| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The name phosphorus comes from the Greek words meaning light bringing. When phosphorus was first isolated, scientists noted that it glowed in the dark and burned when exposed to air. Phosphorus is the only member of its group that does not occur in the uncombined state in nature; it exists in many allotropic forms. We will consider two of those forms: white phosphorus and red phosphorus.
White phosphorus is a white, waxy solid that melts at 44.2 °C and boils at 280 °C. It is insoluble in water (in which it is stored—see [link] ), is very soluble in carbon disulfide, and bursts into flame in air. As a solid, as a liquid, as a gas, and in solution, white phosphorus exists as P 4 molecules with four phosphorus atoms at the corners of a regular tetrahedron, as illustrated in [link] . Each phosphorus atom covalently bonds to the other three atoms in the molecule by single covalent bonds. White phosphorus is the most reactive allotrope and is very toxic.
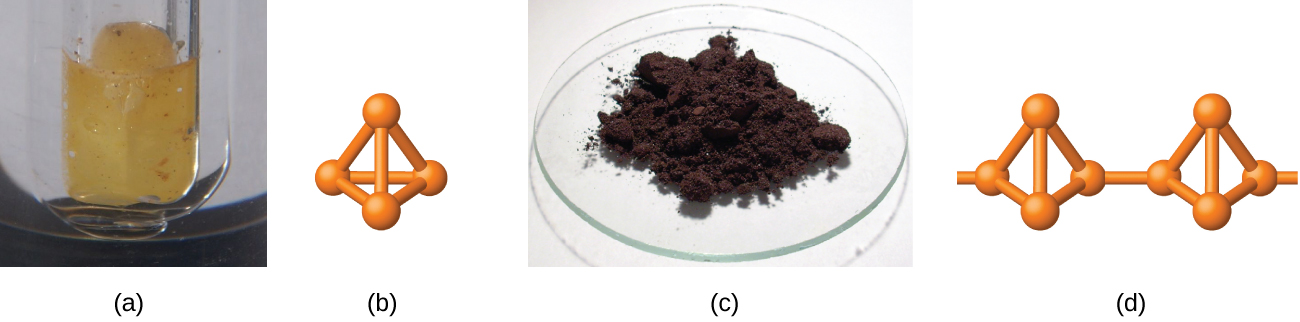
Heating white phosphorus to 270–300 °C in the absence of air yields red phosphorus. Red phosphorus (shown in [link] ) is denser, has a higher melting point (~600 °C), is much less reactive, is essentially nontoxic, and is easier and safer to handle than is white phosphorus. Its structure is highly polymeric and appears to contain three-dimensional networks of P 4 tetrahedra joined by P-P single bonds. Red phosphorus is insoluble in solvents that dissolve white phosphorus. When red phosphorus is heated, P 4 molecules sublime from the solid.
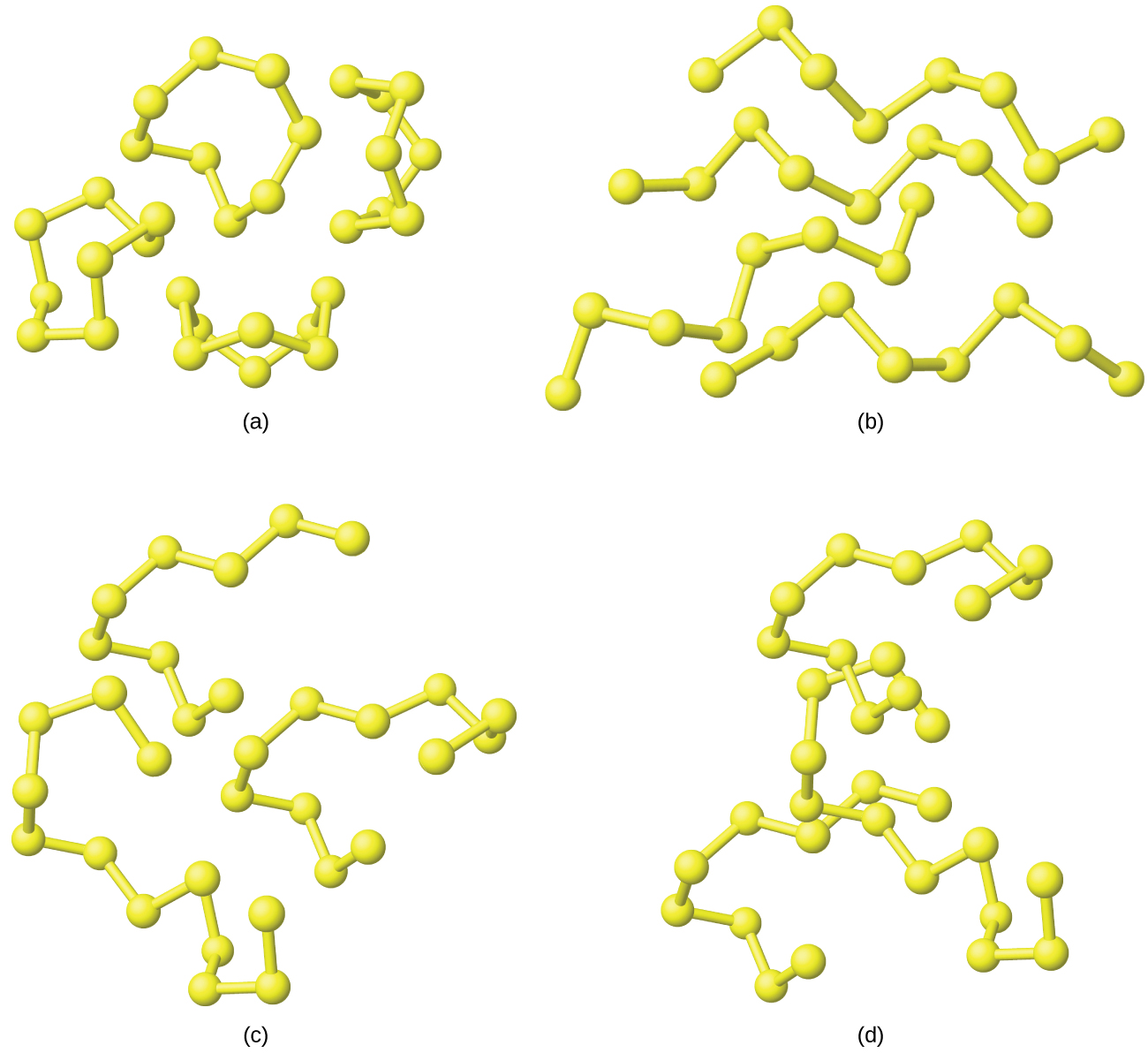
The allotropy of sulfur is far greater and more complex than that of any other element. Sulfur is the brimstone referred to in the Bible and other places, and references to sulfur occur throughout recorded history—right up to the relatively recent discovery that it is a component of the atmospheres of Venus and of Io, a moon of Jupiter. The most common and most stable allotrope of sulfur is yellow, rhombic sulfur, so named because of the shape of its crystals. Rhombic sulfur is the form to which all other allotropes revert at room temperature. Crystals of rhombic sulfur melt at 113 °C. Cooling this liquid gives long needles of monoclinic sulfur. This form is stable from 96 °C to the melting point, 119 °C. At room temperature, it gradually reverts to the rhombic form.
Both rhombic sulfur and monoclinic sulfur contain S 8 molecules in which atoms form eight-membered, puckered rings that resemble crowns, as illustrated in [link] . Each sulfur atom is bonded to each of its two neighbors in the ring by covalent S-S single bonds.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?