| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
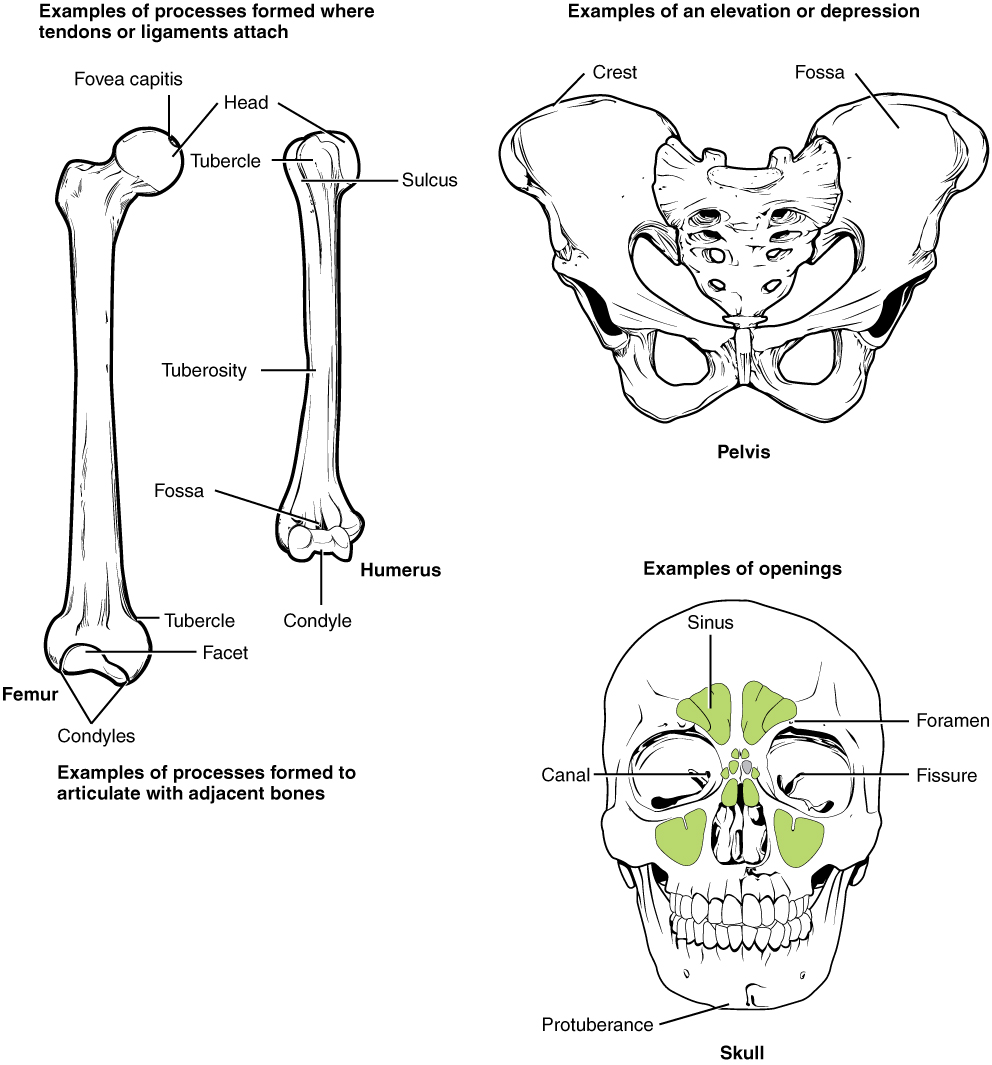
The surface features of bones vary considerably, depending on the function and location in the body. [link] describes the bone markings, which are illustrated in ( [link] ). There are three general classes of bone markings: (1) articulations, (2) projections, and (3) holes. As the name implies, an articulation is where two bone surfaces come together (articulus = “joint”). These surfaces tend to conform to one another, such as one being rounded and the other cupped, to facilitate the function of the articulation. A projection is an area of a bone that projects above the surface of the bone. These are the attachment points for tendons and ligaments. In general, their size and shape is an indication of the forces exerted through the attachment to the bone. A hole is an opening or groove in the bone that allows blood vessels and nerves to enter the bone. As with the other markings, their size and shape reflect the size of the vessels and nerves that penetrate the bone at these points.
