| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
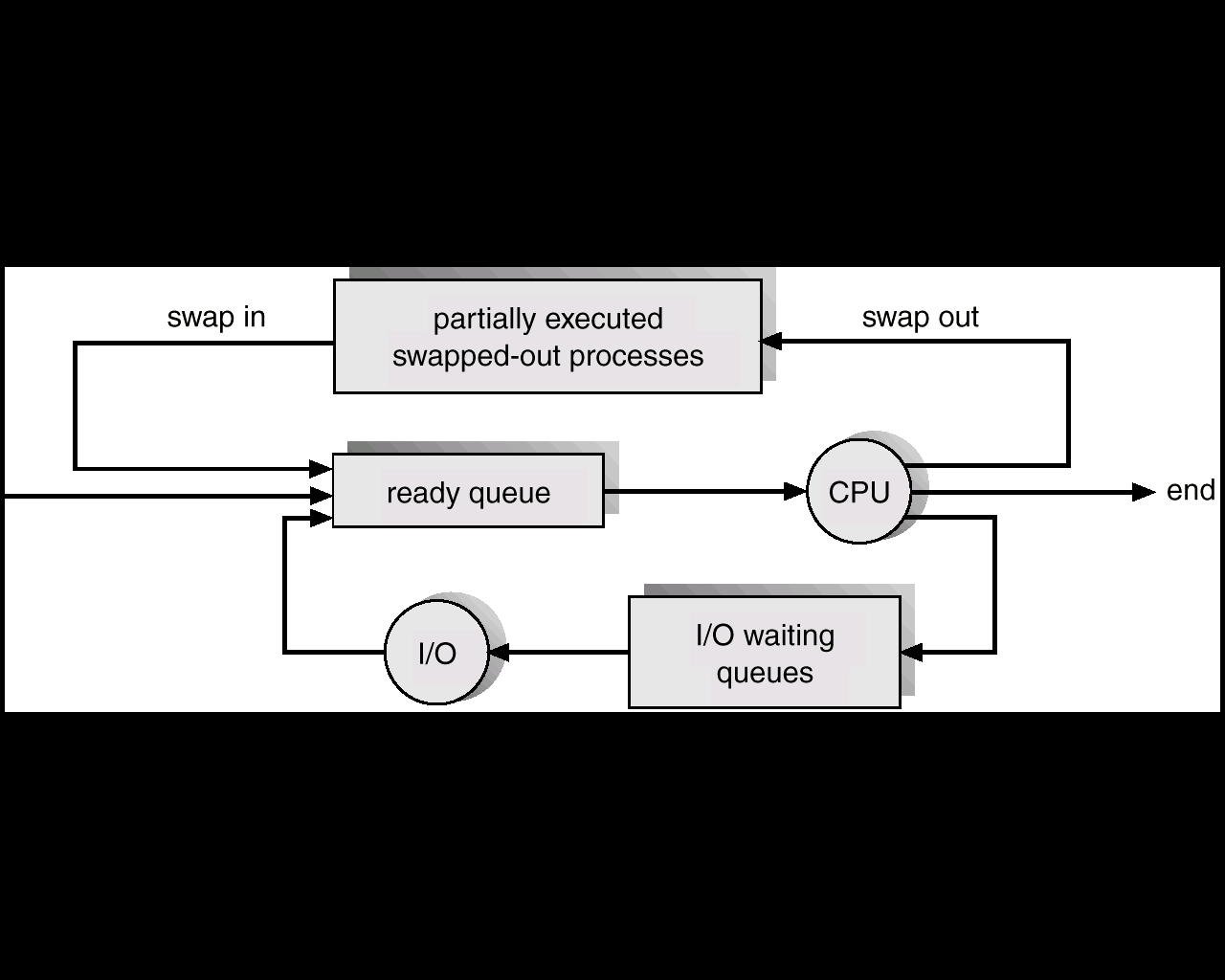
Hình III‑6-Lưu đồ bổ sung định thời trung bình tới hàng đợi
Chuyển CPU tới một quá trình khác yêu cầu lưu trạng thái của quá trình cũ và nạp trạng thái được lưu cho quá trình mới. Tác vụ này được xem như chuyển ngữ cảnh (context switch). Ngữ cảnh của quá trình được hiện diện trong PCB của quá trình; Nó chứa giá trị các thanh ghi, trạng thái quá trình (hình III.1) và thông tin quản lý bộ nhớ. Khi chuyển ngữ cảnh ngữ cảnh xảy ra, nhân lưu ngữ cảnh của quá trình cũ trong PCB của nó và nạp ngữ cảnh được lưu của quá trình mới được định thời để chạy. Thời gian chuyển ngữ cảnh là chi phí thuần vì hệ thống không thực hiện công việc có ích trong khi chuyển. Tốc độ của nó khác từ máy này tới máy khác phụ thuộc vào tốc độ bộ nhớ, số lượng thanh ghi phải được chép và sự tồn tại của các chỉ thị đặc biệt (như chỉ thị để nạp và lưu tất cả thanh ghi). Điển hình dãy tốc độ từ 1 tới 1000 mili giây.
