| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
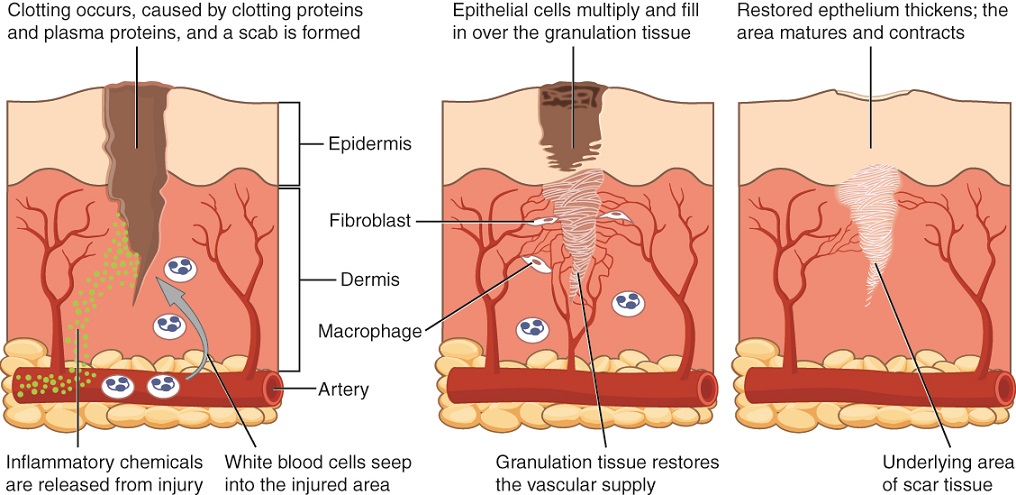
After containment of an injury, the tissue repair phase starts with removal of toxins and waste products. Clotting (coagulation) reduces blood loss from damaged blood vessels and forms a network of fibrin proteins that trap blood cells and bind the edges of the wound together. A scab forms when the clot dries, reducing the risk of infection. Sometimes a mixture of dead leukocytes and fluid called pus accumulates in the wound. As healing progresses, fibroblasts from the surrounding connective tissues replace the collagen and extracellular material lost by the injury. Angiogenesis, the growth of new blood vessels, results in vascularization of the new tissue known as granulation tissue. The clot retracts pulling the edges of the wound together, and it slowly dissolves as the tissue is repaired. When a large amount of granulation tissue forms and capillaries disappear, a pale scar is often visible in the healed area. A primary union describes the healing of a wound where the edges are close together. When there is a gaping wound, it takes longer to refill the area with cells and collagen. The process called secondary union occurs as the edges of the wound are pulled together by what is called wound contraction . When a wound is more than one quarter of an inch deep, sutures (stitches) are recommended to promote a primary union and avoid the formation of a disfiguring scar. Regeneration is the addition of new cells of the same type as the ones that were injured ( [link] ).
Watch this video to see a hand heal. Over what period of time do you think these images were taken?
According to poet Ralph Waldo Emerson, “The surest poison is time.” In fact, biology confirms that many functions of the body decline with age. All the cells, tissues, and organs are affected by senescence, with noticeable variability between individuals owing to different genetic makeup and lifestyles. The outward signs of aging are easily recognizable. The skin and other tissues become thinner and drier, reducing their elasticity, contributing to wrinkles and high blood pressure. Hair turns gray because follicles produce less melanin, the brown pigment of hair and the iris of the eye. The face looks flabby because elastic and collagen fibers decrease in connective tissue and muscle tone is lost. Glasses and hearing aids may become parts of life as the senses slowly deteriorate, all due to reduced elasticity. Overall height decreases as the bones lose calcium and other minerals. With age, fluid decreases in the fibrous cartilage disks intercalated between the vertebrae in the spine. Joints lose cartilage and stiffen. Many tissues, including those in muscles, lose mass through a process called atrophy . Lumps and rigidity become more widespread. As a consequence, the passageways, blood vessels, and airways become more rigid. The brain and spinal cord lose mass. Nerves do not transmit impulses with the same speed and frequency as in the past. Some loss of thought clarity and memory can accompany aging. More severe problems are not necessarily associated with the aging process and may be symptoms of underlying illness.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?