| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
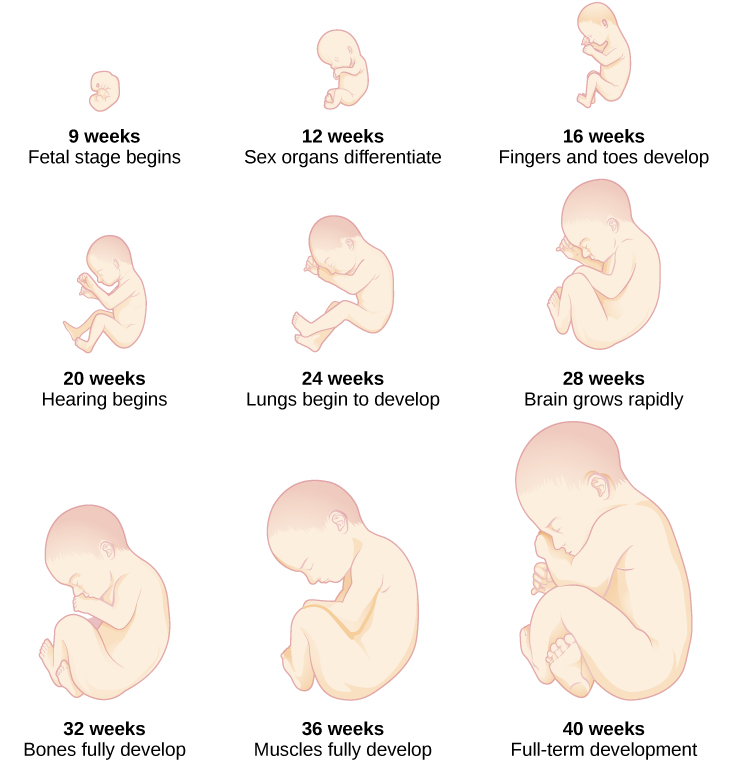
When the organism is about nine weeks old, the embryo is called a fetus. At this stage, the fetus is about the size of a kidney bean and begins to take on the recognizable form of a human being as the “tail” begins to disappear.
From 9–12 weeks, the sex organs begin to differentiate. At about 16 weeks, the fetus is approximately 4.5 inches long. Fingers and toes are fully developed, and fingerprints are visible. By the time the fetus reaches the sixth month of development (24 weeks), it weighs up to 1.4 pounds. Hearing has developed, so the fetus can respond to sounds. The internal organs, such as the lungs, heart, stomach, and intestines, have formed enough that a fetus born prematurely at this point has a chance to survive outside of the mother’s womb. Throughout the fetal stage the brain continues to grow and develop, nearly doubling in size from weeks 16 to 28. Around 36 weeks, the fetus is almost ready for birth. It weighs about 6 pounds and is about 18.5 inches long, and by week 37 all of the fetus’s organ systems are developed enough that it could survive outside the mother’s uterus without many of the risks associated with premature birth. The fetus continues to gain weight and grow in length until approximately 40 weeks. By then, the fetus has very little room to move around and birth becomes imminent. The progression through the stages is shown in [link] .
For an amazing look at prenatal development and the process of birth, view the video Life’s Greatest Miracle from Nova and PBS.
During each prenatal stage, genetic and environmental factors can affect development. The developing fetus is completely dependent on the mother for life. It is important that the mother takes good care of herself and receives prenatal care , which is medical care during pregnancy that monitors the health of both the mother and the fetus ( [link] ). According to the National Institutes of Health ([NIH], 2013), routine prenatal care is important because it can reduce the risk of complications to the mother and fetus during pregnancy. In fact, women who are trying to become pregnant or who may become pregnant should discuss pregnancy planning with their doctor. They may be advised, for example, to take a vitamin containing folic acid, which helps prevent certain birth defects, or to monitor aspects of their diet or exercise routines.
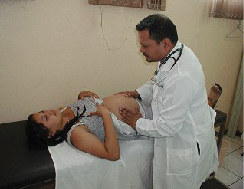
Recall that when the zygote attaches to the wall of the mother’s uterus, the placenta is formed. The placenta provides nourishment and oxygen to the fetus. Most everything the mother ingests, including food, liquid, and even medication, travels through the placenta to the fetus, hence the common phrase “eating for two.” Anything the mother is exposed to in the environment affects the fetus; if the mother is exposed to something harmful, the child can show life-long effects.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?