| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
If you have chosen the transposition because you want a particular key, then you should already know what key signature to use. (If you don't, see Key Signature .) If you have chosen the transposition because you wanted a particular interval (say, a whole step lower or a perfect fifth higher), then the key changes by the same interval. For example, if you want to transpose a piece in D major up one whole step , the key also moves up one whole step, to E major. Transposing a piece in B minor down a major third will move the key signature down a major third to G minor. For more information on and practice identifying intervals, see Interval . For further information on how moving music up or down changes the key signature, see The Circle of Fifths .

Now rewrite the music, changing all the notes by the correct interval. You can do this for all the notes in the key signature simply by counting lines and spaces. As long as your key signature is correct, you do not have to worry about whether an interval is major, minor, or perfect.
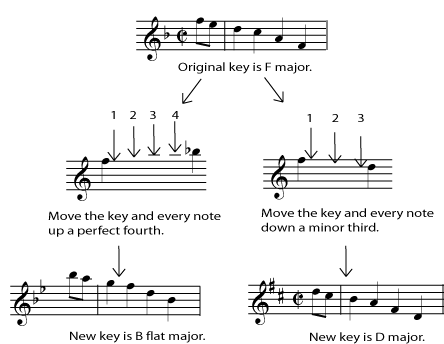
Most notes can simply be moved the correct number of lines and spaces. Whether the interval is minor, major, or perfect will take care of itself if the correct key signature has been chosen. But some care must be taken to correctly transpose accidentals. Put the note on the line or space where it would fall if it were not an accidental, and then either lower or raise it from your new key signature. For example, an accidental B natural in the key of E flat major has been raised a half step from the note in the key (which is B flat). In transposing down to the key of D major, you need to raise the A natural in the key up a half step, to A sharp. If this is confusing, keep in mind that the interval between the old and new (transposed) notes (B natural and A sharp) must be one half step, just as it is for the notes in the key.


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Understanding your french horn' conversation and receive update notifications?