| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
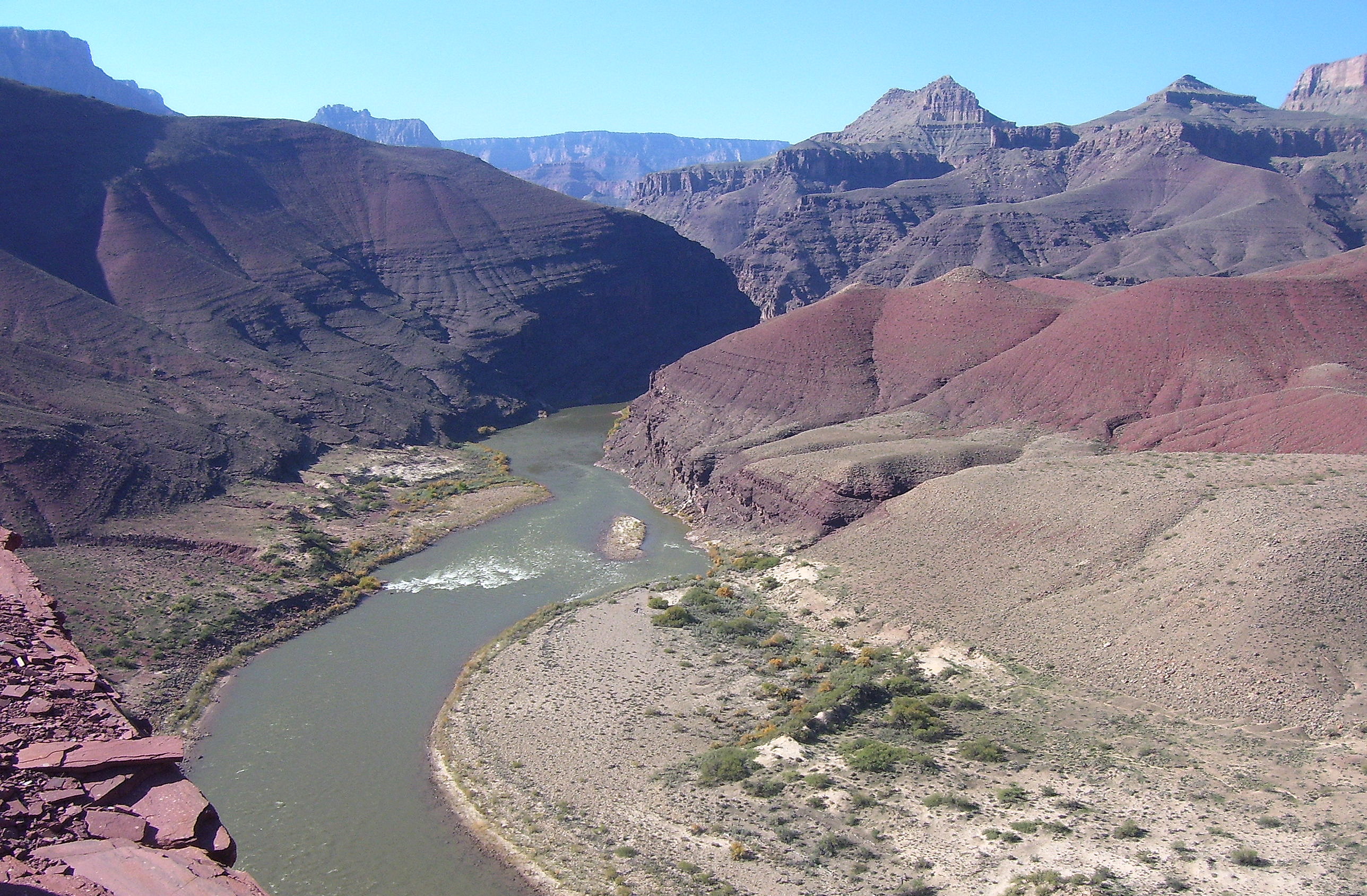



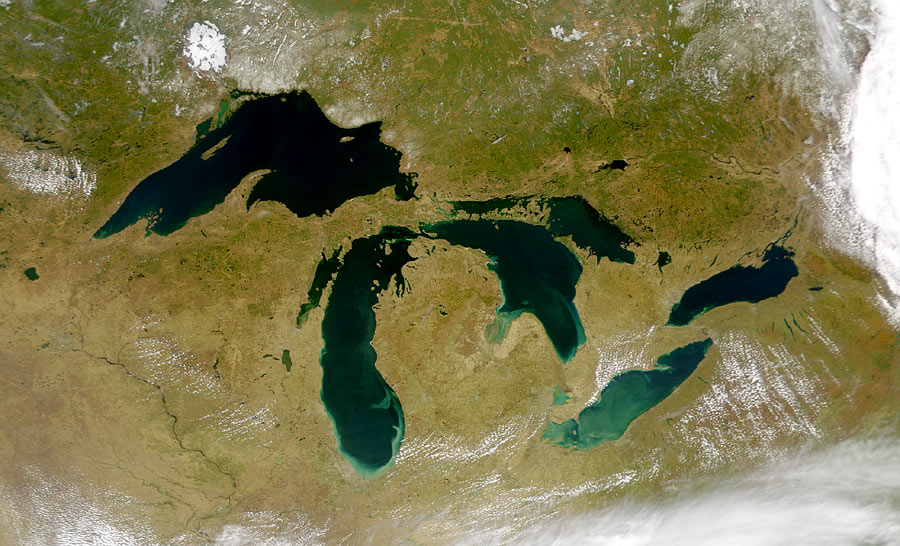
Lakes can also be an excellent source of fresh water for human use. They usually receive water from surface runoff and groundwater discharge. They tend to be short-lived on a geological time-scale because they are constantly filling in with sediment supplied by rivers. Lakes form in a variety of ways including glaciation (Great Lakes, North America, See Figure Great Lakes from Space ), recent tectonic uplift (Lake Tanganyika, Africa), and volcanic eruptions (Crater Lake, Oregon). People also create artificial lakes ( reservoirs ) by damming rivers. Large changes in climate can result in major changes in a lake’s size. As Earth was coming out of the last Ice Age about fifteen thousand years ago, the climate in the western U.S. changed from cool and moist to warm and arid, which caused more than100 large lakes to disappear. The Great Salt Lake in Utah is a remnant of a much larger lake called Lake Bonneville.
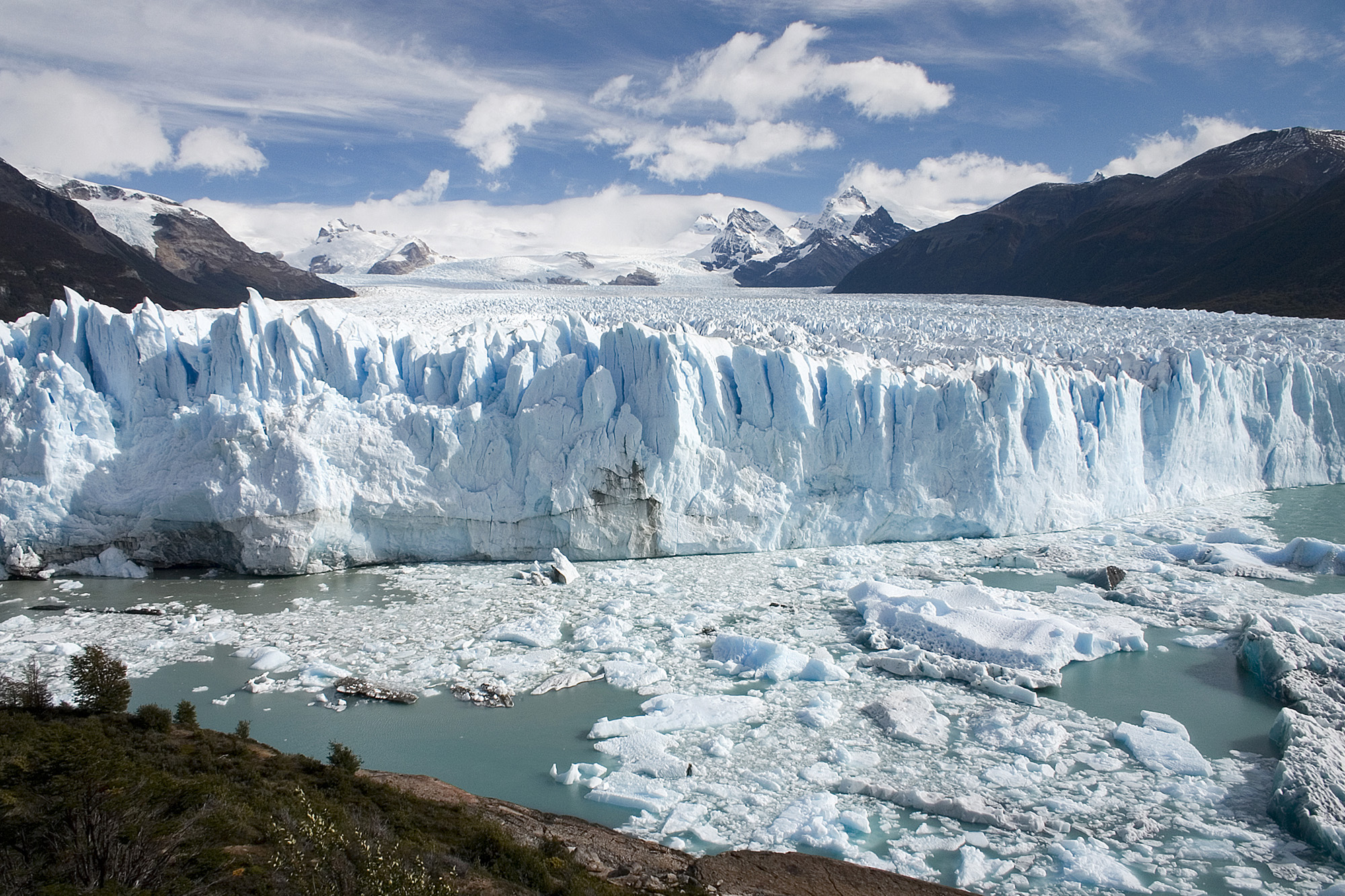
