| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A tree diagram use branches to show the different outcomes of experiments and makes complex probability questions easy to visualize.
A Venn diagram is a picture that represents the outcomes of an experiment. It generally consists of a box that represents the sample space S together with circles or ovals. The circles or ovals represent events. A Venn diagram is especially helpful for visualizing the OR event, the AND event, and the complement of an event and for understanding conditional probabilities.
The probability that a man develops some form of cancer in his lifetime is 0.4567. The probability that a man has at least one false positive test result (meaning the test comes back for cancer when the man does not have it) is 0.51. Let: C = a man develops cancer in his lifetime; P = man has at least one false positive. Construct a tree diagram of the situation.

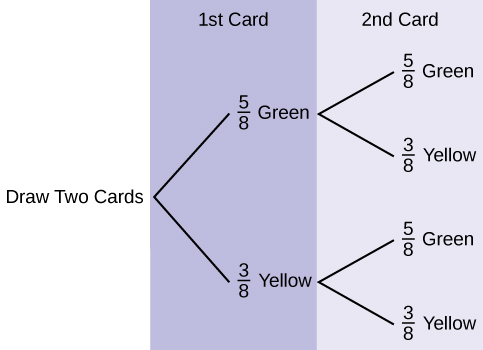
Use the following information to answer the next two exercises. Suppose that you have eight cards. Five are green and three are yellow. The cards are well shuffled.
Suppose that you randomly draw two cards, one at a time,
with replacement .
Let
G
1 = first card is green
Let
G
2 = second card is green
Suppose that you randomly draw two cards, one at a time,
without replacement .
G
1 = first card is green
G
2 = second card is green
Use the following information to answer the next two exercises. The percent of licensed U.S. drivers (from a recent year) that are female is 48.60. Of the females, 5.03% are age 19 and under; 81.36% are age 20–64; 13.61% are age 65 or over. Of the licensed U.S. male drivers, 5.04% are age 19 and under; 81.43% are age 20–64; 13.53% are age 65 or over.
Complete the following.
| <20 | 20–64 | >64 | Totals | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 0.0244 | 0.3954 | 0.0661 | 0.486 |
| Male | 0.0259 | 0.4186 | 0.0695 | 0.514 |
| Totals | 0.0503 | 0.8140 | 0.1356 | 1 |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introductory statistics' conversation and receive update notifications?