| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Given a sum of cubes or difference of cubes, factor it.
Factor
Notice that and are cubes because Rewrite the sum of cubes as
Factor
Notice that and are cubes because and Write the difference of cubes as
Expressions with fractional or negative exponents can be factored by pulling out a GCF. Look for the variable or exponent that is common to each term of the expression and pull out that variable or exponent raised to the lowest power. These expressions follow the same factoring rules as those with integer exponents. For instance, can be factored by pulling out and being rewritten as
Factor
Factor out the term with the lowest value of the exponent. In this case, that would be
Access these online resources for additional instruction and practice with factoring polynomials.
| difference of squares | |
| perfect square trinomial | |
| sum of cubes | |
| difference of cubes |
If the terms of a polynomial do not have a GCF, does that mean it is not factorable? Explain.
The terms of a polynomial do not have to have a common factor for the entire polynomial to be factorable. For example, and don’t have a common factor, but the whole polynomial is still factorable:
A polynomial is factorable, but it is not a perfect square trinomial or a difference of two squares. Can you factor the polynomial without finding the GCF?
How do you factor by grouping?
Divide the term into the sum of two terms, factor each portion of the expression separately, and then factor out the GCF of the entire expression.
For the following exercises, find the greatest common factor.
For the following exercises, factor by grouping.
For the following exercises, factor the polynomial.
For the following exercises, factor the polynomials.
For the following exercises, consider this scenario:
Charlotte has appointed a chairperson to lead a city beautification project. The first act is to install statues and fountains in one of the city’s parks. The park is a rectangle with an area of m 2 , as shown in the figure below. The length and width of the park are perfect factors of the area.
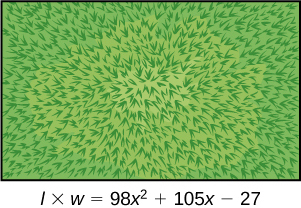
Factor by grouping to find the length and width of the park.
A statue is to be placed in the center of the park. The area of the base of the statue is Factor the area to find the lengths of the sides of the statue.
At the northwest corner of the park, the city is going to install a fountain. The area of the base of the fountain is Factor the area to find the lengths of the sides of the fountain.
For the following exercise, consider the following scenario:
A school is installing a flagpole in the central plaza. The plaza is a square with side length 100 yd. as shown in the figure below. The flagpole will take up a square plot with area yd 2 .
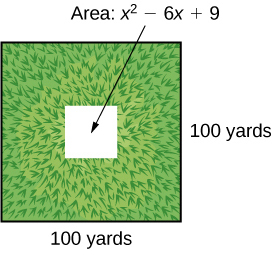
Find the length of the base of the flagpole by factoring.
For the following exercises, factor the polynomials completely.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?