| Bone Markings | ||
|---|---|---|
| Marking | Description | Example |
| Articulations | Where two bones meet | Knee joint |
| Head | Prominent rounded surface | Head of femur |
| Facet | Flat surface | Vertebrae |
| Condyle | Rounded surface | Occipital condyles |
| Projections | Raised markings | Spinous process of the vertebrae |
| Protuberance | Protruding | Chin |
| Process | Prominence feature | Transverse process of vertebra |
| Spine | Sharp process | Ischial spine |
| Tubercle | Small, rounded process | Tubercle of humerus |
| Tuberosity | Rough surface | Deltoid tuberosity |
| Line | Slight, elongated ridge | Temporal lines of the parietal bones |
| Crest | Ridge | Iliac crest |
| Holes | Holes and depressions | Foramen (holes through which blood vessels can pass through) |
| Fossa | Elongated basin | Mandibular fossa |
| Fovea | Small pit | Fovea capitis on the head of the femur |
| Sulcus | Groove | Sigmoid sulcus of the temporal bones |
| Canal | Passage in bone | Auditory canal |
| Fissure | Slit through bone | Auricular fissure |
| Foramen | Hole through bone | Foramen magnum in the occipital bone |
| Meatus | Opening into canal | External auditory meatus |
| Sinus | Air-filled space in bone | Nasal sinus |
Bone contains a relatively small number of cells entrenched in a matrix of collagen fibers that provide a surface for inorganic salt crystals to adhere. These salt crystals form when calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate combine to create hydroxyapatite, which incorporates other inorganic salts like magnesium hydroxide, fluoride, and sulfate as it crystallizes, or calcifies, on the collagen fibers. The hydroxyapatite crystals give bones their hardness and strength, while the collagen fibers give them flexibility so that they are not brittle.
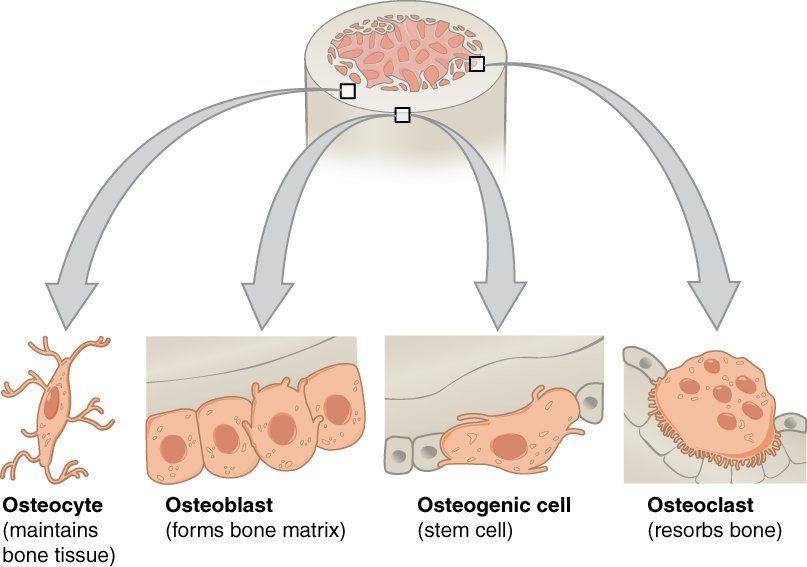
Although bone cells compose a small amount of the bone volume, they are crucial to the function of bones. Four types of cells are found within bone tissue: osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteogenic cells, and osteoclasts ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?