| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The most important thing to learn about the indication of the beat is that the beat must be clear to the ensemble. In order for this to occur, the conductor must make one beat, the downbeat, slightly more important than the others. The ensemble cannot determine beats two, three, or four if they are not certain which beat is beat one. The downbeat should be the only beat that is made at the center of the base of the conducting plane. Some conductors describe all beats as arriving at the same point as the downbeat. In this author's opinion, this action blurs the beat distinction for the ensemble and weakens the gesture noting the first beat of the measure.
Clarity is of utmost importance in a conductor's gestures. The ensemble is relying on a conductor for many things but most importantly, for a clear indication of the beat. In any work, but particularly in a work with complex rhythms, the ensemble is most interested in knowing where beat one is. Orchestral players are probably the most critical of the choral conductor whose gestures are so mushy that they cannot determine the beat. Occasionally, when a conductor hears that the precision is slipping in a performance, he will quickly stop any extraneous motion with his hands and concentrate on giving the ensemble nothing more than the simple beat pattern. This pattern must be the core of every conductor's conducting style.
The conductor's gesture must have some sort of rebound in order for the ensemble to be able to discern the ictus ; the exact moment when the conducting gesture indicates the rhythmic pulse. The rebound should not be too high or it will confuse the motion toward the next beat. The exact distance will depend upon the style and tempo of the piece. In faster tempos the rebound will be short and quick, whereas in slower tempos it may be a little higher and slower.
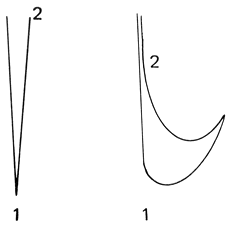
The following beat patterns are the ones that will be used in almost all conducting situations. There are some examples of new music that involve combinations of these patterns or are so different that new patterns must be created by the conductor to fit the music.
All of the patterns assume that the conductor is conducting with the right hand. The left hand is reserved primarily for gestures other than time-beating. Although a few conductors conduct witht the left hand it is best, to avoid confusion as one conducts various ensembles, to use the right hand, if possible, to conduct the patterns given below. Practice each pattern until it becomes comfortable to you. Do not attempt the combination practicing suggested later until you have practiced each pattern separately.
The most fundamental of the patterns is the two-beat pattern (the first figure in figure 1). In fast tempos this pattern is simply down-up. When the tempo is slower, the pattern will be as indicated in the second figure in figure 1.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Choral techniques' conversation and receive update notifications?