| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The thoracic aorta begins at the level of vertebra T5 and continues through to the diaphragm at the level of T12, initially traveling within the mediastinum to the left of the vertebral column. As it passes through the thoracic region, the thoracic aorta gives rise to several branches, which are collectively referred to as visceral branches and parietal branches ( [link] ). Those branches that supply blood primarily to visceral organs are known as the visceral branches and include the bronchial arteries, pericardial arteries, esophageal arteries, and the mediastinal arteries, each named after the tissues it supplies. Each bronchial artery (typically two on the left and one on the right) supplies systemic blood to the lungs and visceral pleura, in addition to the blood pumped to the lungs for oxygenation via the pulmonary circuit. The bronchial arteries follow the same path as the respiratory branches, beginning with the bronchi and ending with the bronchioles. There is considerable, but not total, intermingling of the systemic and pulmonary blood at anastomoses in the smaller branches of the lungs. This may sound incongruous—that is, the mixing of systemic arterial blood high in oxygen with the pulmonary arterial blood lower in oxygen—but the systemic vessels also deliver nutrients to the lung tissue just as they do elsewhere in the body. The mixed blood drains into typical pulmonary veins, whereas the bronchial artery branches remain separate and drain into bronchial veins described later. Each pericardial artery supplies blood to the pericardium, the esophageal artery provides blood to the esophagus, and the mediastinal artery provides blood to the mediastinum. The remaining thoracic aorta branches are collectively referred to as parietal branches or somatic branches, and include the intercostal and superior phrenic arteries. Each intercostal artery provides blood to the muscles of the thoracic cavity and vertebral column. The superior phrenic artery provides blood to the superior surface of the diaphragm. [link] lists the arteries of the thoracic region.
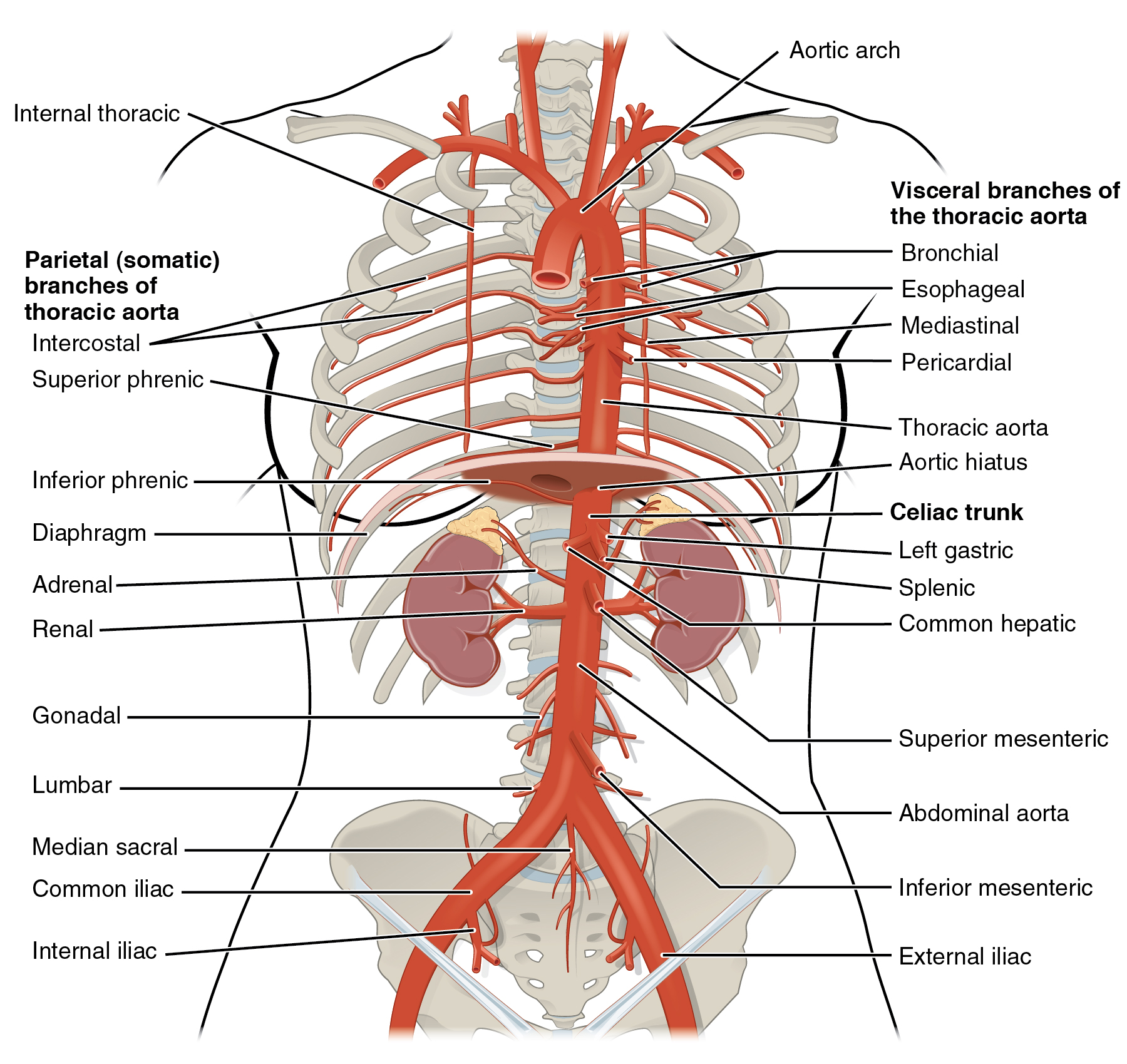
| Arteries of the Thoracic Region | |
|---|---|
| Vessel | Description |
| Visceral branches | A group of arterial branches of the thoracic aorta; supplies blood to the viscera (i.e., organs) of the thorax |
| Bronchial artery | Systemic branch from the aorta that provides oxygenated blood to the lungs; this blood supply is in addition to the pulmonary circuit that brings blood for oxygenation |
| Pericardial artery | Branch of the thoracic aorta; supplies blood to the pericardium |
| Esophageal artery | Branch of the thoracic aorta; supplies blood to the esophagus |
| Mediastinal artery | Branch of the thoracic aorta; supplies blood to the mediastinum |
| Parietal branches | Also called somatic branches, a group of arterial branches of the thoracic aorta; include those that supply blood to the thoracic wall, vertebral column, and the superior surface of the diaphragm |
| Intercostal artery | Branch of the thoracic aorta; supplies blood to the muscles of the thoracic cavity and vertebral column |
| Superior phrenic artery | Branch of the thoracic aorta; supplies blood to the superior surface of the diaphragm |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?