andrew Fieldhouse, and Heidi Shierholz. “From Free-fall to Stagnation: Five Years After the Start of the Great Recession, Extraordinary Policy Measures Are Still Needed, But Are Not Forthcoming.” Economic Policy Institute . Last modified February 14, 2013. http://www.epi.org/publication/bp355-five-years-after-start-of-great-recession/.
Lucking, Brian, and Dan Wilson. Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco, “FRBSF Economic Letter—U.S. Fiscal Policy: Headwind or Tailwind?” Last modified July 2, 2012. http://www.frbsf.org/economic-research/publications/economic-letter/2012/july/us-fiscal-policy/.
Greenstone, Michael, and Adam Looney. Brookings. “The Role of Fiscal Stimulus in the Ongoing Recovery.” Last modified July 6, 2012. http://www.brookings.edu/blogs/jobs/posts/2012/07/06-jobs-greenstone-looney.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Macroeconomics' conversation and receive update notifications?