| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In some data sets, there are values (observed data points) called outliers . Outliers are observed data points that are far from the least squares line. They have large "errors", where the "error" or residual is the vertical distance from the line to the point.
Outliers need to be examined closely. Sometimes, for some reason or another, they should not be included in the analysis of the data. It is possible that an outlier is a result of erroneous data. Other times, an outlier may hold valuable information about the population under study and should remain included in the data. The key is to examine carefully what causes a data point to be an outlier.
Besides outliers, a sample may contain one or a few points that are called influential points . Influential points are observed data points that are far from the other observed data points in the horizontal direction. These points may have a big effect on the slope of the regression line. To begin to identify an influential point, you can remove it from the data set and see if the slope of the regression line is changed significantly.
Computers and many calculators can be used to identify outliers from the data. Computer output for regression analysis will often identify both outliers and influential points so that you can examine them.
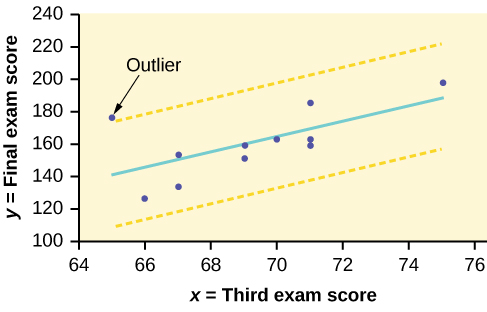
We could guess at outliers by looking at a graph of the scatterplot and best fit-line. However, we would like some guideline as to how far away a point needs to be in order to be considered an outlier. As a rough rule of thumb, we can flag any point that is located further than two standard deviations above or below the best-fit line as an outlier . The standard deviation used is the standard deviation of the residuals or errors.
We can do this visually in the scatter plot by drawing an extra pair of lines that are two standard deviations above and below the best-fit line. Any data points that are outside this extra pair of lines are flagged as potential outliers. Or we can do this numerically by calculating each residual and comparing it to twice the standard deviation. On the TI-83, 83+, or 84+, the graphical approach is easier. The graphical procedure is shown first, followed by the numerical calculations. You would generally need to use only one of these methods.
In the third exam/final exam example , you can determine if there is an outlier or not. If there is an outlier, as an exercise, delete it and fit the remaining data to a new line. For this example, the new line ought to fit the remaining data better. This means the SSE should be smaller and the correlation coefficient ought to be closer to 1 or –1.
As we did with the equation of the regression line and the correlation coefficient, we will use technology to calculate this standard deviation for us. Using the LinRegTTest with this data, scroll down through the output screens to find s = 16.412 .
Line Y2 = –173.5 + 4.83
x –2(16.4) and line Y3 = –173.5 + 4.83
x + 2(16.4)
where
ŷ = –173.5 + 4.83
x is the line of best fit. Y2 and Y3 have the same slope as the line of best fit.
Graph the scatterplot with the best fit line in equation Y1, then enter the two extra lines as Y2 and Y3 in the "Y="equation editor and press ZOOM 9. You will find that the only data point that is not between lines Y2 and Y3 is the point x = 65, y = 175. On the calculator screen it is just barely outside these lines. The outlier is the student who had a grade of 65 on the third exam and 175 on the final exam; this point is further than two standard deviations away from the best-fit line.
Sometimes a point is so close to the lines used to flag outliers on the graph that it is difficult to tell if the point is between or outside the lines. On a computer, enlarging the graph may help; on a small calculator screen, zooming in may make the graph clearer. Note that when the graph does not give a clear enough picture, you can use the numerical comparisons to identify outliers.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introductory statistics' conversation and receive update notifications?