| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The purpose of a One-Way ANOVA test is to determine the existence of a statistically significant difference among several group means. The test actually uses variances to help determine if the means are equal or not.
In order to perform a One-Way ANOVA test, there are five basic assumptions to be fulfilled:
The null hypothesis is simply that all the group population means are the same. The alternate hypothesis is that at least one pair of means is different. For example, if there are groups:
At least two of the group means are not equal.
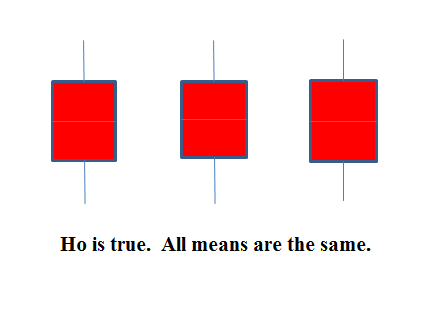
The graphs help in the understanding of the hypothesis test. In the first graph (red box plots),
and the three populations have the same distribution if the null hypothesis is true. The variance of the combined data is approximately the same as the variance of each of the populations.
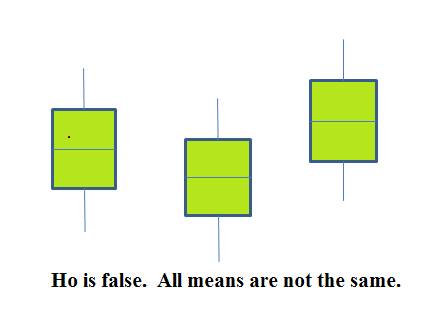
If the null hypothesis is false, then the variance of the combined data is larger which is caused by the different means as shown in the second graph (green box plots).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Collaborative statistics' conversation and receive update notifications?