| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Somatosensation is a mixed sensory category and includes all sensation received from the skin and mucous membranes, as well from as the limbs and joints. Somatosensation is also known as tactile sense, or more familiarly, as the sense of touch. Somatosensation occurs all over the exterior of the body and at some interior locations as well. A variety of receptor types—embedded in the skin, mucous membranes, muscles, joints, internal organs, and cardiovascular system—play a role.
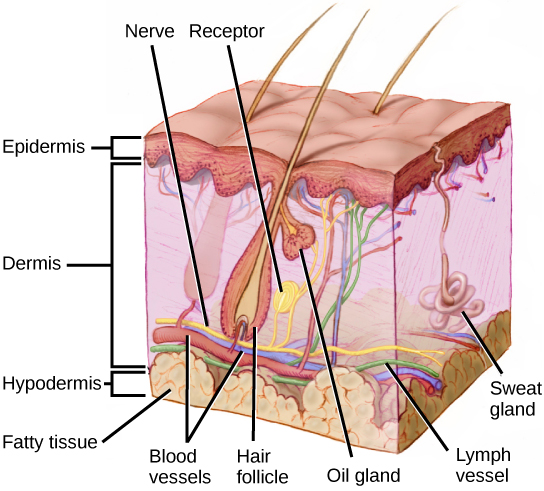
Recall that the epidermis is the outermost layer of skin in mammals. It is relatively thin, is composed of keratin-filled cells, and has no blood supply. The epidermis serves as a barrier to water and to invasion by pathogens. Below this, the much thicker dermis contains blood vessels, sweat glands, hair follicles, lymph vessels, and lipid-secreting sebaceous glands ( [link] ). Below the epidermis and dermis is the subcutaneous tissue, or hypodermis, the fatty layer that contains blood vessels, connective tissue, and the axons of sensory neurons. The hypodermis, which holds about 50 percent of the body’s fat, attaches the dermis to the bone and muscle, and supplies nerves and blood vessels to the dermis.
Sensory receptors are classified into five categories: mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptors, proprioceptors, pain receptors, and chemoreceptors. These categories are based on the nature of stimuli each receptor class transduces. What is commonly referred to as “touch” involves more than one kind of stimulus and more than one kind of receptor. Mechanoreceptors in the skin are described as encapsulated (that is, surrounded by a capsule) or unencapsulated (a group that includes free nerve endings). A free nerve ending , as its name implies, is an unencapsulated dendrite of a sensory neuron. Free nerve endings are the most common nerve endings in skin, and they extend into the middle of the epidermis. Free nerve endings are sensitive to painful stimuli, to hot and cold, and to light touch. They are slow to adjust to a stimulus and so are less sensitive to abrupt changes in stimulation.
There are three classes of mechanoreceptors: tactile, proprioceptors, and baroreceptors. Mechanoreceptors sense stimuli due to physical deformation of their plasma membranes. They contain mechanically gated ion channels whose gates open or close in response to pressure, touch, stretching, and sound.” There are four primary tactile mechanoreceptors in human skin: Merkel’s disks, Meissner’s corpuscles, Ruffini endings, and Pacinian corpuscle; two are located toward the surface of the skin and two are located deeper. A fifth type of mechanoreceptor, Krause end bulbs, are found only in specialized regions. Merkel’s disks (shown in [link] ) are found in the upper layers of skin near the base of the epidermis, both in skin that has hair and on glabrous skin, that is, the hairless skin found on the palms and fingers, the soles of the feet, and the lips of humans and other primates. Merkel’s disks are densely distributed in the fingertips and lips. They are slow-adapting, unencapsulated nerve endings, and they respond to light touch. Light touch, also known as discriminative touch, is a light pressure that allows the location of a stimulus to be pinpointed. The receptive fields of Merkel’s disks are small with well-defined borders. That makes them finely sensitive to edges and they come into use in tasks such as typing on a keyboard.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?