| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

How can the height of a mountain be measured? What about the distance from Earth to the sun? Like many seemingly impossible problems, we rely on mathematical formulas to find the answers. The trigonometric identities, commonly used in mathematical proofs, have had real-world applications for centuries, including their use in calculating long distances.
The trigonometric identities we will examine in this section can be traced to a Persian astronomer who lived around 950 AD, but the ancient Greeks discovered these same formulas much earlier and stated them in terms of chords. These are special equations or postulates, true for all values input to the equations, and with innumerable applications.
In this section, we will learn techniques that will enable us to solve problems such as the ones presented above. The formulas that follow will simplify many trigonometric expressions and equations. Keep in mind that, throughout this section, the term formula is used synonymously with the word identity .
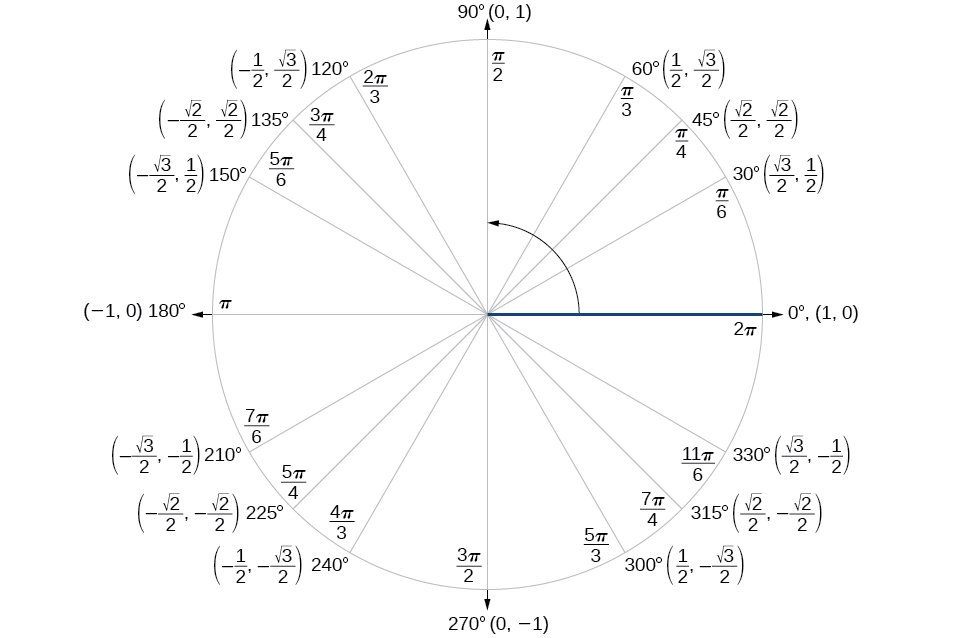
Finding the exact value of the sine, cosine, or tangent of an angle is often easier if we can rewrite the given angle in terms of two angles that have known trigonometric values. We can use the special angles , which we can review in the unit circle shown in [link] .
We will begin with the sum and difference formulas for cosine , so that we can find the cosine of a given angle if we can break it up into the sum or difference of two of the special angles. See [link] .
| Sum formula for cosine | |
| Difference formula for cosine |
First, we will prove the difference formula for cosines. Let’s consider two points on the unit circle. See [link] . Point is at an angle from the positive x- axis with coordinates and point is at an angle of from the positive x- axis with coordinates Note the measure of angle is
Label two more points: at an angle of from the positive x- axis with coordinates and point with coordinates Triangle is a rotation of triangle and thus the distance from to is the same as the distance from to
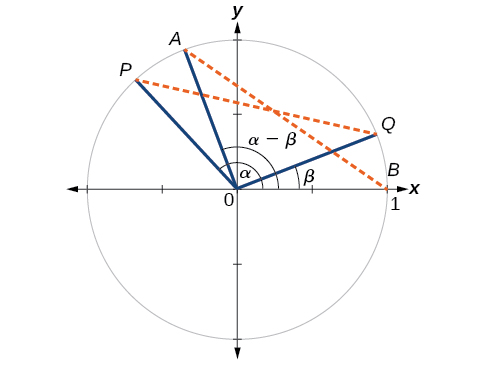
We can find the distance from
to
using the
distance formula .
Then we apply the Pythagorean identity and simplify.
Similarly, using the distance formula we can find the distance from to

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?