| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Many functions have the property that their graphs can be traced with a pencil without lifting the pencil from the page. Such functions are called continuous . Other functions have points at which a break in the graph occurs, but satisfy this property over intervals contained in their domains. They are continuous on these intervals and are said to have a discontinuity at a point where a break occurs.
We begin our investigation of continuity by exploring what it means for a function to have continuity at a point . Intuitively, a function is continuous at a particular point if there is no break in its graph at that point.
Before we look at a formal definition of what it means for a function to be continuous at a point, let’s consider various functions that fail to meet our intuitive notion of what it means to be continuous at a point. We then create a list of conditions that prevent such failures.
Our first function of interest is shown in [link] . We see that the graph of has a hole at a . In fact, is undefined. At the very least, for to be continuous at a , we need the following condition:
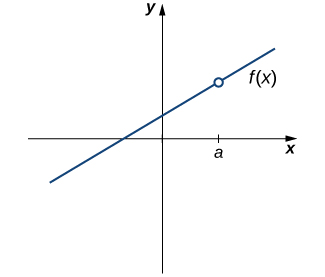
However, as we see in [link] , this condition alone is insufficient to guarantee continuity at the point a . Although is defined, the function has a gap at a . In this example, the gap exists because does not exist. We must add another condition for continuity at a —namely,
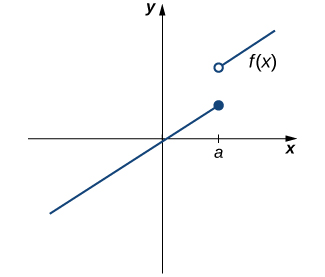
However, as we see in [link] , these two conditions by themselves do not guarantee continuity at a point. The function in this figure satisfies both of our first two conditions, but is still not continuous at a . We must add a third condition to our list:
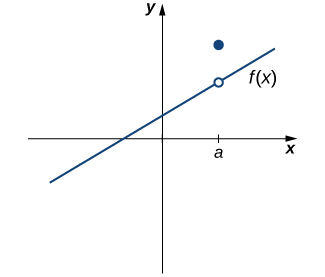
Now we put our list of conditions together and form a definition of continuity at a point.
A function is continuous at a point a if and only if the following three conditions are satisfied:
A function is discontinuous at a point a if it fails to be continuous at a .
The following procedure can be used to analyze the continuity of a function at a point using this definition.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?