Although glaciers represent the largest reservoir of fresh water, they generally are not used as a water source because they are located too far from most people (see Figure Mountain Glacier in Argentina ). Melting glaciers do provide a natural source of river water and groundwater. During the last Ice Age there was as much as 50% more water in glaciers than there is today, which caused sea level to be about 100 m lower. Over the past century, sea level has been rising in part due to melting glaciers. If Earth’s climate continues to warm, the melting glaciers will cause an additional rise in sea level.

Although most people in the U.S. and the world use surface water, groundwater is a much larger reservoir of usable fresh water, containing more than 30 times more water than rivers and lakes combined. Groundwater is a particularly important resource in arid climates, where surface water may be scarce. In addition, groundwater is the primary water source for rural homeowners, providing 98% of that water demand in the U.S.. Groundwater is water located in small spaces, called pore space , between mineral grains and fractures in subsurface earth materials (rock or sediment, i.e., loose grains). Groundwater is not located in underground rivers or lakes except where there are caves, which are relatively rare. Between the land surface and the depth where there is groundwater is the unsaturated zone , where pore spaces contain only air and water films on mineral grains (see Figure Subsurface Water Terminology ). Groundwater is the name for water in the saturated zone and soil moisture describes water in the unsaturated zone. Therefore, groundwater is the underground water resource used by society but soil moisture is the principal water supply for most plants and is an important factor in agricultural productivity. Below the unsaturated zone is the saturated zone , where groundwater completely fills pore spaces in earth materials. The interface between the unsaturated zone and saturated zone is the water table . Most groundwater originates from rain or snowmelt, which infiltrates the ground and moves downward until it reaches the saturated zone. Other sources of groundwater include seepage from surface water (lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and swamps), surface water deliberately pumped into the ground, irrigation, and underground wastewater treatment systems, i.e., septic tanks. Recharge areas are locations where surface water infiltrates the ground rather than running off into rivers or evaporating. Wetlands and flat vegetated areas in general are excellent recharge areas.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Sustainability: a comprehensive foundation' conversation and receive update notifications?