| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
One of the fundamental facts of life at Earth’s midlatitudes, where most of this book’s readers live, is that there are significant variations in the heat we receive from the Sun during the course of the year. We thus divide the year into seasons , each with its different amount of sunlight. The difference between seasons gets more pronounced the farther north or south from the equator we travel, and the seasons in the Southern Hemisphere are the opposite of what we find on the northern half of Earth. With these observed facts in mind, let us ask what causes the seasons.
Many people have believed that the seasons were the result of the changing distance between Earth and the Sun. This sounds reasonable at first: it should be colder when Earth is farther from the Sun. But the facts don’t bear out this hypothesis. Although Earth’s orbit around the Sun is an ellipse, its distance from the Sun varies by only about 3%. That’s not enough to cause significant variations in the Sun’s heating. To make matters worse for people in North America who hold this hypothesis, Earth is actually closest to the Sun in January, when the Northern Hemisphere is in the middle of winter. And if distance were the governing factor, why would the two hemispheres have opposite seasons? As we shall show, the seasons are actually caused by the 23.5° tilt of Earth’s axis.
[link] shows Earth’s annual path around the Sun , with Earth’s axis tilted by 23.5°. Note that our axis continues to point the same direction in the sky throughout the year. As Earth travels around the Sun, in June the Northern Hemisphere “leans into” the Sun and is more directly illuminated. In December, the situation is reversed: the Southern Hemisphere leans into the Sun, and the Northern Hemisphere leans away. In September and March, Earth leans “sideways”—neither into the Sun nor away from it—so the two hemispheres are equally favored with sunshine.
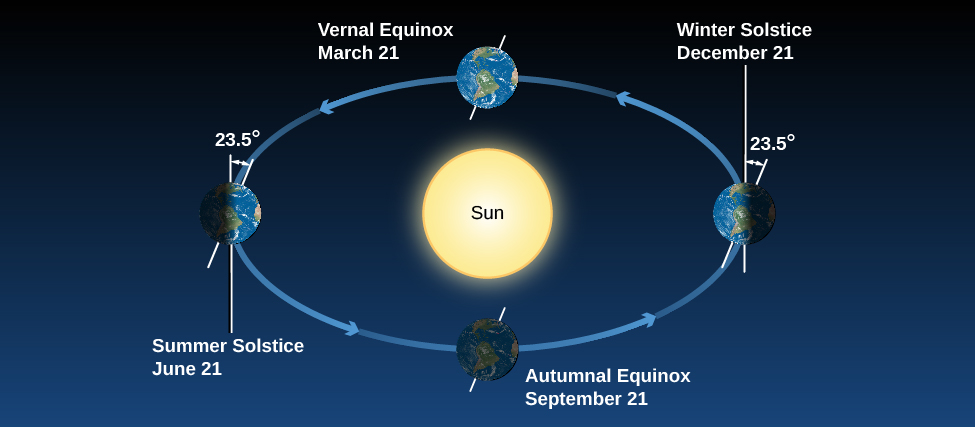
How does the Sun’s favoring one hemisphere translate into making it warmer for us down on the surface of Earth? There are two effects we need to consider. When we lean into the Sun, sunlight hits us at a more direct angle and is more effective at heating Earth’s surface ( [link] ). You can get a similar effect by shining a flashlight onto a wall. If you shine the flashlight straight on, you get an intense spot of light on the wall. But if you hold the flashlight at an angle (if the wall “leans out” of the beam), then the spot of light is more spread out. Like the straight-on light, the sunlight in June is more direct and intense in the Northern Hemisphere, and hence more effective at heating.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?