Những lần chuyển đổi ngữ cảnh phụ thuộc nhiều vào hỗ trợ phần cứng. Thí dụ, vài bộ xử lý (như Sun UltraSPARC) cung cấp nhiều tập thanh ghi. Một chuyển ngữ cảnh đơn giản chứa chuyển đổi con trỏ tới tập thanh ghi hiện hành. Dĩ nhiên, nếu quá trình hoạt động vượt quá tập thanh ghi thì hệ thống sắp xếp lại dữ liệu thanh ghi tới và từ bộ nhớ. Cũng vì thế mà hệ điều hành phức tạp hơn và nhiều công việc được làm hơn trong khi chuyển ngữ cảnh. Kỹ thuật quản lý bộ nhớ nâng cao có thể yêu cầu dữ liệu bổ sung để được chuyển với mỗi ngữ cảnh. Thí dụ, không gian địa chỉ của quá trình hiện hành phải được lưu khi không gian của tác vụ kế tiếp được chuẩn bị dùng. Không gian địa chỉ được lưu như thế nào và lượng công việc được yêu cầu để lưu nó phụ thuộc vào phương pháp quản lý bộ nhớ của hệ điều hành. Chuyển ngữ cảnh có thể dẫn đến thắt cổ chai năng lực thực hiện vì thế các lập trình viên đang sử dụng các cấu trúc mới để tránh nó bất cứ khi nào có thể.
Các quá trình trong hệ thống có thể thực thi đồng hành và chúng phải được tạo và xóa tự động. Do đó, hệ điều hành phải cung cấp một cơ chế (hay phương tiện) cho việc tạo quá trình và kết thúc quá trình.
Quá trình có thể tạo nhiều quá trình mới, bằng một lời gọi hệ thống create-process, trong khi thực thi. Quá trình tạo gọi là quá trình cha, ngược lại các quá trình mới được gọi là quá trình con của quá trình đó. Mỗi quá trình mới này sau đó có thể tạo các quá trình khác, hình thành một cây quá trình (hình III-7).
