| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
( is defined in exercise 1)


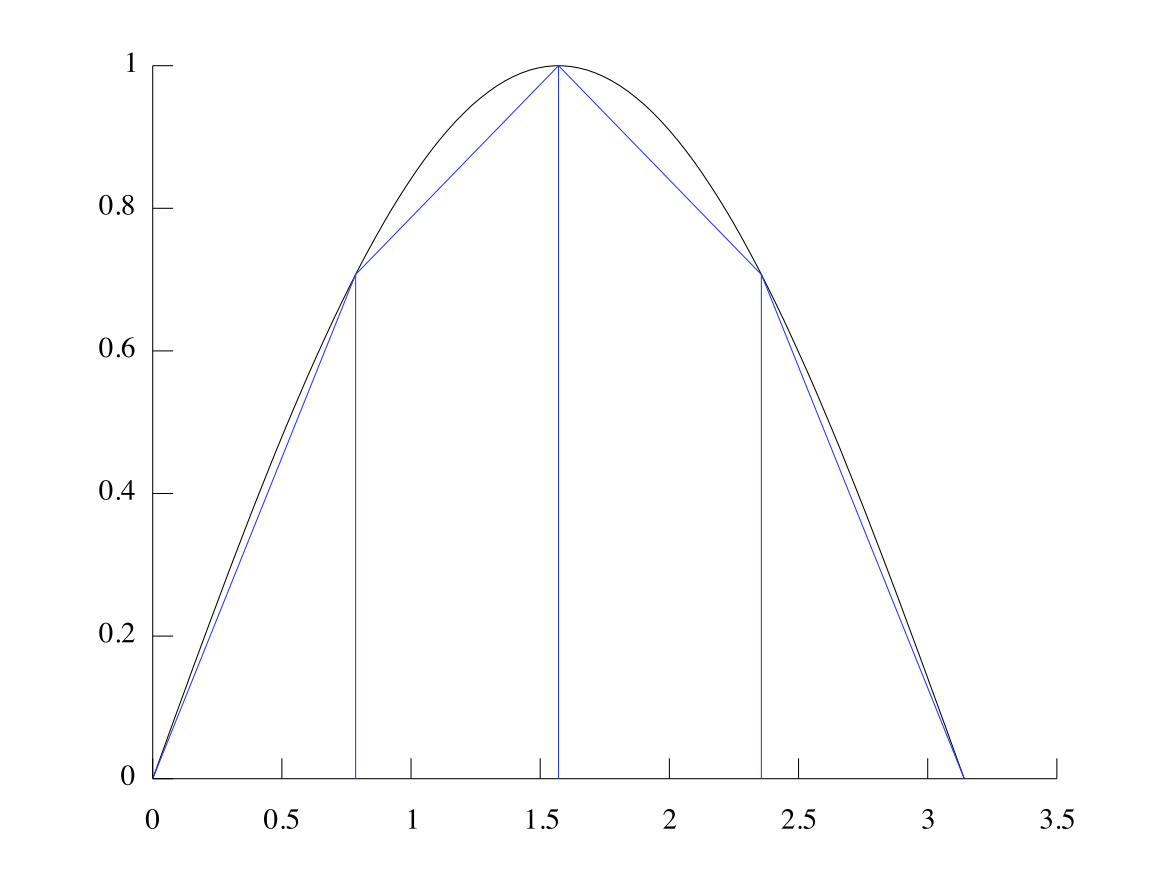
A useful tool for analyzing curves is finding the area underneath them. When we have an unknown combination of waves, we can estimate the area under the curve using the trapezoid rule . We will use as an example. If we were to estimate part of the area under the curve with one trapezoid, we might do the following:

We have labeled the two heights, and , and the length of the base . The area of the square is:
The area of the top triangle is:
The total area of the trapezoid is then:
If we know that the two points on the -axis are and , then . In the figure above, and . Then the heights follow from the function: and . Thus in general, the area of a trapezoid approximating the area under between the points and is:
In order to get a good estimate, we split up the domain of the function into several intervals . For each interval, we calculate the area of the trapezoid that approximates the area under that curve. For example, we could approximate over using four equal intervals. This would look like:
In this case, our estimate would be
As we take smaller and smaller intervals, our approximation will get better, because there will be less space between the trapezoids and the curve. We can prove that the trapezoid rule given `order 2' convergence–that is, if we cut our intervals in half, our error gets four times smaller.
In the general case, if we split up the domain of the function at points , then the rule for the estimate is
This formula can be further reduced, which is the subject of Exercise 2.1.
Here we present a code that uses the trapezoid rule to find the area under any function we provide. We need a vector
x that holds the values of the domain, for example
x = 0:.01:pi . We then need a vector
y that holds the function values at those
x points, for example
y = sin(x) .
function curve_area = mytrapz(x, y, fast)
% function curve_area = mytrapz(x, y, fast)%
% mytrapz.m performs the trapezoid rule on the vector given by x and y.% Input:
% x - a vector containing the domain of the function% y - a vector containing values of the function corresponding to the
curve_area = 0;%loop through and add up trapezoids for as many points as we are givenfor n = 2 : numel(x)
We start the code with zero area under the curve, since we haven't counted anything yet. Then we create a
for loop to count each triangle individually. As we see above, more trapezoids leads to better answers, so we want to use as many trapezoids as we possibly can. In this situation, that means using every point in
x and
y . The function
numel simply counts the number of elements in
x . We then calculate the area of the current triangle (within the loop):

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'The art of the pfug' conversation and receive update notifications?