| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Perhaps the simplest form of (analog) transmission system modulates the message signal by a high frequency carrier in a two-stepprocedure: multiply the message by the carrier, then add the product to the carrier.At the receiver, the message can be demodulated by extracting the envelope of the received signal.
Consider the transmitted/modulated signal
diagrammed in [link] . The process of multiplying the signal in timeby a (co)sinusoid is called mixing . This can be rewritten in the frequency domainby mimicking the development from [link] to [link] . Using the convolution property of Fourier Transforms [link] , the transform of is
The spectra of and are sketched in [link] (a) and (b). The vertical arrows in (b) represent the transform of the cosine carrierat frequency (i.e., a pair of delta functions at ) and the scaling by is indicated next to the arrowheads.

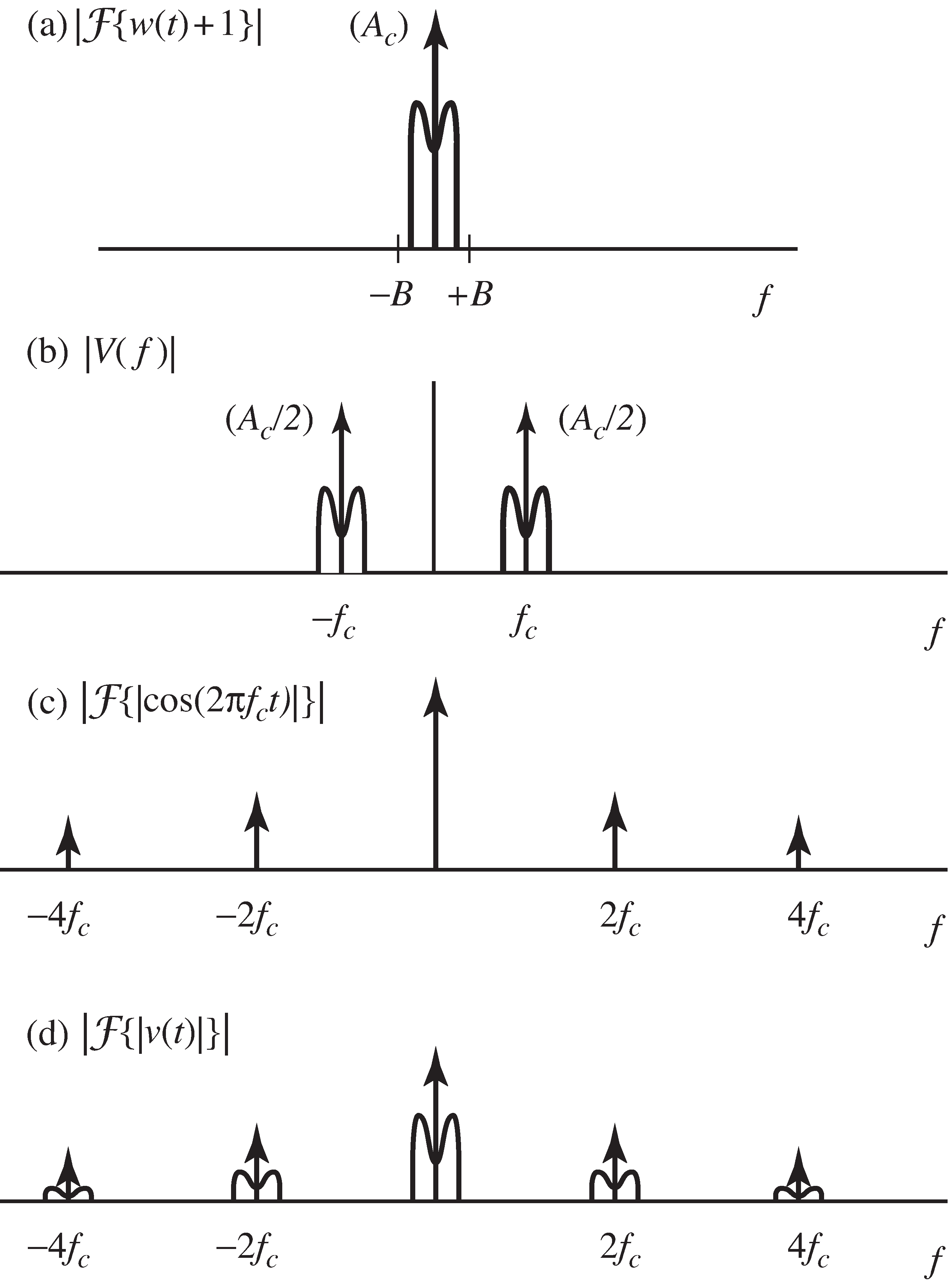
If , the envelope of is the same as and an envelope detector can be used as a demodulator. One way to find the envelope of a signal is to lowpass filterthe absolute value. To see this analytically, observe that
where the absolute value can be removed from because (by assumption). The spectrum of , shown in [link] (c), may be familiar from Exercise [link] . Accordingly, is the convolution shown in [link] (d). Low pass filtering this returns , which is the envelope of offset by the constant one.
An example is given in the following M atlab program. The “message” signal is a sinusoid with a drift in the DC offset,and the carrier wave is at a much higher frequency.
time=.33; Ts=1/10000; % sampling interval and time
t=0:Ts:time; lent=length(t); % define a "time" vectorfc=1000; c=cos(2*pi*fc*t); % define carrier at freq fc
fm=20; w=10/lent*[1:lent]+cos(2*pi*fm*t); % create "message" > -1
v=c.*w+c; % modulate with large carrierfbe=[0 0.05 0.1 1]; damps=[1 1 0 0]; fl=100; % low pass filter design
b=firpm(fl,fbe,damps); % impulse response of LPFenvv=(pi/2)*filter(b,1,abs(v)); % find envelope
AMlarge.m large carrier AM demodulated with “envelope”
(download file)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Software receiver design' conversation and receive update notifications?