| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Different kinds of pigments exist, and each absorbs only certain wavelengths (colors) of visible light. Pigments reflect the color of the wavelengths that they cannot absorb.
All photosynthetic organisms contain a pigment called chlorophyll a , which humans see as the common green color associated with plants. Chlorophyll a absorbs wavelengths from either end of the visible spectrum (blue and red), but not from green. Because green is reflected, chlorophyll appears green.
Other pigment types include chlorophyll b (which absorbs blue and red-orange light) and the carotenoids. Each type of pigment can be identified by the specific pattern of wavelengths it absorbs from visible light, which is its absorption spectrum .
Many photosynthetic organisms have a mixture of pigments; between them, the organism can absorb energy from a wider range of visible-light wavelengths. Not all photosynthetic organisms have full access to sunlight. Some organisms grow underwater where light intensity decreases with depth, and certain wavelengths are absorbed by the water. Other organisms grow in competition for light. Plants on the rainforest floor must be able to absorb any bit of light that comes through, because the taller trees block most of the sunlight ( [link] ).

The overall purpose of the light-dependent reactions is to convert light energy into chemical energy. This chemical energy will be used by the Calvin cycle to fuel the assembly of sugar molecules.
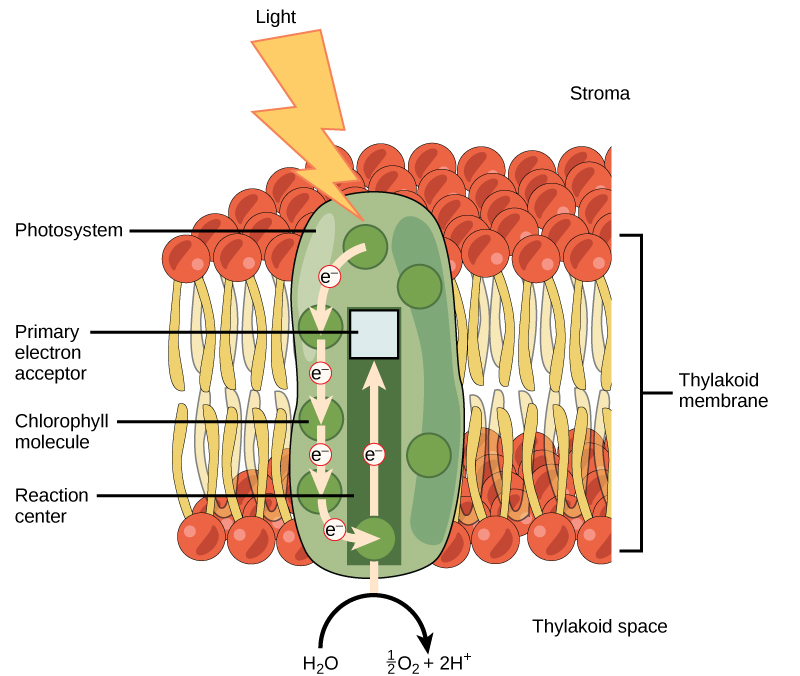
The light-dependent reactions begin in a grouping of pigment molecules and proteins called a photosystem . Photosystems exist in the membranes of thylakoids. A pigment molecule in the photosystem absorbs one photon , a quantity or “packet” of light energy, at a time.
A photon of light energy travels until it reaches a molecule of chlorophyll. The photon causes an electron in the chlorophyll to become “excited.” The energy given to the electron allows it to break free from an atom of the chlorophyll molecule. Chlorophyll is therefore said to “donate” an electron ( [link] ).
To replace the electron in the chlorophyll, a molecule of water is split. This splitting releases an electron and results in the formation of oxygen (O 2 ) and hydrogen ions (H + ) in the thylakoid space. Technically, each breaking of a water molecule releases a pair of electrons, and therefore can replace two donated electrons.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?