| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
How will we write the grams in the table above as kg?
I know 1 000 g = 1 kg
Thus: 1 g = kg= 0,001 kg
In the same way 17 g will be 17 thousandths of a kg.
17 g = 0,017 kg
and 234 g = 0,234 kg
4 387 g = 4 kg 387 g = 4,387 kg
1. Write the following as kg.
a) 9 g ............................
b) 26 g ............................
c) 89 g ............................
d) 436 g ............................
e) 2 309 g ............................
f) 5 006 g ............................
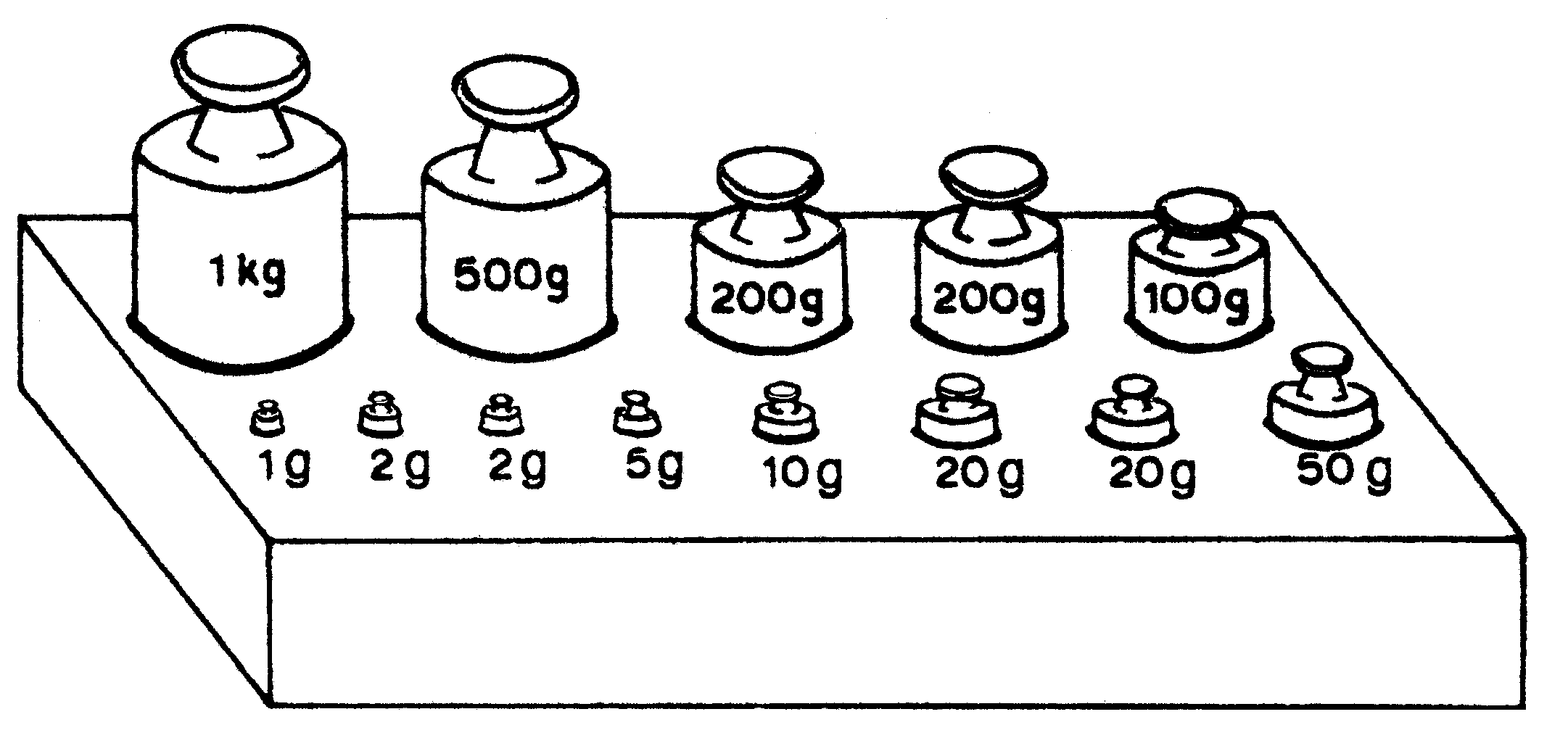
| Mass | Weights needed | |
| e.g. | 1,010 kg | 1 kg ; 10 g |
| 1,023 kg | .................................................................................................... | |
| 1,023 kg | .................................................................................................... | |
| 1,007 kg | .................................................................................................... | |
| 1,056 kg | .................................................................................................... | |
| 983 g | .................................................................................................... | |
| 724 g | .................................................................................................... |
4. Rounding off
4.1 Can you round off the following to the nearest kg?
(a) 7,6 kg .........................
(b) 0,5 kg .........................
(c) 4,2 kg .........................
(d) 2,5 kg .........................
4.2 Round off the following to the nearest ton:
(a) 20,8 t .........................
(b) 29,4 t .........................
(c) 1,5 t .........................
(d) 34,9 t .........................
BRAIN-TEASER!
You want to determine the mass of a chair. You have a bathroom scale, but the chair is too big for it and falls off. How can you determine the mass of the chair without using a bigger scale?
| LO 4 |
| MeasurementThe learner will be able to use appropriate measuring units, instruments and formulae in a variety of contexts. |
| We know this when the learner: |
| 4.1 reads, tells and writes analogue, digital and 24-hour time to at least the nearest minute and second; |
| 4.2 solves problems involving calculation and conversion between appropriate time units including decades, centuries and millennia; |
| 4.3 uses time-measuring instruments to appropriate levels of precision including watches and stopwatches; |
| 4.4 describes and illustrates ways of representing time in different cultures throughout history; |
4.5 estimates, measures, records, compares and orders two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects using S.I. units with appropriate precision for:
|
| 4.6 solves problems involving selecting, calculating with and converting between appropriate S.I. units listed above, integrating appropriate contexts for Technology and Natural Sciences; |
4.7 uses appropriate measuring instruments (with understanding of their limitations) to appropriate levels of precision including:
|
ACTIVITY 1
| √ | √ | ||||
| √ | √ | ||||
| √ |
ACTIVITY 2
Bathroom scale; spring balance; kitchen scale; balance/scale
1.
1.1: 6,25 kg
1.2: 88,5 kg
1.3: 3 kg
1.4: 17,68 kg
1.5: 210 g
1.6: 172 kg
2.
2.1: 3,050 kg
2.2: 5,710 kg
2.3: 1,215 kg
2.4: 0,604 kg
ACTIVITY 4
1. 1.1: 0,009
1.2: 0,026
1.3: 0,089
1.4 0,436
1.5 2,309
1.6 5,006
3.
| MASS | PIECES NEEDED |
| 1 kg; 20 g; 2 g; 1 g | |
| 1 kg; 20 g; 5 g; 2 g; 1 g | |
| 1 kg; 5 g; 2 g | |
| 1 kg; 50 g; 5 g; 1 g | |
| 20 g; 10 g; 2 g; 1 g500 g; 200 g; 200 g; 50 g | |
| 500 g; 200 g; 20 g; 2 g; 2 g |
4.
4.1
a) 8
b) 1
c) 4
d) 3
4.2
a) 21
b) 29
c) 2
d) 35
BRAIN-TEASER!
Stand on scale and take the reading; then hold chair above your head while on the scale and take reading again (or vive versa); the difference in the readings is the mass of the chair.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 5' conversation and receive update notifications?