| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In scientific terms, the evolutionary history and relationship of an organism or group of organisms is called its phylogeny . A phylogeny describes the relationships of an organism, such as from which organisms it is thought to have evolved, to which species it is most closely related, and so forth. Phylogenetic relationships provide information on shared ancestry but not necessarily on how organisms are similar or different.
Scientists use a tool called a phylogenetic tree to show the evolutionary pathways and connections among organisms. A phylogenetic tree is a diagram used to reflect evolutionary relationships among organisms or groups of organisms. Scientists consider phylogenetic trees to be a hypothesis of the evolutionary past since one cannot go back to confirm the proposed relationships. In other words, a “tree of life” can be constructed to illustrate when different organisms evolved and to show the relationships among different organisms ( [link] ).
Unlike a taxonomic classification diagram, a phylogenetic tree can be read like a map of evolutionary history. Many phylogenetic trees have a single lineage at the base representing a common ancestor. Scientists call such trees rooted , which means there is a single ancestral lineage (typically drawn from the bottom or left) to which all organisms represented in the diagram relate. Notice in the rooted phylogenetic tree that the three domains— Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya—diverge from a single point and branch off. The small branch that plants and animals (including humans) occupy in this diagram shows how recent and miniscule these groups are compared with other organisms. Unrooted trees don’t show a common ancestor but do show relationships among species.
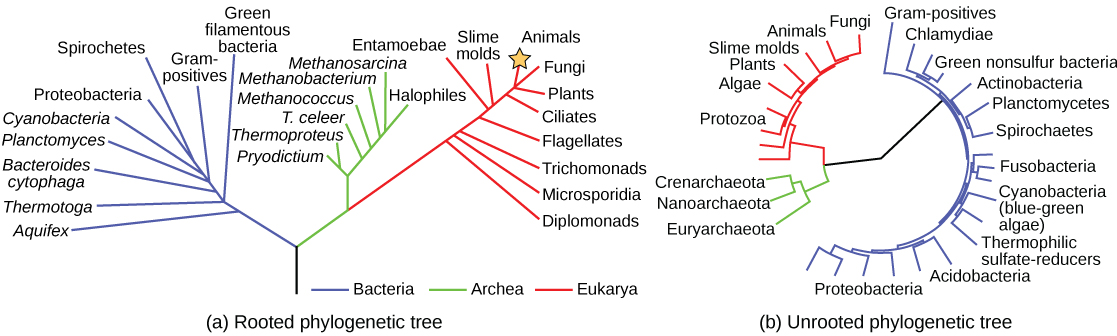
In a rooted tree, the branching indicates evolutionary relationships ( [link] ). The point where a split occurs, called a branch point , represents where a single lineage evolved into a distinct new one. A lineage that evolved early from the root and remains unbranched is called basal taxon . When two lineages stem from the same branch point, they are called sister taxa . A branch with more than two lineages is called a polytomy and serves to illustrate where scientists have not definitively determined all of the relationships. It is important to note that although sister taxa and polytomy do share an ancestor, it does not mean that the groups of organisms split or evolved from each other. Organisms in two taxa may have split apart at a specific branch point, but neither taxa gave rise to the other.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?