| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Radiation can harm either the whole body (somatic damage) or eggs and sperm (genetic damage). Its effects are more pronounced in cells that reproduce rapidly, such as the stomach lining, hair follicles, bone marrow, and embryos. This is why patients undergoing radiation therapy often feel nauseous or sick to their stomach, lose hair, have bone aches, and so on, and why particular care must be taken when undergoing radiation therapy during pregnancy.
Different types of radiation have differing abilities to pass through material ( [link] ). A very thin barrier, such as a sheet or two of paper, or the top layer of skin cells, usually stops alpha particles. Because of this, alpha particle sources are usually not dangerous if outside the body, but are quite hazardous if ingested or inhaled (see the Chemistry in Everyday Life feature on Radon Exposure). Beta particles will pass through a hand, or a thin layer of material like paper or wood, but are stopped by a thin layer of metal. Gamma radiation is very penetrating and can pass through a thick layer of most materials. Some high-energy gamma radiation is able to pass through a few feet of concrete. Certain dense, high atomic number elements (such as lead) can effectively attenuate gamma radiation with thinner material and are used for shielding. The ability of various kinds of emissions to cause ionization varies greatly, and some particles have almost no tendency to produce ionization. Alpha particles have about twice the ionizing power of fast-moving neutrons, about 10 times that of β particles, and about 20 times that of γ rays and X-rays.

For many people, one of the largest sources of exposure to radiation is from radon gas (Rn-222). Radon-222 is an α emitter with a half–life of 3.82 days. It is one of the products of the radioactive decay series of U-238 ( [link] ), which is found in trace amounts in soil and rocks. The radon gas that is produced slowly escapes from the ground and gradually seeps into homes and other structures above. Since it is about eight times more dense than air, radon gas accumulates in basements and lower floors, and slowly diffuses throughout buildings ( [link] ).
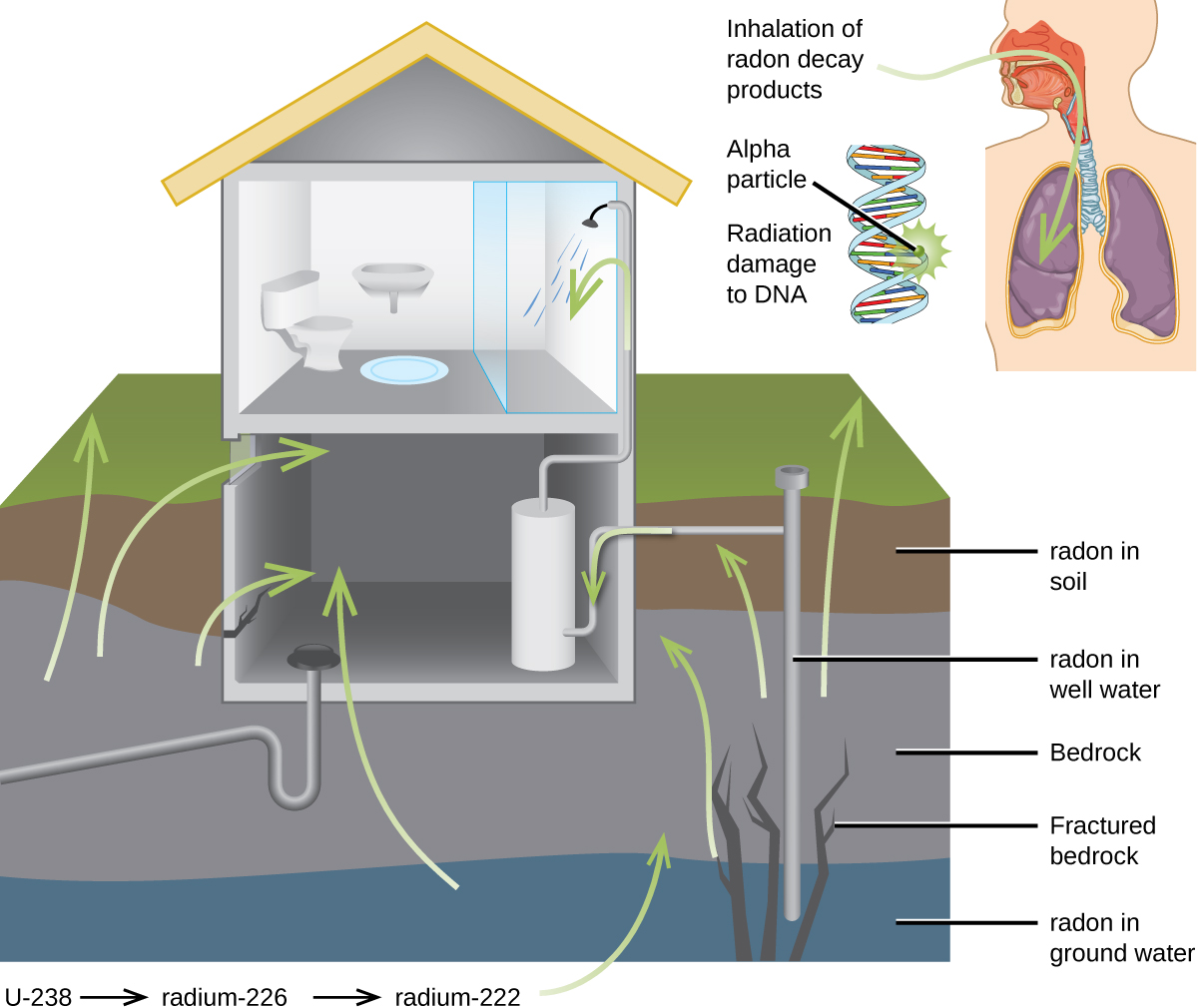
Radon is found in buildings across the country, with amounts depending on where you live. The average concentration of radon inside houses in the US (1.25 pCi/L) is about three times the levels found in outside air, and about one in six houses have radon levels high enough that remediation efforts to reduce the radon concentration are recommended. Exposure to radon increases one’s risk of getting cancer (especially lung cancer), and high radon levels can be as bad for health as smoking a carton of cigarettes a day. Radon is the number one cause of lung cancer in nonsmokers and the second leading cause of lung cancer overall. Radon exposure is believed to cause over 20,000 deaths in the US per year.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?