| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
After reading this module, students should be able to
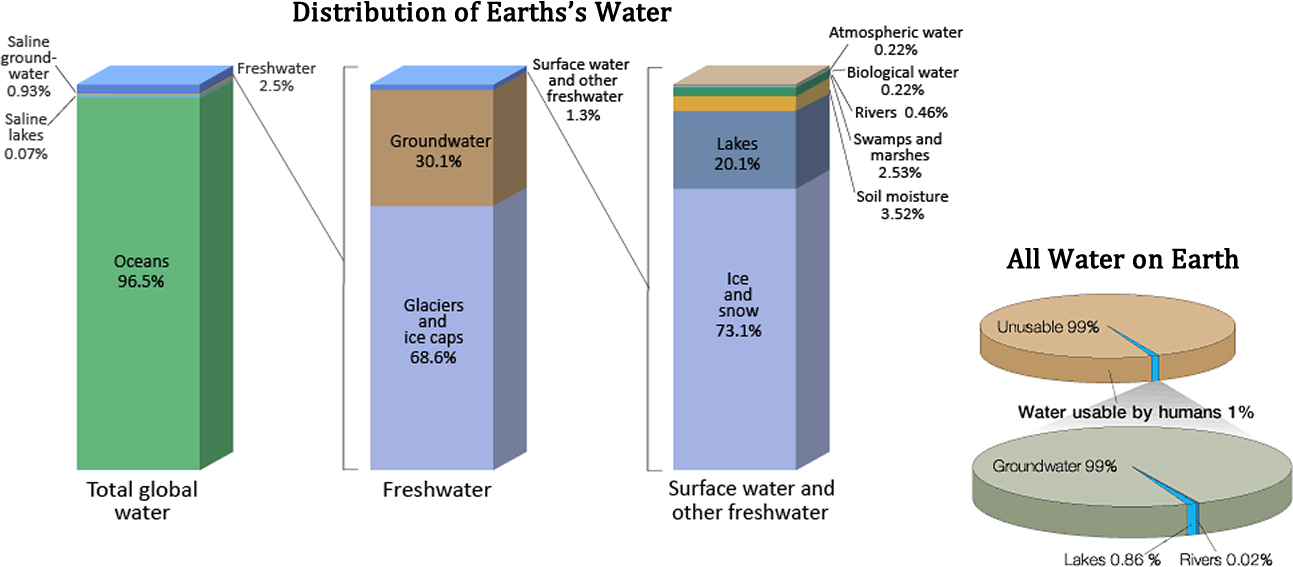
Water is the only substance that occurs naturally on earth in three forms: solid, liquid and gas. It is distributed in various locations, called water reservoirs . The oceans are by far the largest of the reservoirs with about 97% of all water but that water is too saline for most human uses (see Figure Earth's Water Reservoirs ). Ice caps and glaciers are the largest reservoirs of fresh water but this water is inconveniently located, mostly in Antarctica and Greenland. Shallow groundwater is the largest reservoir of usable fresh water. Although rivers and lakes are the most heavily used water resources, they represent only a tiny amount of the world’s water. If all of world's water was shrunk to the size of 1 gallon, then the total amount of fresh water would be about 1/3 cup, and the amount of readily usable fresh water would be 2 tablespoons.
The water cycle shows the movement of water through different reservoirs, which include oceans, atmosphere, glaciers, groundwater, lakes, rivers, and biosphere (see Figure The Water Cycle ). Solar energy and gravity drive the motion of water in the water cycle. Simply put, the water cycle involves water moving from the ocean to the atmosphere by evaporation, forming clouds. From clouds, it falls as precipitation (rain and snow) on both water and land, where it can move in a variety of ways. The water on land can either return to the ocean by surface runoff (unchannelized overland flow), rivers, glaciers, and subsurface groundwater flow, or return to the atmosphere by evaporation or transpiration (loss of water by plants to the atmosphere).
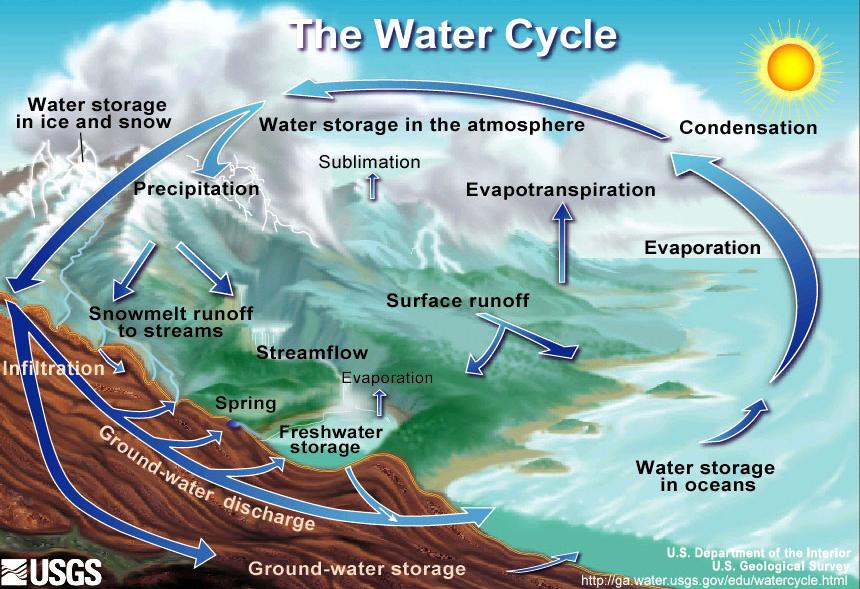
An important part of the water cycle is how water varies in salinity, which is the abundance of dissolved ions in water. Ocean water is called salt water because it is highly saline, with about 35,000 mg of dissolved ions per liter of seawater. Evaporation (where water changes from liquid to gas at ambient temperatures) is a distillation process that produces nearly pure water with almost no dissolved ions. As water vaporizes, it leaves the dissolved ions in the original liquid phase. Eventually, condensation (where water changes from gas to liquid) forms clouds and sometimes precipitation (rain and snow). After rainwater falls onto land, it dissolves minerals, which increases its salinity. Most lakes, rivers, and near-surface groundwater have a relatively low salinity and are called fresh water. The next several sections discuss important parts of the water cycle relative to fresh water resources.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Sustainability: a comprehensive foundation' conversation and receive update notifications?