| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Conversely, the same amount of energy is released when one mole of H 2 molecules forms from two moles of H atoms:
If the atoms that form a covalent bond are identical, as in H 2 , Cl 2 , and other diatomic molecules, then the electrons in the bond must be shared equally. We refer to this as a pure covalent bond . Electrons shared in pure covalent bonds have an equal probability of being near each nucleus.
In the case of Cl 2 , each atom starts off with seven valence electrons, and each Cl shares one electron with the other, forming one covalent bond:
The total number of electrons around each individual atom consists of six nonbonding electrons and two shared (i.e., bonding) electrons for eight total electrons, matching the number of valence electrons in the noble gas argon. Since the bonding atoms are identical, Cl 2 also features a pure covalent bond.
When the atoms linked by a covalent bond are different, the bonding electrons are shared, but no longer equally. Instead, the bonding electrons are more attracted to one atom than the other, giving rise to a shift of electron density toward that atom. This unequal distribution of electrons is known as a polar covalent bond , characterized by a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other. The atom that attracts the electrons more strongly acquires the partial negative charge and vice versa. For example, the electrons in the H–Cl bond of a hydrogen chloride molecule spend more time near the chlorine atom than near the hydrogen atom. Thus, in an HCl molecule, the chlorine atom carries a partial negative charge and the hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge. [link] shows the distribution of electrons in the H–Cl bond. Note that the shaded area around Cl is much larger than it is around H. Compare this to [link] , which shows the even distribution of electrons in the H 2 nonpolar bond.
We sometimes designate the positive and negative atoms in a polar covalent bond using a lowercase Greek letter “delta,” δ, with a plus sign or minus sign to indicate whether the atom has a partial positive charge (δ+) or a partial negative charge (δ–). This symbolism is shown for the H–Cl molecule in [link] .
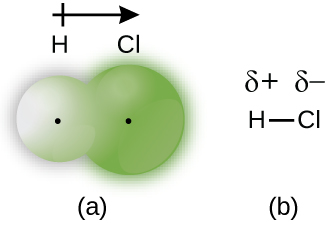
Whether a bond is nonpolar or polar covalent is determined by a property of the bonding atoms called electronegativity . Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. It determines how the shared electrons are distributed between the two atoms in a bond. The more strongly an atom attracts the electrons in its bonds, the larger its electronegativity. Electrons in a polar covalent bond are shifted toward the more electronegative atom; thus, the more electronegative atom is the one with the partial negative charge. The greater the difference in electronegativity, the more polarized the electron distribution and the larger the partial charges of the atoms.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?