| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
1. Can you remember what each of the following represents?
N = { ........................................................................... }
N 0 = { ........................................................................... }
Z = { ........................................................................... }
R = { ........................................................................... }
2. Provide the definition for:
a rational number:
an irrational number:
3. How would you represent each of the following?
3.1 Rational number......................... 3.2 Irrational number .........................
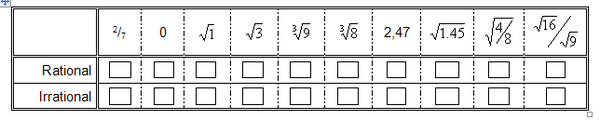
4. Complete the following table by marking relevant numbers with an X:
5. Select the required numbers from the list:
; 1 + ; ; -4 ; ;
5.1 Integers:
5.2 Rational numbers:
5.3 Irrational numbers:
6. Explain what you know about an equivalent fraction.
7. Provide two equivalent fractions for the following: = ............... = ...............
8. Provide the terms used to identify each of the following (e.g. proper fraction):
8.1
8.2
8.3
8.4 0,67
8.5
8.6 23 %
Any of the above can be reduced to any of the others.
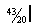
2. Explain how you would reduce this to a decimal number without the use of your pocket calculator. There are two methods:
Method 1: .................................................. (reduce denominator to 10 / 100 / 1 000)
Method 2: .................................................. (do division)
(Let your educator assist you.)
3. Now reduce each of the following to decimal numbers (round off, if necessary, to two digits):
3.1 ..................................................
3.2 ..................................................
3.3 ..................................................
3.4 ..................................................
3.5 ..................................................
3.6 ..................................................
4. Write the following decimal numbers as fractions or mixed numbers:(N.B.: All fractions have to be presented in their simplest form.)
4.1 6,008 ..................................................
4.2 4,65 ..................................................
4.3 0,375 ..................................................
4.4 7,075 ..................................................
4.5 13,65 ..................................................
4.6 0,125 ..................................................
5. How do we reduce fractions to recurring decimal numbers?
E.g.
Step 1: place a comma after the 5, i.e. 5, 0000

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 8' conversation and receive update notifications?