| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When light travels from one medium to another, it will be bent away from its original path. When it travels from an optically dense medium like water or glass to a less dense medium like air, it will be refracted away from the normal ( [link] ). Whereas, if it travels from a less dense medium to a denser one, it will be refracted towards the normal ( [link] ).

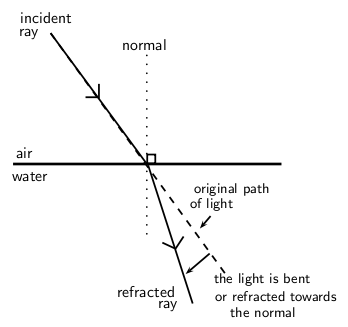
Just as we defined an angle of reflection in the previous section, we can similarly define an angle of refraction as the angle between the surface normal and the refracted ray. This is shown in [link] .


Which is easier to travel through, air or water? People usually travel faster through air. So does light! The speed of light and therefore the degree of bending of the light depends on the refractive index of material through which the light passes. The refractive index (symbol ) is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to its speed in the material.
The refractive index of a material is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to its speed in the medium.
The symbol is used to represent the speed of light in a vacuum.
For purposes of calculation, we use . A vacuum is a region with no matter in it, not even air. However, the speed of light in air is very close to that in a vacuum.
The refractive index (symbol ) of a material is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to its speed in the material and gives an indication of how difficult it is for light to get through the material.
where
| = | refractive index (no unit) |
| = | speed of light in a vacuum ( ) |
| = | speed of light in a given medium ( ) |
Using
we can also examine how the speed of light changes in different media, because the speed of light in a vacuum ( ) is constant.
If the refractive index increases, the speed of light in the material must decrease. Light therefore travels slowly through materials of high .
[link] shows refractive indices for various materials. Light travels slower in any material than it does in a vacuum, so all values for are greater than 1.
| Medium | Refractive Index |
| Vacuum | 1 |
| Helium | 1,000036 |
| Air* | 1,0002926 |
| Carbon dioxide | 1,00045 |
| Water: Ice | 1,31 |
| Water: Liquid ( C) | 1,333 |
| Acetone | 1,36 |
| Ethyl Alcohol (Ethanol) | 1,36 |
| Sugar solution (30%) | 1,38 |
| Fused quartz | 1,46 |
| Glycerine | 1,4729 |
| Sugar solution (80%) | 1,49 |
| Rock salt | 1,516 |
| Crown Glass | 1,52 |
| Sodium chloride | 1,54 |
| Polystyrene | 1,55 to 1,59 |
| Bromine | 1,661 |
| Sapphire | 1,77 |
| Glass (typical) | 1,5 to 1,9 |
| Cubic zirconia | 2,15 to 2,18 |
| Diamond | 2,419 |
| Silicon | 4,01 |
Now that we know that the degree of bending, or the angle of refraction, is dependent on the refractive index of a medium, how do we calculate the angle of refraction?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Maths test' conversation and receive update notifications?