| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Discuss any difficult vocabulary.
2. Look at Susan’s last sentence. Discuss what would happen when they take Lisa home.
Then ask the children to consider: Do they think Lisa will find her parents? What could have happened to them? Remind them that they would naturally want to find her.
Stress that their suggestions must be reasonable and realistic.
Their answers could be evaluated for LO 5, as well as LO 2.
If the answer is completely unrealistic, and doesn’t take any known factors into account, it would be rated 1.
If they take into account that Lisa has only been missing for two days and that her parents could have landed elsewhere and are now looking for her - that would be rated 3.
To be rated 5, they would have to have thought of radio contact and that a generalised search would already be in progress.
The children must listen to each other’s answers and comment on the likelihood of any of the solutions.
Depending on your time, the stories may be read out aloud to the class or allow learners to swap stories and read each other’s silently.
Encourage the children to find out about early writing in different civilisations. Let them tell the class what they have found out or make a small poster about their findings. Some children could also copy out examples of hieroglyphics or cuneiform for display purposes.
Paul and Susan went to the beach. They wanted to find some shells. Susan was looking in the rock pools. She saw lots of little fish and crabs. “I’m sorry I forgot to bring my net,” she thought.
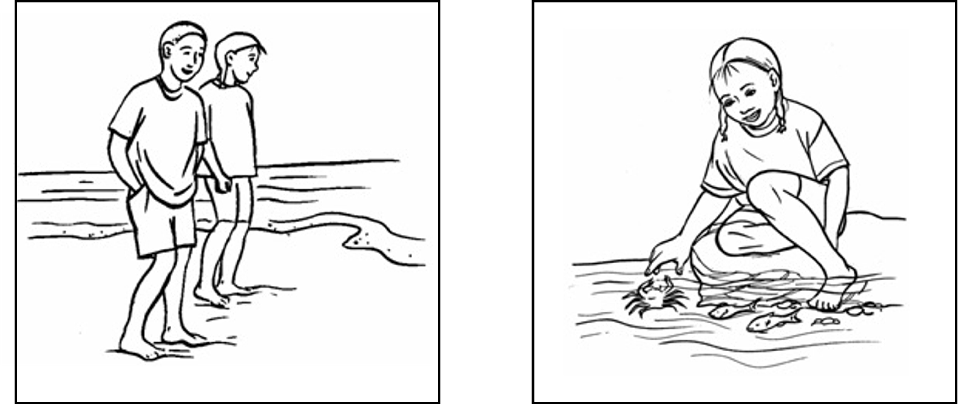
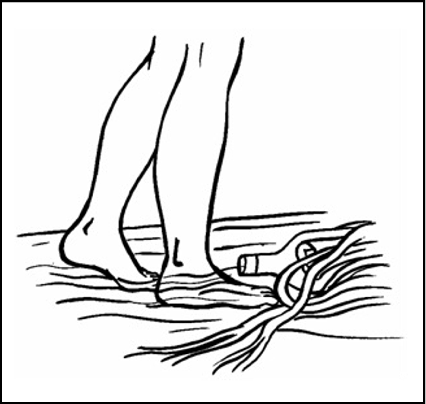
Paul was walking along the beach. He went into the water. The waves splashed over his toes. He saw the green seaweed. He wanted to pick it up.
“Yugh! It’s so slimy!” he said. Then he looked again. There was a bottle in the seaweed!
| LO 3.2.1 |
“Susan!” he shouted. “Come and look here!”
Susan ran to him. “What is it?” she asked.
“Look at this.” Paul showed her the bottle.
“So what? It’s only a bottle. People are very bad. They litter everywhere.” Susan wanted to go back to her rock pool.
“No wait. Can’t you see? There is something in the bottle”, said Paul.
Sure enough, the bottle had a cork top and inside was a piece of paper.
“It’s a message in a bottle!” Susan was so excited. “Open it quickly!”
