| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Alle materie bestaan uit klein deeltjies (atome) wat voortdurend heen en weer beweeg en teen mekaar bots. Die deeltjies en hul beweging is baie, baie klein en ons kan dit nie sien nie. Vir ons lyk 'n stuk yster bloot soos 'n harde, soliede stuk metaal, maar selfs die hardste metaal bestaan uit sulke bewegende deeltjies (atome).
Materie sit uit as dit verhit word omdat die atome waaruit dit bestaan energie absorbeer en dus meer beweeg en harder teen mekaar bots. Die atome word dus van mekaar af weg geforseer en die stof sit uit.
Wanneer die temperatuur daal (die stof verloor hitte), verloor die deeltjies energie en beweeg minder. Die spasie tussen hulle word kleiner omdat hulle minder teen mekaar bots, en die stof krimp.
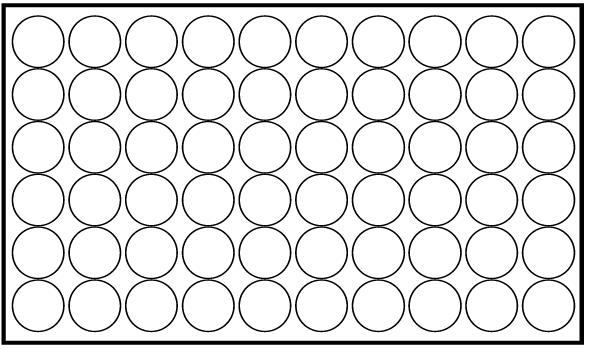
Inkrimping
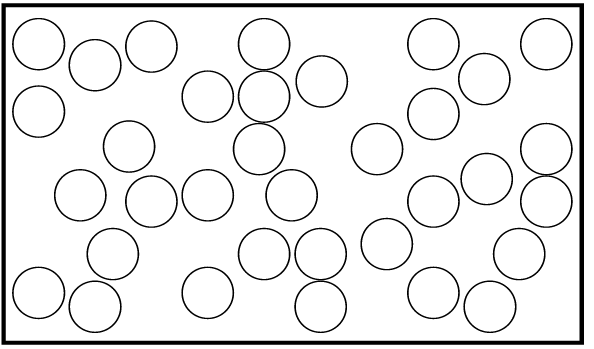
Uitsetting
Kom ons kyk nou na hierdie uitwerking van energie op vaste stowwe, vloeistowwe en gasse.
Verfris jou geheue. Voltooi die volgende sin deur die woorde vastestowwe of vloeistowwe of gasse in te vul:
By normale toestande (kamertemperatuur, gewone lugdruk) neem
die vorm van die houer waarin dit gehou word
aan, terwyl die fatsoen van nie verander nie
en die meeste in alle rigtings versprei en die
beskikbare ruimte vul.
Jou onderwyser gaan 'n demonstrasie doen. Kyk mooi wat gebeur en beantwoord die vrae wat volg.
Waarom?
Gaan dit makliker?
Verklaar:
Kom ons kyk na voorbeelde in ons alledaagse lewe:
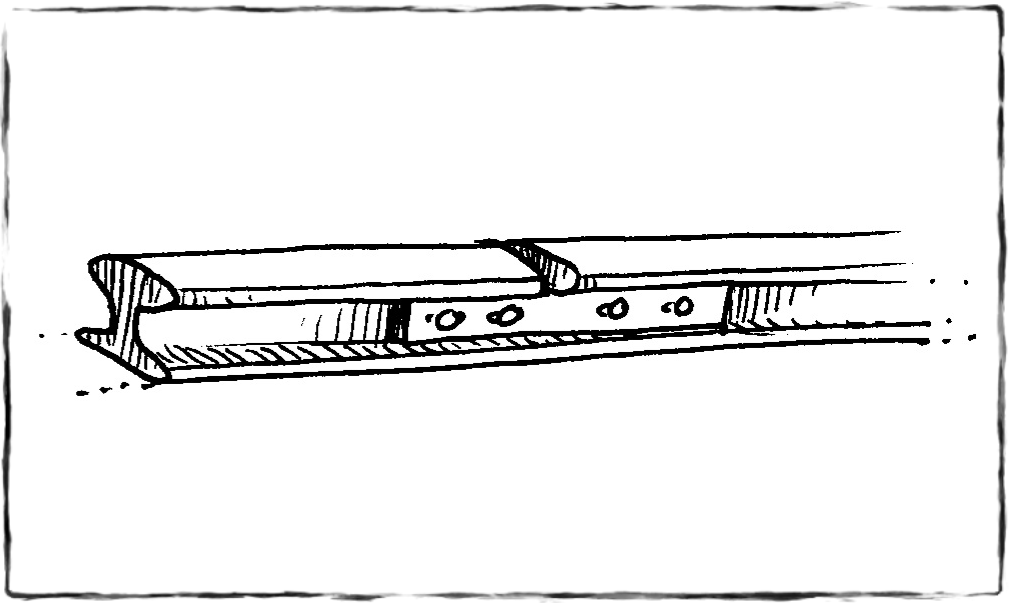
Treinspore se stawe moet gelê word met spasies tussenin, want tydens verhitting (hoër temperature) sal die metaal uitsit en sonder die nodige spasies tussenin sal die spoor buig.

Die ruit vir 'n venster word gewoonlik kleiner as die raam gesny, omdat albei (veral as dit ‘n staalraam is) op warm dae uitsit en op koue dae inkrimp.
Wat kan gebeur indien die ruit presies in die raam pas?

Sien jy die verskil tussen die twee prente?
Verduidelik aan 'n maat wat plaasvind. Maak nou jul eie afleiding en skryf dit neer.
Kyk of jy die volgende in die wetenskaplaboratorium kan kry:
'n Saamgestelde staaf

'n Koperbal-en-ring

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natuurwetenskappe graad 5' conversation and receive update notifications?