| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Chemical stoichiometry describes the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions.
We have previously measured quantities of reactants and products using masses for solids and volumes in conjunction with the molarity for solutions; now we can also use gas volumes to indicate quantities. If we know the volume, pressure, and temperature of a gas, we can use the ideal gas equation to calculate how many moles of the gas are present. If we know how many moles of a gas are involved, we can calculate the volume of a gas at any temperature and pressure.
Sometimes we can take advantage of a simplifying feature of the stoichiometry of gases that solids and solutions do not exhibit: All gases that show ideal behavior contain the same number of molecules in the same volume (at the same temperature and pressure). Thus, the ratios of volumes of gases involved in a chemical reaction are given by the coefficients in the equation for the reaction, provided that the gas volumes are measured at the same temperature and pressure.
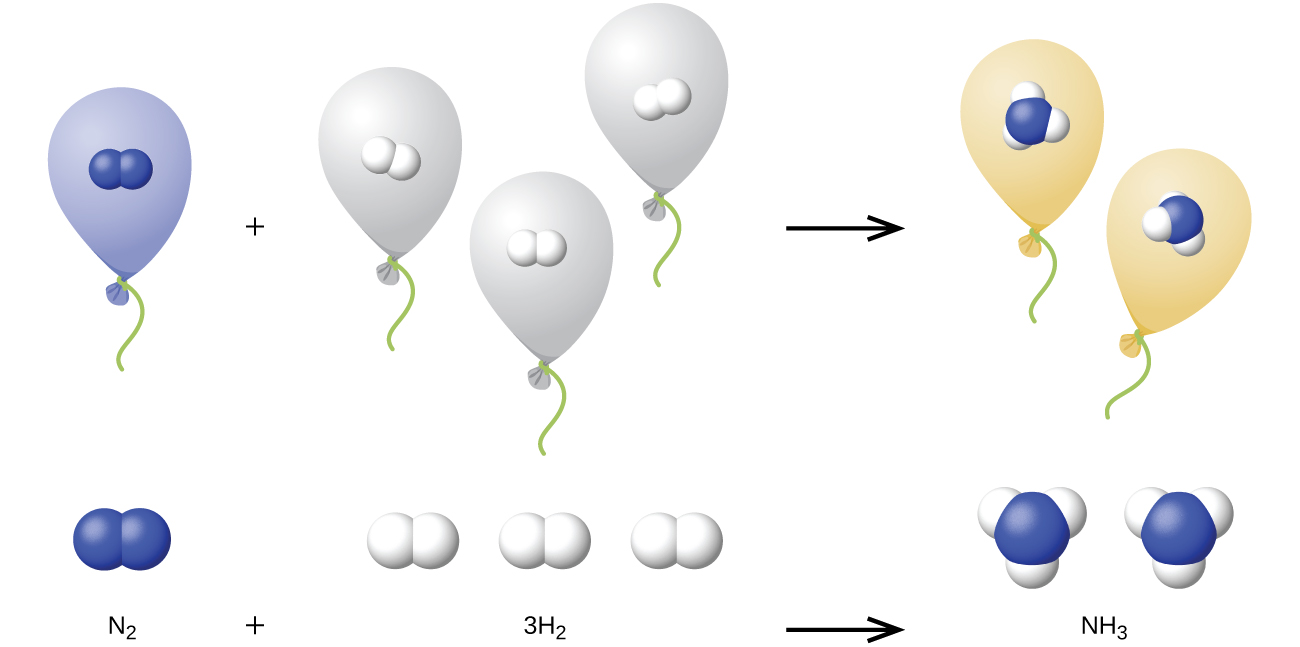
We can extend Avogadro’s law (that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of the gas) to chemical reactions with gases: Gases combine, or react, in definite and simple proportions by volume, provided that all gas volumes are measured at the same temperature and pressure. For example, since nitrogen and hydrogen gases react to produce ammonia gas according to a given volume of nitrogen gas reacts with three times that volume of hydrogen gas to produce two times that volume of ammonia gas, if pressure and temperature remain constant.
The explanation for this is illustrated in [link] . According to Avogadro’s law, equal volumes of gaseous N 2 , H 2 , and NH 3 , at the same temperature and pressure, contain the same number of molecules. Because one molecule of N 2 reacts with three molecules of H 2 to produce two molecules of NH 3 , the volume of H 2 required is three times the volume of N 2 , and the volume of NH 3 produced is two times the volume of N 2 .
From the equation, we see that one volume of C 3 H 8 will react with five volumes of O 2 :
A volume of 13.5 L of O 2 will be required to react with 2.7 L of C 3 H 8 .
3.34 tanks (2.34 10 4 L)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?