| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
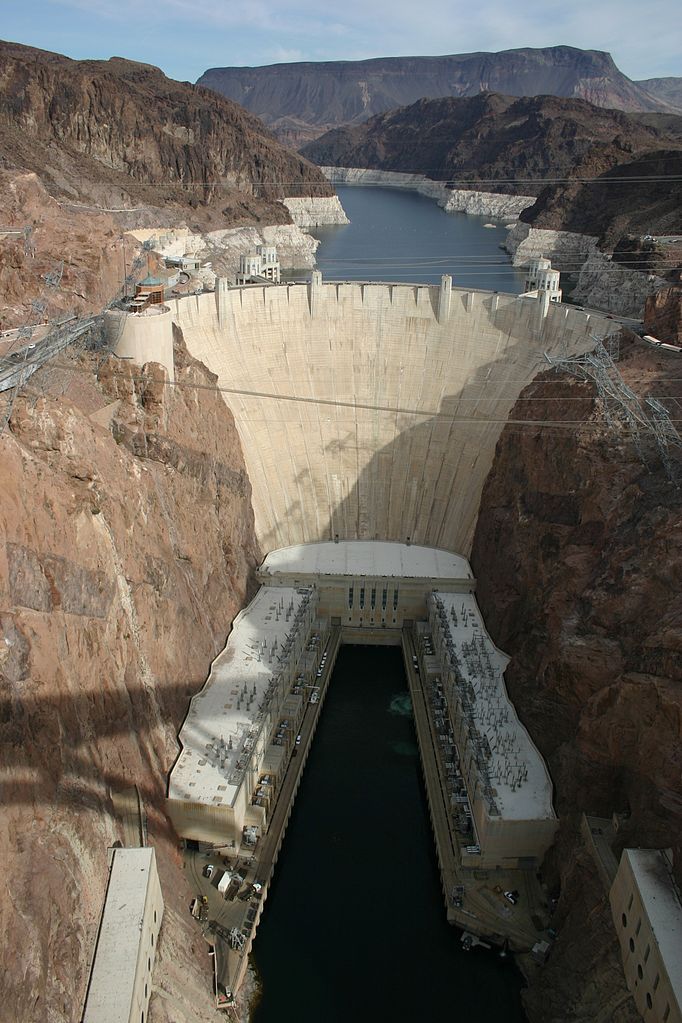
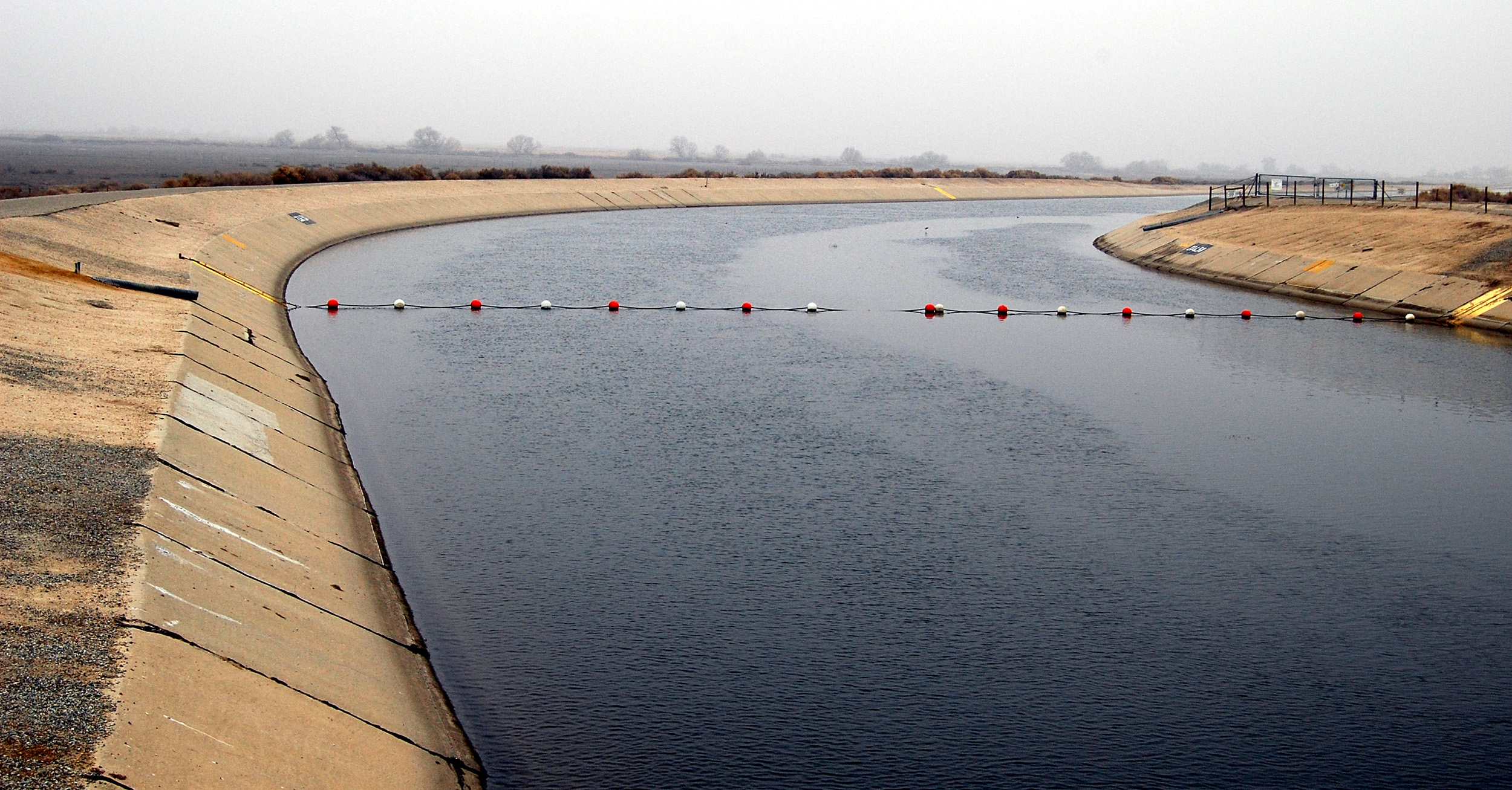
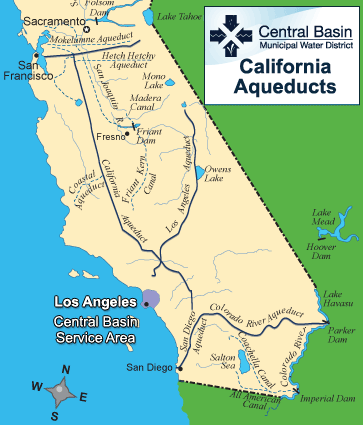
The current and future water crisis described above requires multiple approaches to extending our fresh water supply and moving towards sustainability. Some of the longstanding traditional approaches include dams and aqueducts . Reservoirs that form behind dams in rivers can collect water during wet times and store it for use during dry spells (see Figure Hoover Dam, Nevada, U.S. ). They also can be used for urban water supplies. New York City has a large number of reservoirs and controlled lakes up to 200 km away to meet the water demands of its large population. Other benefits of dams and reservoirs are hydroelectricity, flood control, and recreation. Some of the drawbacks are evaporative loss of reservoir water in arid climates, downstream river channel erosion, and impact on the ecosystem including a change from a river to lake habitat and interference with fish migration and spawning. Aqueducts can move water from where it is plentiful to where it is needed (see Figure The California Aqueduct ). Southern California has a large and controversial network of aqueducts that brings in water from the Sierra Nevada Mountains in the north, the valleys in northern and central California, and the Colorado River to the east (see Figure Map of California Aqueducts ). Aqueducts can be controversial and politically difficult especially if the water transfer distances are large. One drawback is the water diversion can cause drought in the area from where the water is drawn. For example, Owens Lake and Mono Lake in central California began to disappear after their river inflow was diverted to the Los Angeles aqueduct. Owens Lake remains almost completely dry, but Mono Lake has recovered more significantly due to legal intervention.


The Colorado River, probably the most exploited river in the U.S., has many dams, some huge reservoirs, and several large aqueducts so that it can provide large amounts of fresh water to 7 states in the arid southwestern U.S. and Mexico. The primary use for the water is for a few large cities (Las Vegas, Phoenix, and Tuscon) and irrigation. Allocation of Colorado River water is strictly regulated. Fortunately, not all states use all of their water allocation because the total amount of allocated water is more than the typical Colorado River discharge. Colorado River water gets so saline due to evaporation along its course that the U.S. was forced to build a desalination plant near the border with Mexico so that it could be used for drinking and irrigation. The wetlands of the Colorado River delta and its associated ecosystem have been sadly degraded by the water overuse; some years, no river flow even reaches the ocean.
