| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this section, we examine the method of cylindrical shells, the final method for finding the volume of a solid of revolution. We can use this method on the same kinds of solids as the disk method or the washer method; however, with the disk and washer methods, we integrate along the coordinate axis parallel to the axis of revolution. With the method of cylindrical shells, we integrate along the coordinate axis perpendicular to the axis of revolution. The ability to choose which variable of integration we want to use can be a significant advantage with more complicated functions. Also, the specific geometry of the solid sometimes makes the method of using cylindrical shells more appealing than using the washer method. In the last part of this section, we review all the methods for finding volume that we have studied and lay out some guidelines to help you determine which method to use in a given situation.
Again, we are working with a solid of revolution. As before, we define a region bounded above by the graph of a function below by the and on the left and right by the lines and respectively, as shown in [link] (a). We then revolve this region around the y -axis, as shown in [link] (b). Note that this is different from what we have done before. Previously, regions defined in terms of functions of were revolved around the or a line parallel to it.
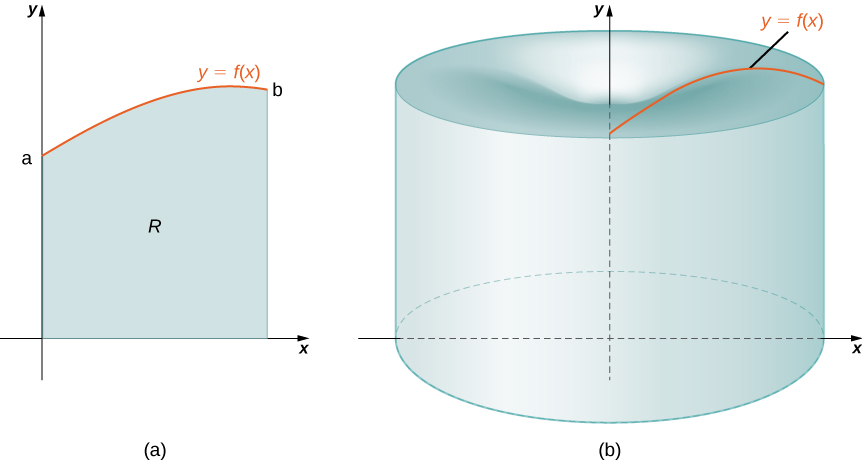
As we have done many times before, partition the interval using a regular partition, and, for choose a point Then, construct a rectangle over the interval of height and width A representative rectangle is shown in [link] (a). When that rectangle is revolved around the y -axis, instead of a disk or a washer, we get a cylindrical shell, as shown in the following figure.
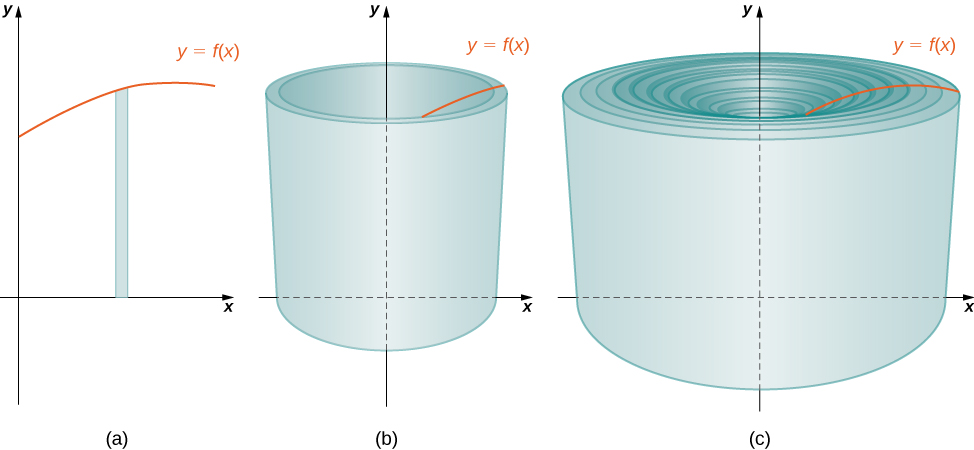
To calculate the volume of this shell, consider [link] .
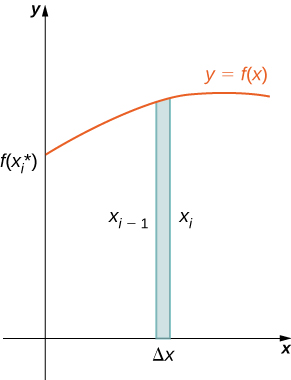
The shell is a cylinder, so its volume is the cross-sectional area multiplied by the height of the cylinder. The cross-sections are annuli (ring-shaped regions—essentially, circles with a hole in the center), with outer radius and inner radius Thus, the cross-sectional area is The height of the cylinder is Then the volume of the shell is
Note that so we have
Furthermore, is both the midpoint of the interval and the average radius of the shell, and we can approximate this by We then have

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?