| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
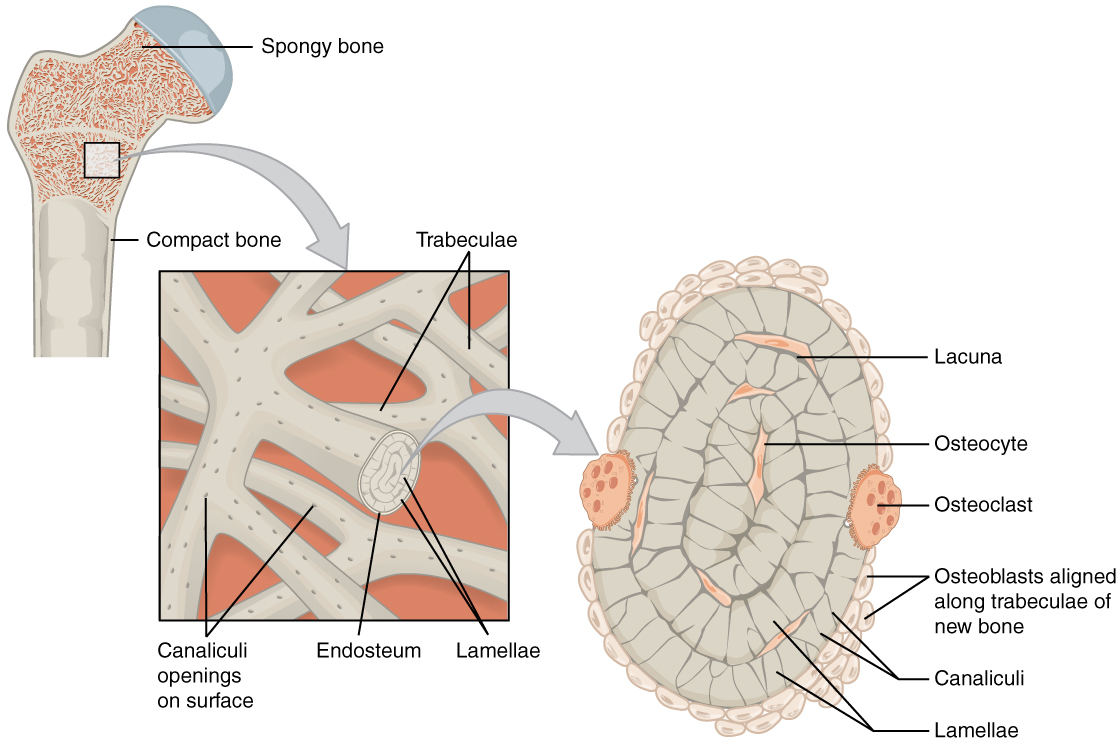
The microscopic structural unit of compact bone is called an osteon , or Haversian system. Each osteon is composed of concentric rings of calcified matrix called lamellae (singular = lamella). Running down the center of each osteon is the central canal , or Haversian canal, which contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels. These vessels and nerves branch off at right angles through a perforating canal , also known as Volkmann’s canals, to extend to the periosteum and endosteum.
The osteocytes are located inside spaces called lacunae (singular = lacuna), found at the borders of adjacent lamellae. As described earlier, canaliculi connect with the canaliculi of other lacunae and eventually with the central canal. This system allows nutrients to be transported to the osteocytes and wastes to be removed from them.
Like compact bone, spongy bone , also known as cancellous bone, contains osteocytes housed in lacunae, but they are not arranged in concentric circles. Instead, the lacunae and osteocytes are found in a lattice-like network of matrix spikes called trabeculae (singular = trabecula) ( [link] ). The trabeculae may appear to be a random network, but each trabecula forms along lines of stress to provide strength to the bone. The spaces of the trabeculated network provide balance to the dense and heavy compact bone by making bones lighter so that muscles can move them more easily. In addition, the spaces in some spongy bones contain red marrow, protected by the trabeculae, where hematopoiesis occurs.
While some people with Paget’s disease have no symptoms, others experience pain, bone fractures, and bone deformities ( [link] ). Bones of the pelvis, skull, spine, and legs are the most commonly affected. When occurring in the skull, Paget’s disease can cause headaches and hearing loss.
