| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
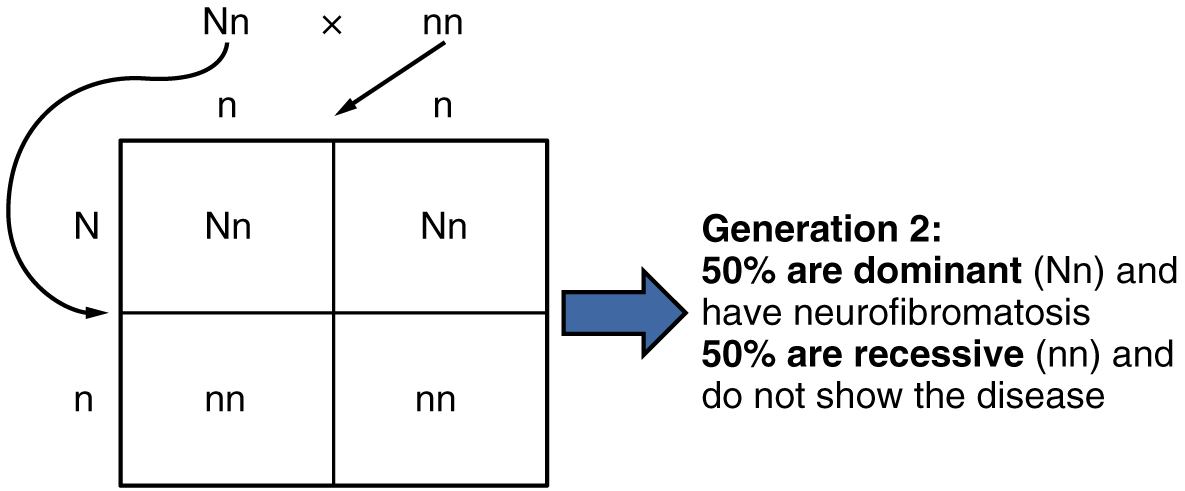
Other genetic diseases that are inherited in this pattern are achondroplastic dwarfism, Marfan syndrome, and Huntington’s disease. Because autosomal dominant disorders are expressed by the presence of just one gene, an individual with the disorder will know that he or she has at least one faulty gene. The expression of the disease may manifest later in life, after the childbearing years, which is the case in Huntington’s disease (discussed in more detail later in this section).
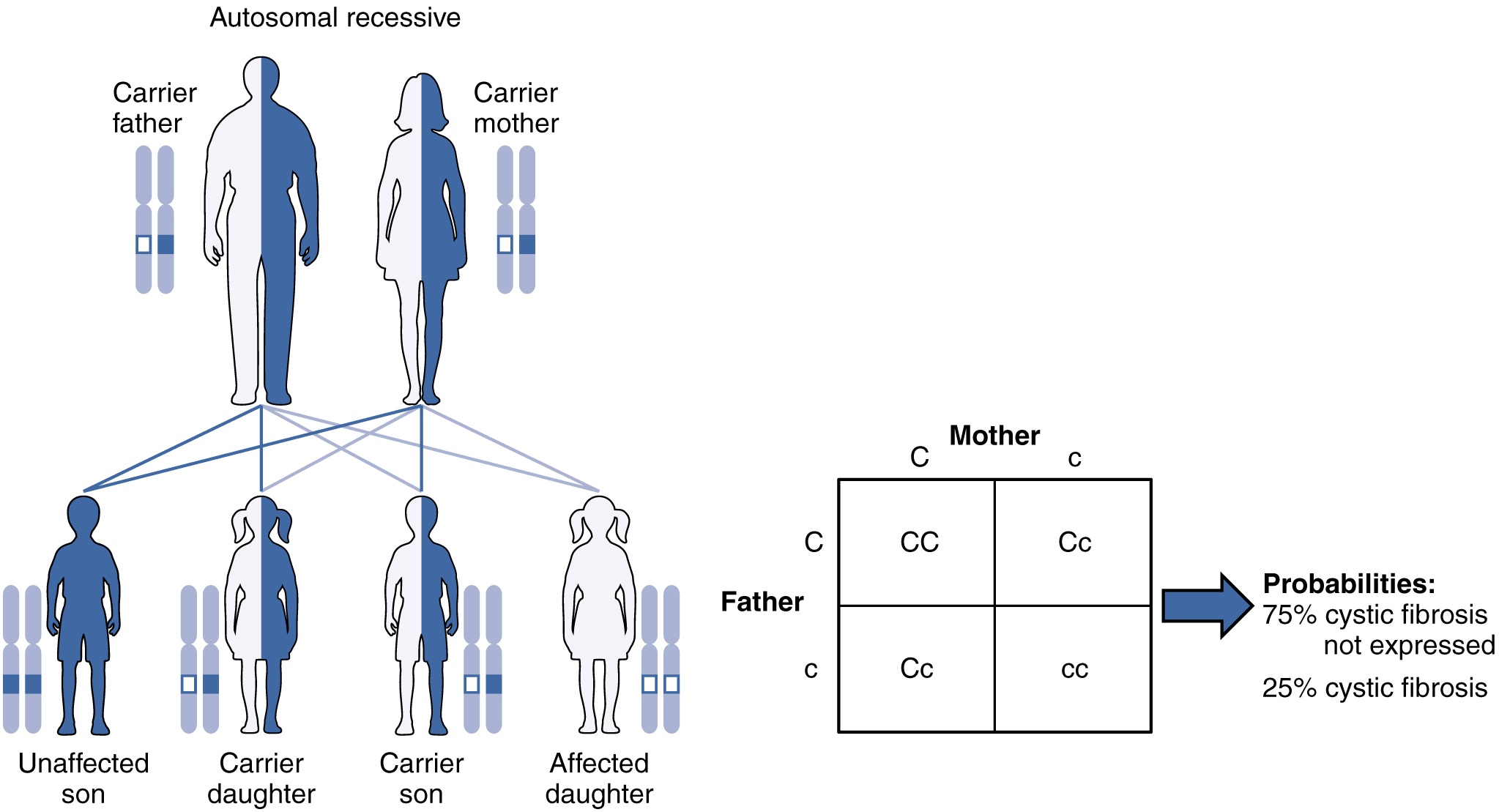
When a genetic disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, the disorder corresponds to the recessive phenotype. Heterozygous individuals will not display symptoms of this disorder, because their unaffected gene will compensate. Such an individual is called a carrier . Carriers for an autosomal recessive disorder may never know their genotype unless they have a child with the disorder.
An example of an autosomal recessive disorder is cystic fibrosis (CF), which we introduced earlier. CF is characterized by the chronic accumulation of a thick, tenacious mucus in the lungs and digestive tract. Decades ago, children with CF rarely lived to adulthood. With advances in medical technology, the average lifespan in developed countries has increased into middle adulthood. CF is a relatively common disorder that occurs in approximately 1 in 2000 Caucasians. A child born to two CF carriers would have a 25 percent chance of inheriting the disease. This is the same 3:1 dominant:recessive ratio that Mendel observed in his pea plants would apply here. The pattern is shown in [link] , using a diagram that tracks the likely incidence of an autosomal recessive disorder on the basis of parental genotypes.
On the other hand, a child born to a CF carrier and someone with two unaffected alleles would have a 0 percent probability of inheriting CF, but would have a 50 percent chance of being a carrier. Other examples of autosome recessive genetic illnesses include the blood disorder sickle-cell anemia, the fatal neurological disorder Tay–Sachs disease, and the metabolic disorder phenylketonuria.
An X-linked transmission pattern involves genes located on the X chromosome of the 23rd pair ( [link] ). Recall that a male has one X and one Y chromosome. When a father transmits a Y chromosome, the child is male, and when he transmits an X chromosome, the child is female. A mother can transmit only an X chromosome, as both her sex chromosomes are X chromosomes.
When an abnormal allele for a gene that occurs on the X chromosome is dominant over the normal allele, the pattern is described as X-linked dominant . This is the case with vitamin D–resistant rickets: an affected father would pass the disease gene to all of his daughters, but none of his sons, because he donates only the Y chromosome to his sons (see [link] a ). If it is the mother who is affected, all of her children—male or female—would have a 50 percent chance of inheriting the disorder because she can only pass an X chromosome on to her children (see [link] b ). For an affected female, the inheritance pattern would be identical to that of an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern in which one parent is heterozygous and the other is homozygous for the normal gene.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?