Paul picked the bottle up and struggled to get the cork out. His hands were shaking he was so excited. Suddenly the cork popped out. He shook the bottle upside down and the paper came out.
This is what it looked like:
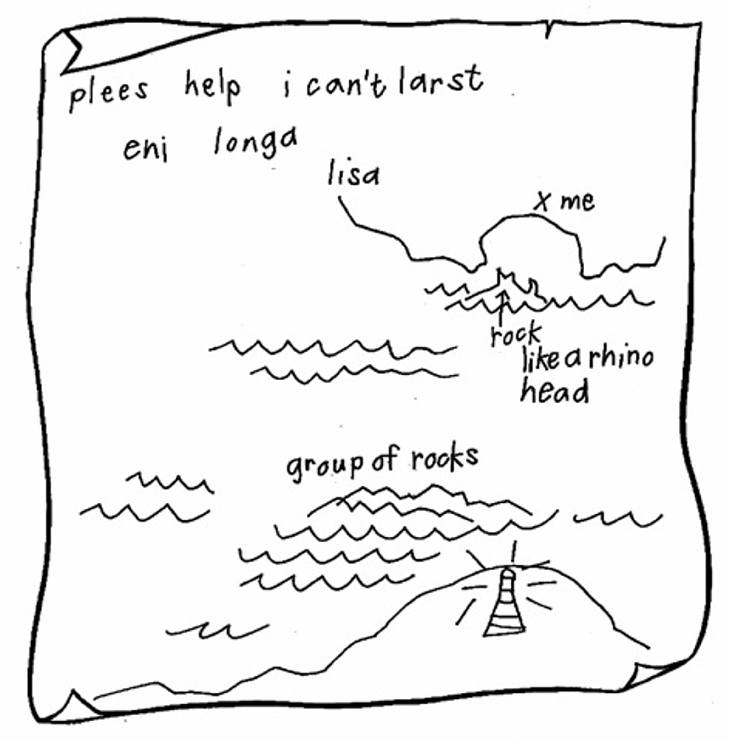
“We’ve got to help!” said Paul.
| LO 3.2.1 | LO 5.4.1 |
1. Why did Paul and Susan go to the beach?
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
2. Why did Susan need a net?
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
3. What did Paul find?
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
4. Was it easy to open the bottle? Yes/No. Find a word in the story to explain why you think so.
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
5. Paul and Susan read the message. What do you think they will do now?
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
6. Find a word which means:
speak loudly - ………………………………………………………………………….
smooth and slippery to touch - …………………………………………………………
throw rubbish about - ………………………………………………………………….
| LO 1.3.7 | LO 2.4.3 | LO 3.2.1 |

| LO 4.7.2 |
Learning Outcome 1: LISTENING : The learner is able to listen for information and enjoyment and respond appropriately and critically in a wider range of situations.
Assessment Standard 1.3: We know this when the learner listens with enjoyment to stories, poems, songs and other oral texts and shows understanding:
1.3.7 works out cause and effect in the oral text.
Learning Outcome 2: SPEAKING : The learner is able to communicate confidently and effectively in spoken language in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 2.4: We know this when the learner contributes to class and group discussions
2.4.3 suggests and elaborates ideas;
Learning Outcome 3: READING AND VIEWING : The learner is able to read and view for information and enjoyment and respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts.
Assessment Standard 3.2: We know this when the learner makes meaning of written text:
3.2.1 reads a story on own or with the teacher;
Learning Outcome 4: WRITING : The learner is able to write different kinds of factual and imaginative texts for a wide range of purposes.
Assessment Standard 4.7: We know this when the learner writes with increasing legibility:
4.7.2 forms letters clearly and easily.
Learning Outcome 5: THINKING AND REASONING : The learner is able to use language to think and reason, and access, process and use information for learning.
Assessment Standard 5.4: We know this when the learner processes information:
5.4.1 picks out selected information from a text and processes it.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English home language grade 2' conversation and receive update notifications?