| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
px2 = px1;
return 1;
}
else if (del>0.0)
{
px1 = (-b + sqrt(del))/(2*a);
px2 = (-b – sqrt(del))/(2*a);
return 2;
}
else
return 3;
}
Note: The called-by-value parameters a, b, and c are used to passed the data from the calling function to the called function, and the two reference parameters px1 and px2 are used to pass the results from the called function to the calling function.
In C++, it’s possible for a function to call itself. Functions that do so are called seft-referential or recursive functions.
Example: To compute factorial of an integer
1! = 1
n! = n*(n-1)!
Example
// Recursive factorial function
#include<iostream.h>
#include<iomanip.h>
unsigned long factorial( unsigned long );
int main()
{
for ( int i = 0; i<= 10; i++ )
cout<<setw( 2 )<<i<<"! = "<<factorial( i )<<endl;
return 0;
}
// Recursive definition of function factorial
unsigned long factorial( unsigned long number )
{
if (number<1) // base case
return 1;
else // recursive case
return number * factorial( number - 1 );
}
The output of the above program:
0! = 1
1! = 1
2! = 2
3! = 6
4! = 24
5! = 120
6! = 720
7! = 5040
8! = 40320
9! = 362880
10! = 3628800
The mechanism that makes it possible for a C++ function to call itself is that C++ allocates new memory locations for all function parameters and local variables as each function is called. There is a dynamic data area for each execution of a function. This allocation is made dynamically, as a program is executed, in a memory area referred as the stack.
A memory stack is an area of memory used for rapidly storing and retrieving data areas for active functions. Each function call reserves memory locations on the stack for its parameters, its local variables, a return value, and the address where execution is to resume in the calling program when the function has completed execution (return address). Inserting and removing items from a stack are based on last-in/first-out mechanism.
Thus, when the function call factorial(n) is made, a data area for the execution of this function call is pushed on top of the stack. This data area is shown as figure below.
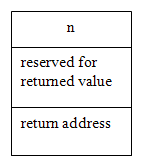
The progress of execution for the recursive function factorial applied with n = 3 is as follows:

During the execution of the function call factorial(3), the memory stack evolves as shown in the figure below. Whenever the recursive function calls itself, a new data area is pushed on top of the stack for that function call. When the execution of the recursive function at a given level is finished, the corresponding data area is popped from the stack and the return value is passed back to its calling function.

Example: Fibonacci numbers:
F(N) = F(N-1) + F(N-2) for N>= 2
F(0) = F(1) = 1
#include<iostream.h>
int fibonacci(int);
int main()
{
int m;
cout<<"Enter a number: ";
cin>>m;
cout<<"The fibonacci of "<<m<<" is: "
<<fibonacci(m)<<endl;
return 0;
}
int fibonacci(int n)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Programming fundamentals in c++' conversation and receive update notifications?