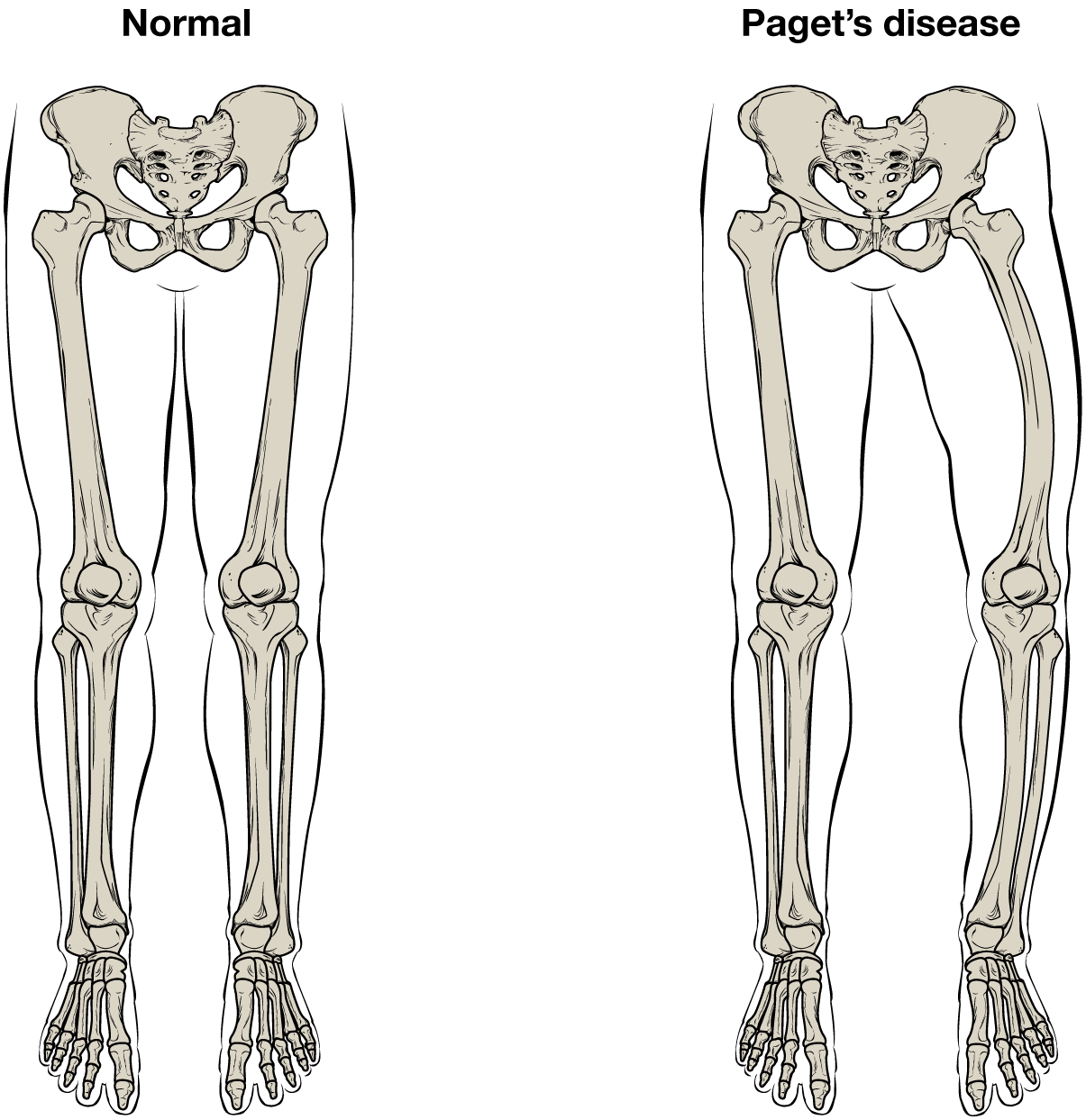
What causes the osteoclasts to become overactive? The answer is still unknown, but hereditary factors seem to play a role. Some scientists believe Paget’s disease is due to an as-yet-unidentified virus.
Paget’s disease is diagnosed via imaging studies and lab tests. X-rays may show bone deformities or areas of bone resorption. Bone scans are also useful. In these studies, a dye containing a radioactive ion is injected into the body. Areas of bone resorption have an affinity for the ion, so they will light up on the scan if the ions are absorbed. In addition, blood levels of an enzyme called alkaline phosphatase are typically elevated in people with Paget’s disease.
