| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

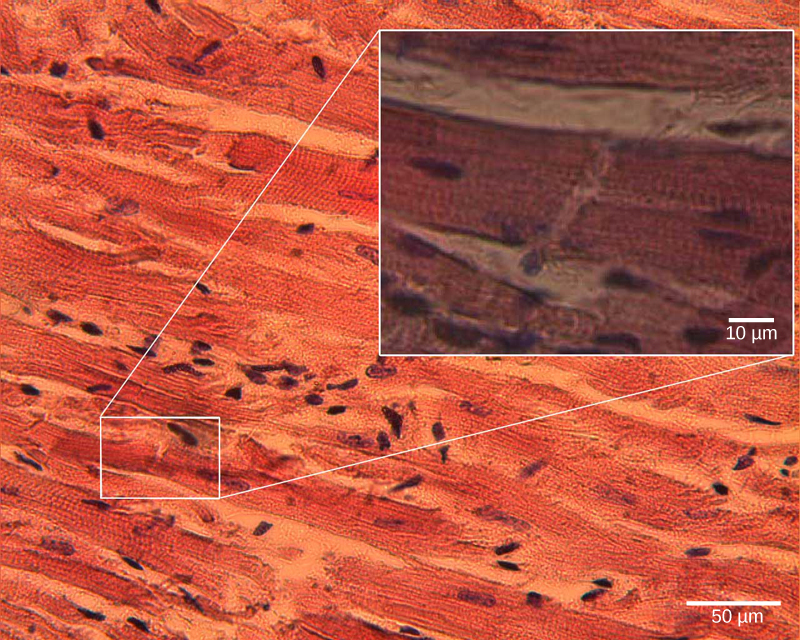
The pumping of the heart is a function of the cardiac muscle cells, or cardiomyocytes, that make up the heart muscle. Cardiomyocytes , shown in [link] , are distinctive muscle cells that are striated like skeletal muscle but pump rhythmically and involuntarily like smooth muscle; they are connected by intercalated disks exclusive to cardiac muscle. They are self-stimulated for a period of time and isolated cardiomyocytes will beat if given the correct balance of nutrients and electrolytes.
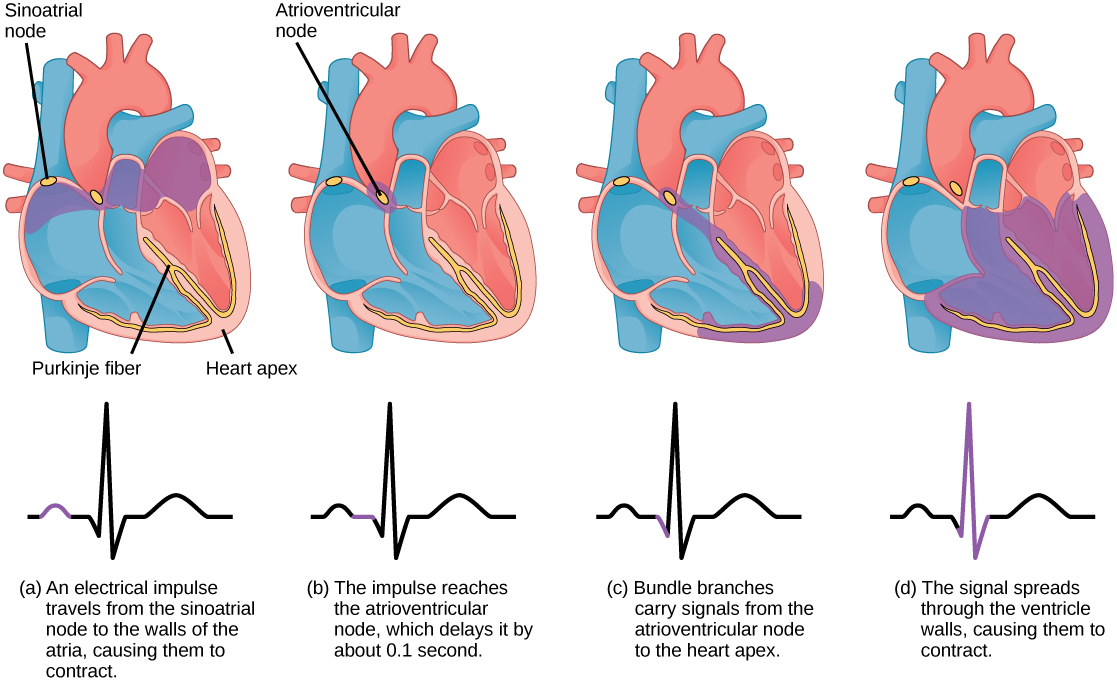
The autonomous beating of cardiac muscle cells is regulated by the heart’s internal pacemaker that uses electrical signals to time the beating of the heart. The electrical signals and mechanical actions, illustrated in [link] , are intimately intertwined. The internal pacemaker starts at the sinoatrial (SA) node , which is located near the wall of the right atrium. Electrical charges spontaneously pulse from the SA node causing the two atria to contract in unison. The pulse reaches a second node, called the atrioventricular (AV) node, between the right atrium and right ventricle where it pauses for approximately 0.1 second before spreading to the walls of the ventricles. From the AV node, the electrical impulse enters the bundle of His, then to the left and right bundle branches extending through the interventricular septum. Finally, the Purkinje fibers conduct the impulse from the apex of the heart up the ventricular myocardium, and then the ventricles contract. This pause allows the atria to empty completely into the ventricles before the ventricles pump out the blood. The electrical impulses in the heart produce electrical currents that flow through the body and can be measured on the skin using electrodes. This information can be observed as an electrocardiogram (ECG) —a recording of the electrical impulses of the cardiac muscle.
Visit this site to see the heart’s “pacemaker” in action.
The blood from the heart is carried through the body by a complex network of blood vessels ( [link] ). Arteries take blood away from the heart. The main artery is the aorta that branches into major arteries that take blood to different limbs and organs. These major arteries include the carotid artery that takes blood to the brain, the brachial arteries that take blood to the arms, and the thoracic artery that takes blood to the thorax and then into the hepatic, renal, and gastric arteries for the liver, kidney, and stomach, respectively. The iliac artery takes blood to the lower limbs. The major arteries diverge into minor arteries, and then smaller vessels called arterioles , to reach more deeply into the muscles and organs of the body.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?