| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
7. hear: …………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
| LO 3.4.5 | LO 4.5.5 | LO 4.6.3 |
For you to do.
1. ……………………………………………………………………………………….
2. ……………………………………………………………………………………….
3. ……………………………………………………………………………………….
| LO 3.5 | LO 3.5.7 | LO 4.4.1 | LO 5.3.4 |
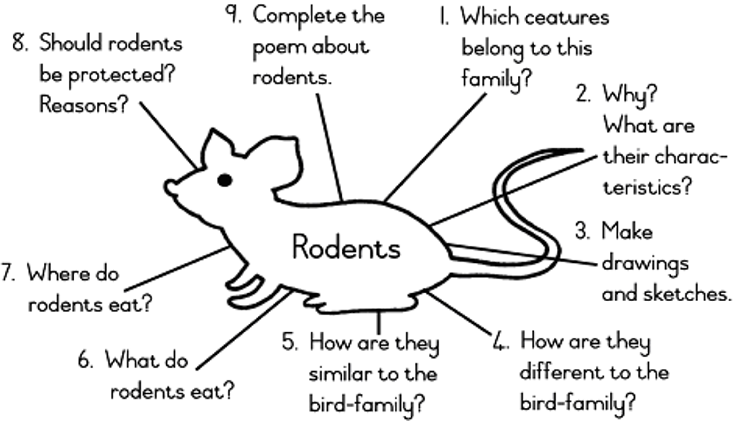
| LO 1.4.8 | LO 2.5.7 | LO 3.1 | LO 3.2 | LO 4.1.1 |
1. ………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
2. ………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
3. ………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
4. ………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
5. ………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
6. ………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
7. ………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
8. ………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
9. ………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
10. …………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
11. …………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
12. ………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
| LO 4.1.1 | LO 4.2.2 | LO 4.6.2 | LO 5.3.6 |
Mice and rats are rodents see
Some are thin and some are fat
……………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………..
by ………………………………………………….. (your name)
| LO 2.2 | LO 3.4.9 |
Learning Outcome 1: LISTENING : The learner is able to listen for information and enjoyment and respond appropriately and critically in a wider range of situations.
Assessment Standard 1.4: We know this when the learner listens with enjoyment to stories, poems, songs and other oral texts and shows understanding;
1.4.8 draws pictures to illustrate understanding of the oral text, and writes it in own words.
Learning Outcome 2: SPEAKING : The learner is able to communicate confidently and effectively in spoken language in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 2.2: We know this when the learner uses language imaginatively for fun and fantasy (e.g. telling jokes, creating own poems and code language).
Assessment Standard 2.5: We know this when the learner contributes to group and class discussions;
2.5.7 answers questions and gives reasons for answers;
Learning Outcome 3: READING AND VIEWING : The learner is able to read and view for information and enjoyment and respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts.
Assessment Standard 3.1: We know this when the learner uses visual cues to make meaning;
Assessment Standard 3.4: We know this when the learner consolidates phonic knowledge:
3.4.5 recognises vowels with two sounds;
3.4.9 recognises rhyming words;
Assessment Standard 3.5: We know this when the learner reads reads for information and enjoyment;
3.5.7 identifies and finds information sources such as community members, library books;
Learning Outcome 4: WRITING : The learner is able to write different kinds of factual and imaginative texts for a wide range of purposes.
Assessment Standard 4.1: We know this when the learner uses pre-writing strategies to initiate writing:
4.1.1 uses various pre-writing strategies to gather information and choose a topic (e.g. brainstorming, free writing, talking with friends, visual images);
Assessment Standard 4.2: We know this when the learner drafts a piece of writing for different purposes:
4.2.2 writes a selection of short texts for different purposes;
Assessment Standard 4.4: We know this when the learner ‘publishes’ (makes public) own writing:
4.4.1 shares work with others by reading it aloud and / or displaying it in the classroom;
Assessment Standard 4.5: We know this when the learner builds vocabulary and spells words independently:
4.5.5 uses knowledge of phonics and spelling rules to write unfamiliar words;
Assessment Standard 4.6: We know this when the learner uses appropriate grammatical structures and writing conventions:
4.6.2 uses punctuation appropriately;
4.6.3 applies knowledge of grammar;
Learning Outcome 5: THINKING AND REASONING : The learner is able to use language to think and reason, and access, process and use information for learning.
Assessment Standard 5.3: We know this when the learner uses language to investigate and explore:
5.3.4 uses simple strategies for getting information.
5.3.6 summarises information and presents it in an appropriate and interesting way.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English home language grade 3' conversation and receive update notifications?