Bisphosphonates, drugs that decrease the activity of osteoclasts, are often used in the treatment of Paget’s disease. However, in a small percentage of cases, bisphosphonates themselves have been linked to an increased risk of fractures because the old bone that is left after bisphosphonates are administered becomes worn out and brittle. Still, most doctors feel that the benefits of bisphosphonates more than outweigh the risk; the medical professional has to weigh the benefits and risks on a case-by-case basis. Bisphosphonate treatment can reduce the overall risk of deformities or fractures, which in turn reduces the risk of surgical repair and its associated risks and complications.
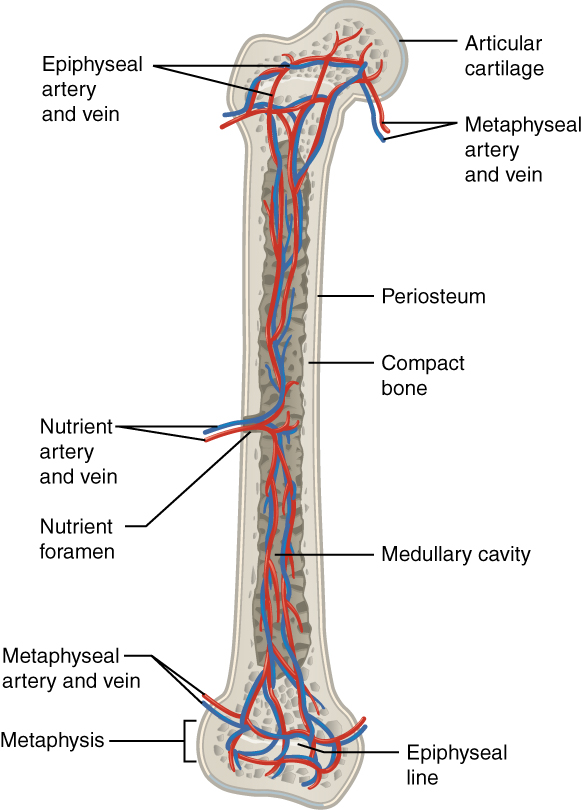
The spongy bone and medullary cavity receive nourishment from arteries that pass through the compact bone. The arteries enter through the nutrient foramen (plural = foramina), small openings in the diaphysis ( [link] ). The osteocytes in spongy bone are nourished by blood vessels of the periosteum that penetrate spongy bone and blood that circulates in the marrow cavities. As the blood passes through the marrow cavities, it is collected by veins, which then pass out of the bone through the foramina.
In addition to the blood vessels, nerves follow the same paths into the bone where they tend to concentrate in the more metabolically active regions of the bone. The nerves sense pain, and it appears the nerves also play roles in regulating blood supplies and in bone growth, hence their concentrations in metabolically active sites of the bone.
Watch this video to see the microscopic features of a bone.
A hollow medullary cavity filled with yellow marrow runs the length of the diaphysis of a long bone. The walls of the diaphysis are compact bone. The epiphyses, which are wider sections at each end of a long bone, are filled with spongy bone and red marrow. The epiphyseal plate, a layer of hyaline cartilage, is replaced by osseous tissue as the organ grows in length. The medullary cavity has a delicate membranous lining called the endosteum. The outer surface of bone, except in regions covered with articular cartilage, is covered with a fibrous membrane called the periosteum. Flat bones consist of two layers of compact bone surrounding a layer of spongy bone. Bone markings depend on the function and location of bones. Articulations are places where two bones meet. Projections stick out from the surface of the bone and provide attachment points for tendons and ligaments. Holes are openings or depressions in the bones.
Bone matrix consists of collagen fibers and organic ground substance, primarily hydroxyapatite formed from calcium salts. Osteogenic cells develop into osteoblasts. Osteoblasts are cells that make new bone. They become osteocytes, the cells of mature bone, when they get trapped in the matrix. Osteoclasts engage in bone resorption. Compact bone is dense and composed of osteons, while spongy bone is less dense and made up of trabeculae. Blood vessels and nerves enter the bone through the nutrient foramina to nourish and innervate bones.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?