| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As its name suggests, a phospholipid is a bond between the glycerol component of a lipid and a phosphorous molecule. In fact, phospholipids are similar in structure to triglycerides. However, instead of having three fatty acids, a phospholipid is generated from a diglyceride, a glycerol with just two fatty acid chains ( [link] ). The third binding site on the glycerol is taken up by the phosphate group, which in turn is attached to a polar “head” region of the molecule. Recall that triglycerides are nonpolar and hydrophobic. This still holds for the fatty acid portion of a phospholipid compound. However, the head of a phospholipid contains charges on the phosphate groups, as well as on the nitrogen atom. These charges make the phospholipid head hydrophilic. Therefore, phospholipids are said to have hydrophobic tails, containing the neutral fatty acids, and hydrophilic heads, containing the charged phosphate groups and nitrogen atom.
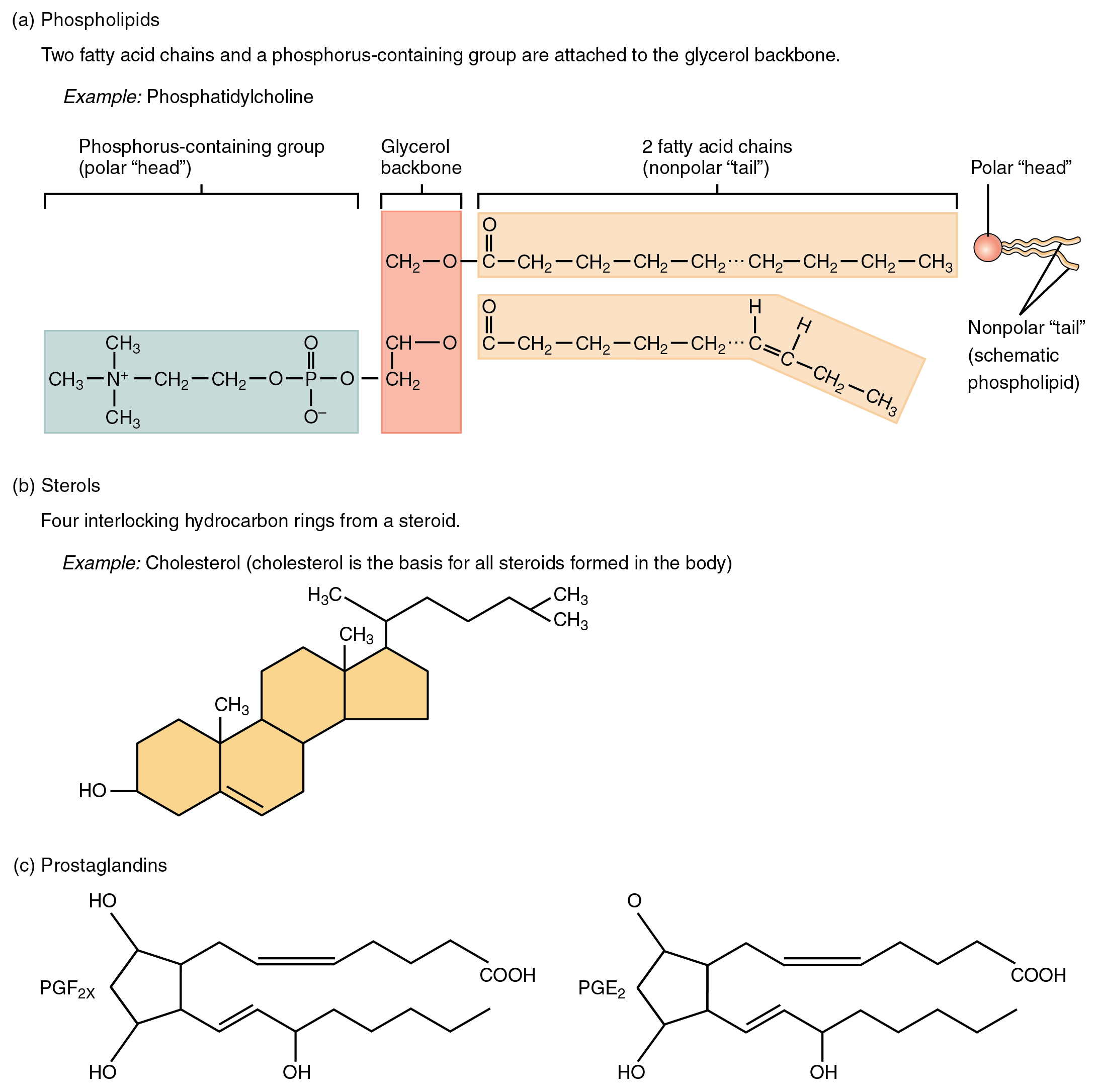
A steroid compound (referred to as a sterol) has as its foundation a set of four hydrocarbon rings bonded to a variety of other atoms and molecules (see [link] b ). Although both plants and animals synthesize sterols, the type that makes the most important contribution to human structure and function is cholesterol, which is synthesized by the liver in humans and animals and is also present in most animal-based foods. Like other lipids, cholesterol’s hydrocarbons make it hydrophobic; however, it has a polar hydroxyl head that is hydrophilic. Cholesterol is an important component of bile acids, compounds that help emulsify dietary fats. In fact, the word root chole- refers to bile. Cholesterol is also a building block of many hormones, signaling molecules that the body releases to regulate processes at distant sites. Finally, like phospholipids, cholesterol molecules are found in the cell membrane, where their hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions help regulate the flow of substances into and out of the cell.
Like a hormone, a prostaglandin is one of a group of signaling molecules, but prostaglandins are derived from unsaturated fatty acids (see [link] c ). One reason that the omega-3 fatty acids found in fish are beneficial is that they stimulate the production of certain prostaglandins that help regulate aspects of blood pressure and inflammation, and thereby reduce the risk for heart disease. Prostaglandins also sensitize nerves to pain. One class of pain-relieving medications called nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) works by reducing the effects of prostaglandins.
You might associate proteins with muscle tissue, but in fact, proteins are critical components of all tissues and organs. A protein is an organic molecule composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Proteins include the keratin in the epidermis of skin that protects underlying tissues, the collagen found in the dermis of skin, in bones, and in the meninges that cover the brain and spinal cord. Proteins are also components of many of the body’s functional chemicals, including digestive enzymes in the digestive tract, antibodies, the neurotransmitters that neurons use to communicate with other cells, and the peptide-based hormones that regulate certain body functions (for instance, growth hormone). While carbohydrates and lipids are composed of hydrocarbons and oxygen, all proteins also contain nitrogen (N), and many contain sulfur (S), in addition to carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?