| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Suppose is a random variable with a distribution that may be known or unknown (it can be any distribution). Using a subscript that matches the random variable, suppose:
~
The Central Limit Theorem for Sample Means says that if you keep drawing
larger and larger samples (like rolling 1, 2, 5, and, finally, 10 dice) and
calculating their means the sample means form their own
normal distribution (the sampling distribution). The normal distribution has the same
mean as the original distribution and a variance that equals the original variance divided by
, the
sample size.
is the number of values that are averaged together not the number of times the
experiment is done.
To put it more formally, if you draw random samples of size
,the distribution of the random variable
, which consists of sample means, is called the
sampling distribution of the mean . The sampling distribution of the mean approaches a normal distribution as
, the sample size, increases.
The random variable has a different z-score associated with it than the random variable . is the value of in one sample.
is both the average of and of .
standard deviation of and is called the standard error of the mean.
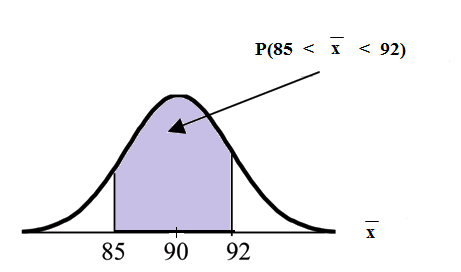
An unknown distribution has a mean of 90 and a standard deviation of 15. Samples of size = 25 are drawn randomly from the population.
Find the probability that the sample mean is between 85 and 92.
Let = one value from the original unknown population. The probability question asks you to find a probability for the sample mean .
Let the mean of a sample of size 25. Since , , and ;
then ~
Find Draw a graph.
The probability that the sample mean is between 85 and 92 is 0.6997.
TI-83 or 84:
normalcdf (lower value, upper value, mean, standard error of the mean)
The parameter list is abbreviated (lower value, upper value, , )
normalcdf
Find the value that is 2 standard deviations above the expected value (it is 90) of the sample mean.
To find the value that is 2 standard deviations above the expected value 90, use the formula
value =
value =
So, the value that is 2 standard deviations above the expected value is 96.
The length of time, in hours, it takes an "over 40" group of people to play one soccer match is normally distributed with a mean of 2 hours and a standard deviation of 0.5 hours . A sample of size = 50 is drawn randomly from the population.
Find the probability that the sample mean is between 1.8 hours and 2.3 hours.
Let = the time, in hours, it takes to play one soccer match.
The probability question asks you to find a probability for the sample mean time, in hours , it takes to play one soccer match.
Let
= the
mean time, in hours, it takes to play one soccer match.
If
_________,
__________,
and
___________,
then
by the Central Limit Theorem for Means.
2 ,
0.5 ,
50 ,
and
Find . Draw a graph.
normalcdf
The probability that the mean time is between 1.8 hours and 2.3 hours is ______.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Collaborative statistics' conversation and receive update notifications?