| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In Europe, a woman was near death from a special kind of cancer. There was one drug that the doctors thought might save her. It was a form of radium that a druggist in the same town had recently discovered. The drug was expensive to make, but the druggist was charging ten times what the drug cost him to make. He paid $200 for the radium and charged $2,000 for a small dose of the drug. The sick woman's husband, Heinz, went to everyone he knew to borrow the money, but he could only get together about $1,000, which is half of what it cost. He told the druggist that his wife was dying and asked him to sell it cheaper or let him pay later. But the druggist said: “No, I discovered the drug and I'm going to make money from it.” So Heinz got desperate and broke into the man's store to steal the drug for his wife. Should the husband have done that? (Kohlberg, 1969, p. 379)
How would you answer this dilemma? Kohlberg was not interested in whether you answer yes or no to the dilemma: Instead, he was interested in the reasoning behind your answer.
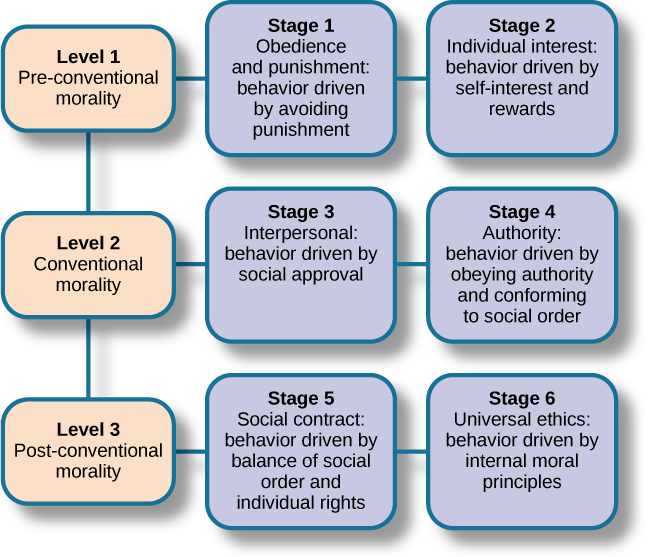
After presenting people with this and various other moral dilemmas, Kohlberg reviewed people’s responses and placed them in different stages of moral reasoning ( [link] ). According to Kohlberg, an individual progresses from the capacity for pre-conventional morality (before age 9) to the capacity for conventional morality (early adolescence), and toward attaining post-conventional morality (once formal operational thought is attained), which only a few fully achieve. Kohlberg placed in the highest stage responses that reflected the reasoning that Heinz should steal the drug because his wife’s life is more important than the pharmacist making money. The value of a human life overrides the pharmacist’s greed.
It is important to realize that even those people who have the most sophisticated, post-conventional reasons for some choices may make other choices for the simplest of pre-conventional reasons. Many psychologists agree with Kohlberg's theory of moral development but point out that moral reasoning is very different from moral behavior. Sometimes what we say we would do in a situation is not what we actually do in that situation. In other words, we might “talk the talk,” but not “walk the walk.”
How does this theory apply to males and females? Kohlberg (1969) felt that more males than females move past stage four in their moral development. He went on to note that women seem to be deficient in their moral reasoning abilities. These ideas were not well received by Carol Gilligan, a research assistant of Kohlberg, who consequently developed her own ideas of moral development. In her groundbreaking book, In a Different Voice: Psychological Theory and Women’s Development , Gilligan (1982) criticized her former mentor’s theory because it was based only on upper class White men and boys. She argued that women are not deficient in their moral reasoning—she proposed that males and females reason differently. Girls and women focus more on staying connected and the importance of interpersonal relationships. Therefore, in the Heinz dilemma, many girls and women respond that Heinz should not steal the medicine. Their reasoning is that if he steals the medicine, is arrested, and is put in jail, then he and his wife will be separated, and she could die while he is still in prison.
There are many theories regarding how babies and children grow and develop into happy, healthy adults. Sigmund Freud suggested that we pass through a series of psychosexual stages in which our energy is focused on certain erogenous zones on the body. Eric Erikson modified Freud’s ideas and suggested a theory of psychosocial development. Erikson said that our social interactions and successful completion of social tasks shape our sense of self. Jean Piaget proposed a theory of cognitive development that explains how children think and reason as they move through various stages. Finally, Lawrence Kohlberg turned his attention to moral development. He said that we pass through three levels of moral thinking that build on our cognitive development.
Explain how you would use your understanding of one of the major developmental theories to deal with each of the difficulties listed below:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?