| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
All of the micro-operations needed to perform one instruction cycle, including all of the micro-operations to execute every instruction in the instruction set, fall into one of these categories.
We can now be somewhat more explicit about the way in which the control unit functions. The control unit performs two basic tasks:
The preceding is a functional description of what the control unit does. The key to how the control unit operates is the use of control signals.
We have defined the elements that make up the processor (ALU, registers, data paths) and the micro-operations that are performed. For the control unit to perform its function, it must have inputs that allow it to determine the slate of the system and outputs that allow it to control the behavior of the system. These are the external specifications of the control unit. Internally, the control unit must have the logic required lo perform its sequencing and execution functions.
Figure 6.4 is a general model of the control unit, showing all of its inputs and outputs.
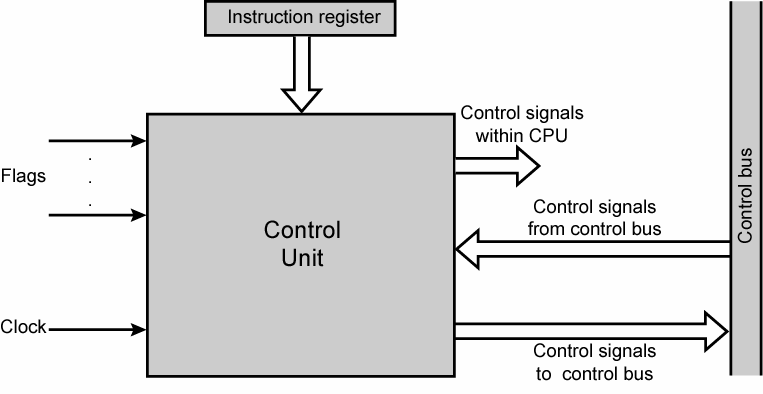
Figure 6.4 Model of Control Unit
The inputs are as follows:
The outputs are as follows:
The new element that has been introduced in this figure is the control signal. Three types of control signals are used: those that activate an ALU function, those that activate a data path, and those that are signals on the external system bus or other external interface. All of these signals are ultimately applied directly as binary inputs lo individual logic gates.
Let us consider again the fetch cycle to see how the control unit maintains control. The control unit keeps track of where it is in the instruction cycle. At a given point, it knows that the fetch cycle is to be performed next. The first step is to transfer the contents of the PC to the MAR. The control unit does this by activating the control signal that opens the gates between the bits of the PC and the bits of the MAR. The next step is to read a word from memory into the MBR and increment the PC. The control unit does this by sending the following control signals simultaneously:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Computer architecture' conversation and receive update notifications?