| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
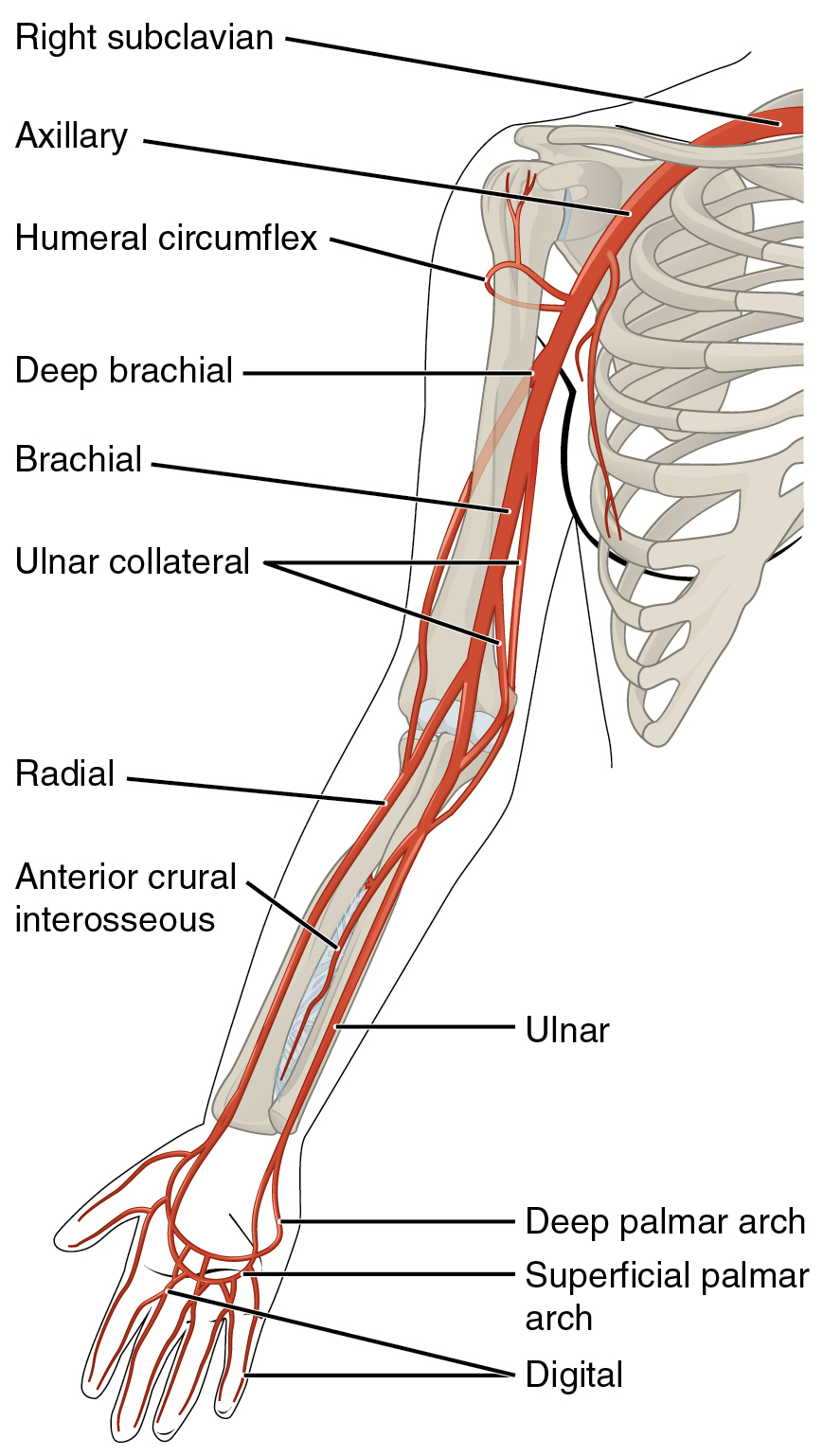
As the subclavian artery exits the thorax into the axillary region, it is renamed the axillary artery . Although it does branch and supply blood to the region near the head of the humerus (via the humeral circumflex arteries), the majority of the vessel continues into the upper arm, or brachium, and becomes the brachial artery ( [link] ). The brachial artery supplies blood to much of the brachial region and divides at the elbow into several smaller branches, including the deep brachial arteries, which provide blood to the posterior surface of the arm, and the ulnar collateral arteries, which supply blood to the region of the elbow. As the brachial artery approaches the coronoid fossa, it bifurcates into the radial and ulnar arteries, which continue into the forearm, or antebrachium. The radial artery and ulnar artery parallel their namesake bones, giving off smaller branches until they reach the wrist, or carpal region. At this level, they fuse to form the superficial and deep palmar arches that supply blood to the hand, as well as the digital arteries that supply blood to the digits. [link] shows the distribution of systemic arteries from the heart into the upper limb. [link] summarizes the arteries serving the upper limbs.

| Arteries Serving the Upper Limbs | |
|---|---|
| Vessel | Description |
| Axillary artery | Continuation of the subclavian artery as it penetrates the body wall and enters the axillary region; supplies blood to the region near the head of the humerus (humeral circumflex arteries); the majority of the vessel continues into the brachium and becomes the brachial artery |
| Brachial artery | Continuation of the axillary artery in the brachium; supplies blood to much of the brachial region; gives off several smaller branches that provide blood to the posterior surface of the arm in the region of the elbow; bifurcates into the radial and ulnar arteries at the coronoid fossa |
| Radial artery | Formed at the bifurcation of the brachial artery; parallels the radius; gives off smaller branches until it reaches the carpal region where it fuses with the ulnar artery to form the superficial and deep palmar arches; supplies blood to the lower arm and carpal region |
| Ulnar artery | Formed at the bifurcation of the brachial artery; parallels the ulna; gives off smaller branches until it reaches the carpal region where it fuses with the radial artery to form the superficial and deep palmar arches; supplies blood to the lower arm and carpal region |
| Palmar arches (superficial and deep) | Formed from anastomosis of the radial and ulnar arteries; supply blood to the hand and digital arteries |
| Digital arteries | Formed from the superficial and deep palmar arches; supply blood to the digits |
The external iliac artery exits the body cavity and enters the femoral region of the lower leg ( [link] ). As it passes through the body wall, it is renamed the femoral artery . It gives off several smaller branches as well as the lateral deep femoral artery that in turn gives rise to a lateral circumflex artery . These arteries supply blood to the deep muscles of the thigh as well as ventral and lateral regions of the integument. The femoral artery also gives rise to the genicular artery , which provides blood to the region of the knee. As the femoral artery passes posterior to the knee near the popliteal fossa, it is called the popliteal artery. The popliteal artery branches into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?