| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Although strict behaviorists such as Skinner and Watson refused to believe that cognition (such as thoughts and expectations) plays a role in learning, another behaviorist, Edward C. Tolman , had a different opinion. Tolman’s experiments with rats demonstrated that organisms can learn even if they do not receive immediate reinforcement (Tolman&Honzik, 1930; Tolman, Ritchie,&Kalish, 1946). This finding was in conflict with the prevailing idea at the time that reinforcement must be immediate in order for learning to occur, thus suggesting a cognitive aspect to learning.
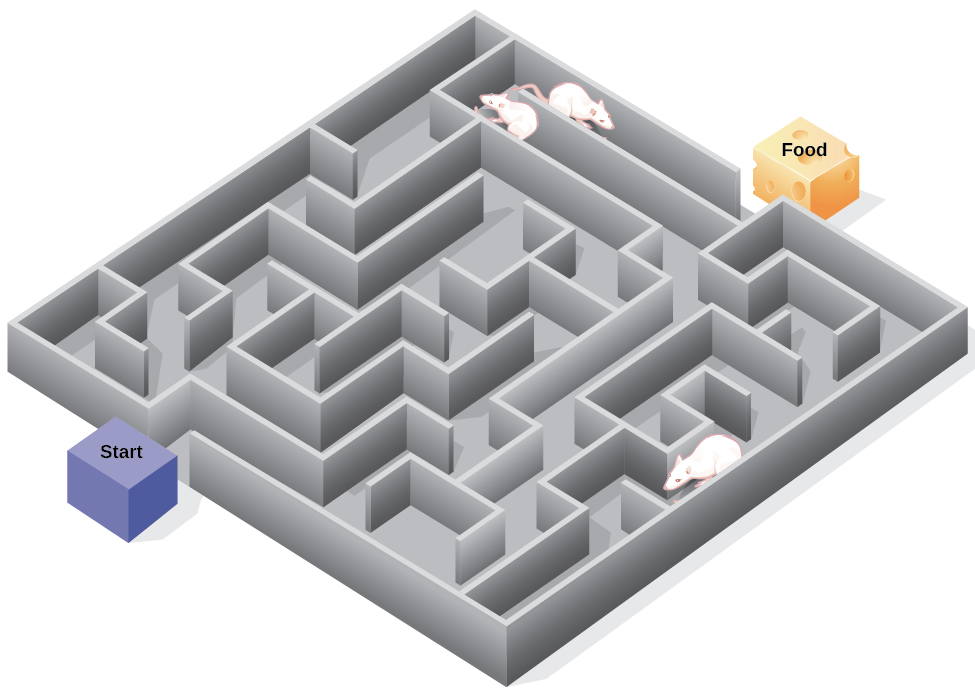
In the experiments, Tolman placed hungry rats in a maze with no reward for finding their way through it. He also studied a comparison group that was rewarded with food at the end of the maze. As the unreinforced rats explored the maze, they developed a cognitive map : a mental picture of the layout of the maze ( [link] ). After 10 sessions in the maze without reinforcement, food was placed in a goal box at the end of the maze. As soon as the rats became aware of the food, they were able to find their way through the maze quickly, just as quickly as the comparison group, which had been rewarded with food all along. This is known as latent learning : learning that occurs but is not observable in behavior until there is a reason to demonstrate it.
Latent learning also occurs in humans. Children may learn by watching the actions of their parents but only demonstrate it at a later date, when the learned material is needed. For example, suppose that Ravi’s dad drives him to school every day. In this way, Ravi learns the route from his house to his school, but he’s never driven there himself, so he has not had a chance to demonstrate that he’s learned the way. One morning Ravi’s dad has to leave early for a meeting, so he can’t drive Ravi to school. Instead, Ravi follows the same route on his bike that his dad would have taken in the car. This demonstrates latent learning. Ravi had learned the route to school, but had no need to demonstrate this knowledge earlier.
Have you ever gotten lost in a building and couldn’t find your way back out? While that can be frustrating, you’re not alone. At one time or another we’ve all gotten lost in places like a museum, hospital, or university library. Whenever we go someplace new, we build a mental representation—or cognitive map—of the location, as Tolman’s rats built a cognitive map of their maze. However, some buildings are confusing because they include many areas that look alike or have short lines of sight. Because of this, it’s often difficult to predict what’s around a corner or decide whether to turn left or right to get out of a building. Psychologist Laura Carlson (2010) suggests that what we place in our cognitive map can impact our success in navigating through the environment. She suggests that paying attention to specific features upon entering a building, such as a picture on the wall, a fountain, a statue, or an escalator, adds information to our cognitive map that can be used later to help find our way out of the building.
Watch this video to learn more about Carlson’s studies on cognitive maps and navigation in buildings.
Operant conditioning is based on the work of B. F. Skinner. Operant conditioning is a form of learning in which the motivation for a behavior happens after the behavior is demonstrated. An animal or a human receives a consequence after performing a specific behavior. The consequence is either a reinforcer or a punisher. All reinforcement (positive or negative) increases the likelihood of a behavioral response. All punishment (positive or negative) decreases the likelihood of a behavioral response. Several types of reinforcement schedules are used to reward behavior depending on either a set or variable period of time.
Explain the difference between negative reinforcement and punishment, and provide several examples of each based on your own experiences.
Think of a behavior that you have that you would like to change. How could you use behavior modification, specifically positive reinforcement, to change your behavior? What is your positive reinforcer?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?