| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
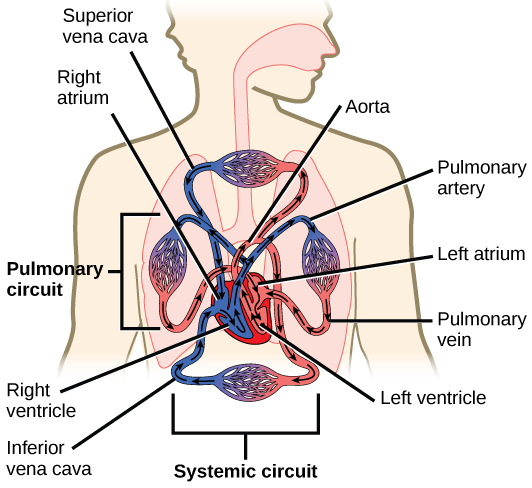
The heart is a complex muscle that pumps blood through the three divisions of the circulatory system: the coronary (vessels that serve the heart), pulmonary (heart and lungs), and systemic (systems of the body), as shown in [link] . Coronary circulation intrinsic to the heart takes blood directly from the main artery (aorta) coming from the heart. For pulmonary and systemic circulation, the heart has to pump blood to the lungs or the rest of the body, respectively. In vertebrates, the lungs are relatively close to the heart in the thoracic cavity. The shorter distance to pump means that the muscle wall on the right side of the heart is not as thick as the left side which must have enough pressure to pump blood all the way to your big toe.
Which of the following statements about the circulatory system is false?
The heart muscle is asymmetrical as a result of the distance blood must travel in the pulmonary and systemic circuits. Since the right side of the heart sends blood to the pulmonary circuit it is smaller than the left side which must send blood out to the whole body in the systemic circuit, as shown in [link] . In humans, the heart is about the size of a clenched fist; it is divided into four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. There is one atrium and one ventricle on the right side and one atrium and one ventricle on the left side. The atria are the chambers that receive blood, and the ventricles are the chambers that pump blood. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the superior vena cava , which drains blood from the jugular vein that comes from the brain and from the veins that come from the arms, as well as from the inferior vena cava which drains blood from the veins that come from the lower organs and the legs. In addition, the right atrium receives blood from the coronary sinus which drains deoxygenated blood from the heart itself. This deoxygenated blood then passes to the right ventricle through the atrioventricular valve or the tricuspid valve , a flap of connective tissue that opens in only one direction to prevent the backflow of blood. The valve separating the chambers on the left side of the heart valve is called the biscuspid or mitral valve. After it is filled, the right ventricle pumps the blood through the pulmonary arteries, by-passing the semilunar valve (or pulmonic valve) to the lungs for re-oxygenation. After blood passes through the pulmonary arteries, the right semilunar valves close preventing the blood from flowing backwards into the right ventricle. The left atrium then receives the oxygen-rich blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins. This blood passes through the bicuspid valve or mitral valve (the atrioventricular valve on the left side of the heart) to the left ventricle where the blood is pumped out through aorta , the major artery of the body, taking oxygenated blood to the organs and muscles of the body. Once blood is pumped out of the left ventricle and into the aorta, the aortic semilunar valve (or aortic valve) closes preventing blood from flowing backward into the left ventricle. This pattern of pumping is referred to as double circulation and is found in all mammals.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?