| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In plant cells, the Golgi has an additional role of synthesizing polysaccharides, some of which are incorporated into the cell wall and some of which are used in other parts of the cell.
In animal cells, the lysosomes are the cell’s “garbage disposal.” Digestive enzymes within the lysosomes aid the breakdown of proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, and even worn-out organelles. In single-celled eukaryotes, lysosomes are important for digestion of the food they ingest and the recycling of organelles. These enzymes are active at a much lower pH (more acidic) than those located in the cytoplasm. Many reactions that take place in the cytoplasm could not occur at a low pH, thus the advantage of compartmentalizing the eukaryotic cell into organelles is apparent.
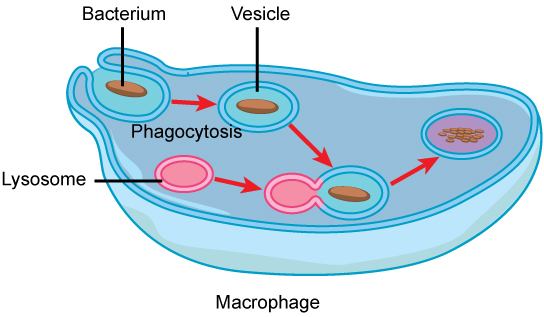
Lysosomes also use their hydrolytic enzymes to destroy disease-causing organisms that might enter the cell. A good example of this occurs in a group of white blood cells called macrophages, which are part of your body’s immune system. In a process known as phagocytosis, a section of the plasma membrane of the macrophage invaginates (folds in) and engulfs a pathogen. The invaginated section, with the pathogen inside, then pinches itself off from the plasma membrane and becomes a vesicle. The vesicle fuses with a lysosome. The lysosome’s hydrolytic enzymes then destroy the pathogen ( [link] ).
Vesicles and vacuoles are membrane-bound sacs that function in storage and transport. Vacuoles are somewhat larger than vesicles, and the membrane of a vacuole does not fuse with the membranes of other cellular components. Vesicles can fuse with other membranes within the cell system. Additionally, enzymes within plant vacuoles can break down macromolecules.
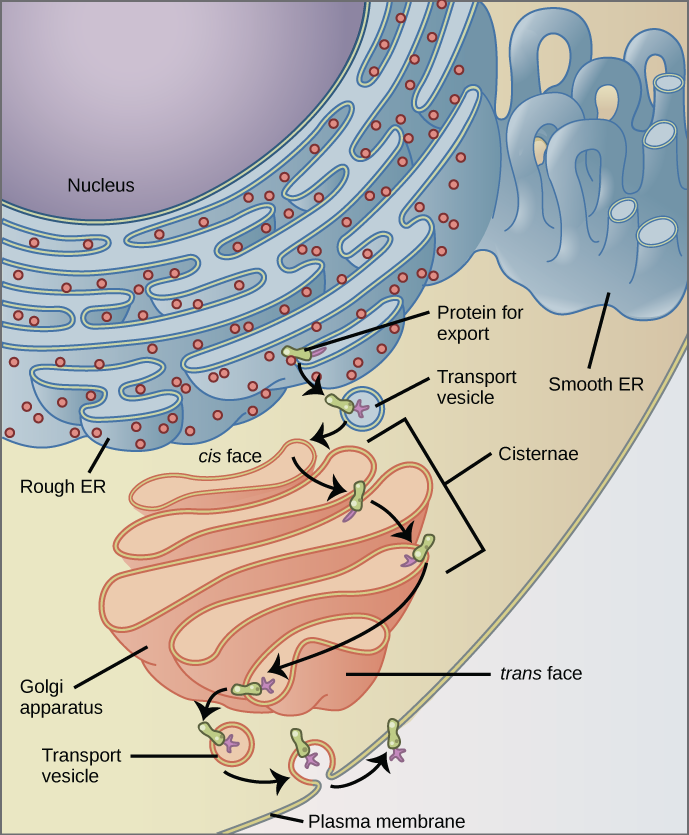
Why does the cis face of the Golgi not face the plasma membrane?
Ribosomes are the cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis. When viewed through an electron microscope, free ribosomes appear as either clusters or single tiny dots floating freely in the cytoplasm. Ribosomes may be attached to either the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane or the cytoplasmic side of the endoplasmic reticulum ( [link] ). Electron microscopy has shown that ribosomes consist of large and small subunits. Ribosomes are enzyme complexes that are responsible for protein synthesis.
Because protein synthesis is essential for all cells, ribosomes are found in practically every cell, although they are smaller in prokaryotic cells. They are particularly abundant in immature red blood cells for the synthesis of hemoglobin, which functions in the transport of oxygen throughout the body.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?