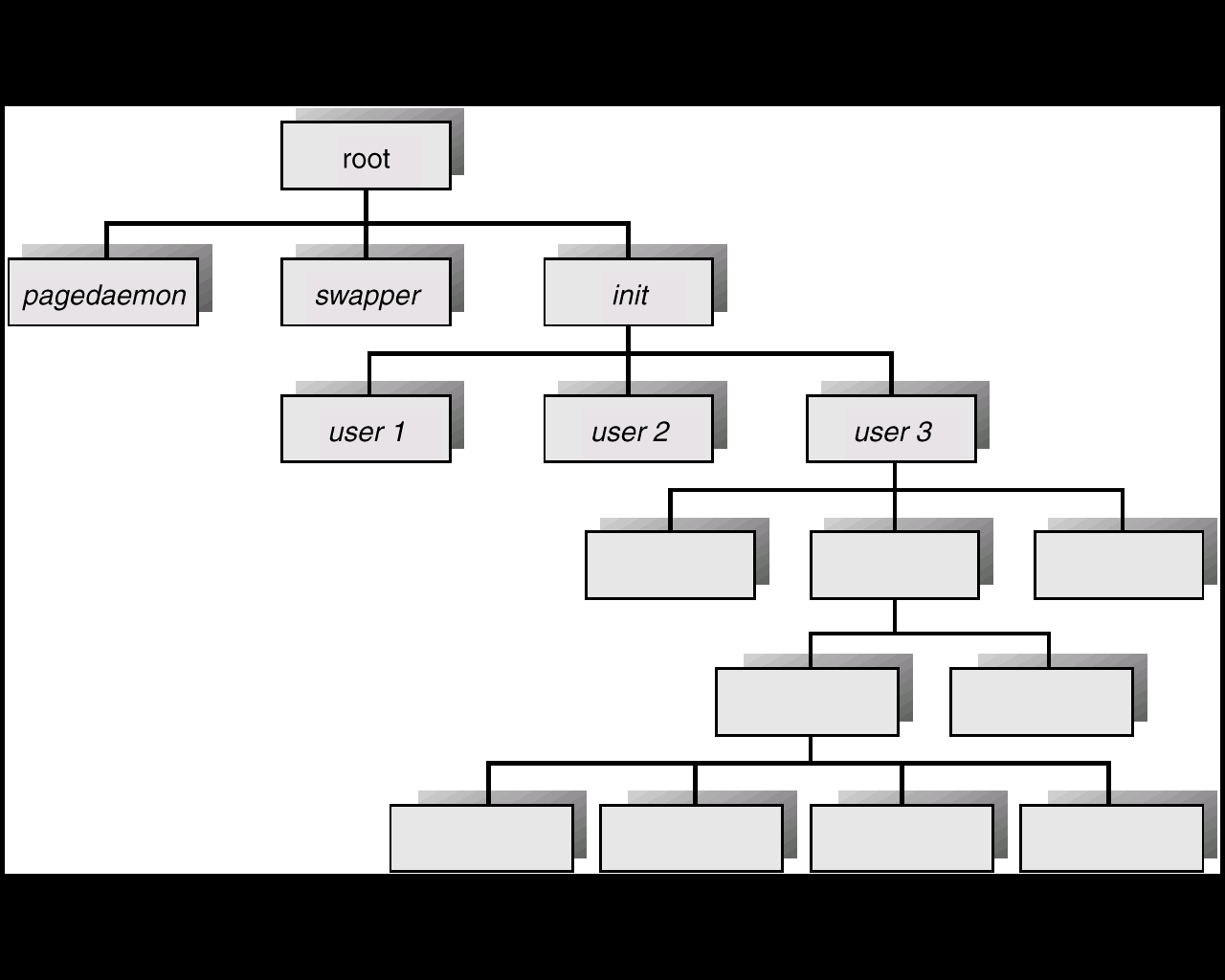
Hình III‑7-Cây quá trình trên một hệ thống UNIX điển hình
Thông thường, một quá trình sẽ cần các tài nguyên xác định (như thời gian CPU, bộ nhớ, tập tin, thiết bị nhập/xuất ) để hoàn thành tác vụ của nó. Khi một quá trình tạo một quá trình con, quá trình con có thể nhận tài nguyên của nó trực tiếp từ hệ điều hành hay nó có thể bị ràng buộc tới một tập con các tài nguyên của quá trình cha. Quá trình cha có thể phải phân chia các tài nguyên giữa các quá trình con hay có thể chia sẻ một số tài nguyên (như bộ nhớ và tập tin) giữa nhiều quá trình con. Giới hạn một quá trình con tới một tập con tài nguyên của quá trình cha ngăn chặn bất cứ quá trình từ nạp chồng hệ thống bằng cách tạo quá nhiều quá trình con.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Hệ điều hành' conversation and receive update notifications?