| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
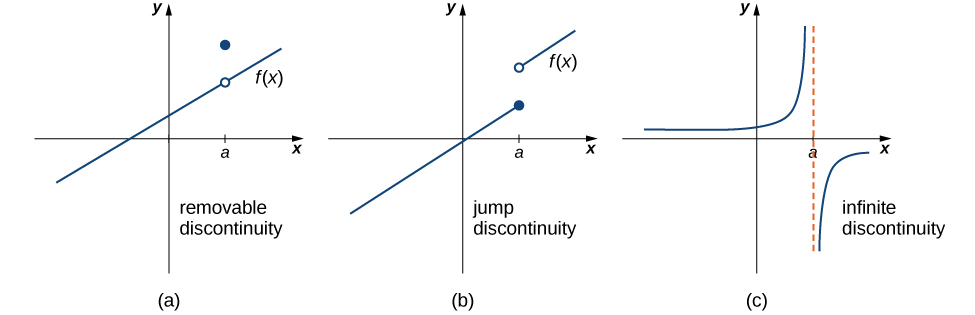
These three discontinuities are formally defined as follows:
If is discontinuous at a , then
In [link] , we showed that is discontinuous at Classify this discontinuity as removable, jump, or infinite.
To classify the discontinuity at 2 we must evaluate
Since f is discontinuous at 2 and exists, f has a removable discontinuity at
In [link] , we showed that is discontinuous at Classify this discontinuity as removable, jump, or infinite.
Earlier, we showed that f is discontinuous at 3 because does not exist. However, since and both exist, we conclude that the function has a jump discontinuity at 3.
Determine whether is continuous at −1. If the function is discontinuous at −1, classify the discontinuity as removable, jump, or infinite.
The function value is undefined. Therefore, the function is not continuous at −1. To determine the type of discontinuity, we must determine the limit at −1. We see that and Therefore, the function has an infinite discontinuity at −1.
For decide whether f is continuous at 1. If f is not continuous at 1, classify the discontinuity as removable, jump, or infinite.
Discontinuous at 1; removable
Now that we have explored the concept of continuity at a point, we extend that idea to continuity over an interval . As we develop this idea for different types of intervals, it may be useful to keep in mind the intuitive idea that a function is continuous over an interval if we can use a pencil to trace the function between any two points in the interval without lifting the pencil from the paper. In preparation for defining continuity on an interval, we begin by looking at the definition of what it means for a function to be continuous from the right at a point and continuous from the left at a point.
A function is said to be continuous from the right at a if
A function is said to be continuous from the left at a if
A function is continuous over an open interval if it is continuous at every point in the interval. A function is continuous over a closed interval of the form if it is continuous at every point in and is continuous from the right at a and is continuous from the left at b . Analogously, a function is continuous over an interval of the form if it is continuous over and is continuous from the left at b . Continuity over other types of intervals are defined in a similar fashion.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?