| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Note that for this function and the function graphed in [link] , the values of are getting smaller as is getting larger. A function with this property is said to be decreasing. On the other hand, for the function graphed in [link] , the values of are getting larger as the values of are getting larger. A function with this property is said to be increasing. It is important to note, however, that a function can be increasing on some interval or intervals and decreasing over a different interval or intervals. For example, using our temperature function in [link] , we can see that the function is decreasing on the interval increasing on the interval and then decreasing on the interval We make the idea of a function increasing or decreasing over a particular interval more precise in the next definition.
We say that a function is increasing on the interval if for all
We say is strictly increasing on the interval if for all
We say that a function is decreasing on the interval if for all
We say that a function is strictly decreasing on the interval if for all
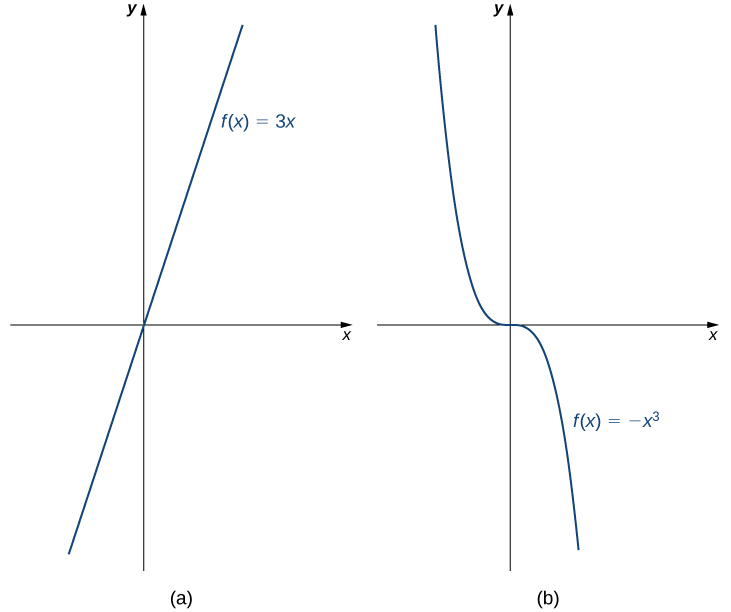
For example, the function is increasing on the interval because whenever On the other hand, the function is decreasing on the interval because whenever ( [link] ).
Now that we have reviewed the basic characteristics of functions, we can see what happens to these properties when we combine functions in different ways, using basic mathematical operations to create new functions. For example, if the cost for a company to manufacture items is described by the function and the revenue created by the sale of items is described by the function then the profit on the manufacture and sale of items is defined as Using the difference between two functions, we created a new function.
Alternatively, we can create a new function by composing two functions. For example, given the functions and the composite function is defined such that
The composite function is defined such that
Note that these two new functions are different from each other.
To combine functions using mathematical operators, we simply write the functions with the operator and simplify. Given two functions and we can define four new functions:
Given the functions and find each of the following functions and state its domain.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?