One method that actually can increase the amount of fresh water on Earth is desalination , which involves removing dissolved salt from seawater or saline groundwater. There are several ways to desalinate seawater including boiling, filtration, electrodialysis, and freezing. All of these procedures are moderately to very expensive and require considerable energy input, making the produced water much more expensive than fresh water from conventional sources. In addition, the processes create highly saline wastewater, which must be disposed of. Desalination is most common in the Middle East, where energy from oil is abundant but water is scarce.
Conservation means using less water and using it more efficiently. Around the home, conservation can involve both engineered features, such as high-efficiency clothes washers and low-flow showers and toilets, as well as behavioral decisions, such as growing native vegetation that require little irrigation in desert climates, turning off the water while you brush your teeth, and fixing leaky faucets. Rainwater harvesting involves catching and storing rainwater for reuse before it reaches the ground. Efficient irrigation is extremely important because irrigation accounts for a much larger water demand than public water supply. Water conservation strategies in agriculture include growing crops in areas where the natural rainfall can support them, more efficient irrigation systems such as drip systems that minimize losses due to evaporation, no-till farming that reduces evaporative losses by covering the soil, and reusing treated wastewater from sewage treatment plants. Recycled wastewater has also been used to recharge aquifers. There are a great many other specific water conservation strategies. Sustainable solutions to the water crisis must use a variety of approaches but they should have water conservation as a high priority.
What is the water cycle and why is it important to fresh water resources?
What are the relative merits of using surface water vs. groundwater as a water resource?
What should society learn from the case history of the Aral Sea?
Why is society facing a crisis involving water supply and how can we solve it?
Watkins, K. (2006). Beyond scarcity: Power, poverty and the global water crisis. Human Development Report 2006, United Nations Development Programme . Retrieved from (External Link)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Sustainability: a comprehensive foundation' conversation and receive update notifications?