| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
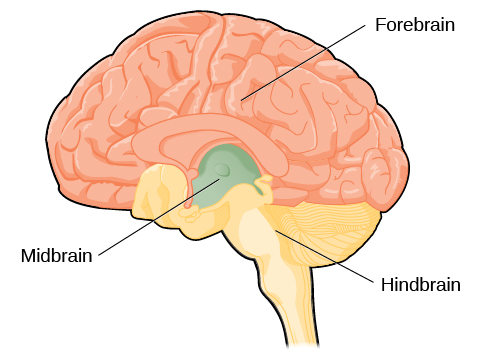
The two hemispheres of the cerebral cortex are part of the forebrain ( [link] ), which is the largest part of the brain. The forebrain contains the cerebral cortex and a number of other structures that lie beneath the cortex (called subcortical structures): thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and the limbic system (collection of structures). The cerebral cortex, which is the outer surface of the brain, is associated with higher level processes such as consciousness, thought, emotion, reasoning, language, and memory. Each cerebral hemisphere can be subdivided into four lobes, each associated with different functions.
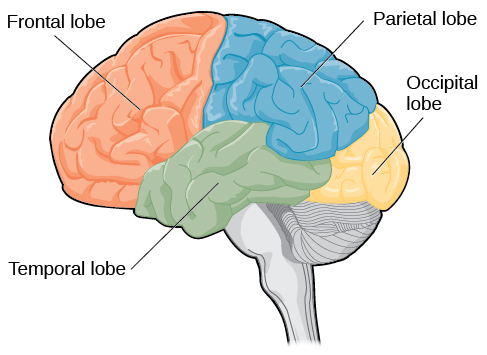
The four lobes of the brain are the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes ( [link] ). The frontal lobe is located in the forward part of the brain, extending back to a fissure known as the central sulcus. The frontal lobe is involved in reasoning, motor control, emotion, and language. It contains the motor cortex , which is involved in planning and coordinating movement; the prefrontal cortex , which is responsible for higher-level cognitive functioning; and Broca’s area , which is essential for language production.
People who suffer damage to Broca’s area have great difficulty producing language of any form ( [link] ). For example, Padma was an electrical engineer who was socially active and a caring, involved mother. About twenty years ago, she was in a car accident and suffered damage to her Broca’s area. She completely lost the ability to speak and form any kind of meaningful language. There is nothing wrong with her mouth or her vocal cords, but she is unable to produce words. She can follow directions but can’t respond verbally, and she can read but no longer write. She can do routine tasks like running to the market to buy milk, but she could not communicate verbally if a situation called for it.
Probably the most famous case of frontal lobe damage is that of a man by the name of Phineas Gage . On September 13, 1848, Gage (age 25) was working as a railroad foreman in Vermont. He and his crew were using an iron rod to tamp explosives down into a blasting hole to remove rock along the railway’s path. Unfortunately, the iron rod created a spark and caused the rod to explode out of the blasting hole, into Gage’s face, and through his skull ( [link] ). Although lying in a pool of his own blood with brain matter emerging from his head, Gage was conscious and able to get up, walk, and speak. But in the months following his accident, people noticed that his personality had changed. Many of his friends described him as no longer being himself. Before the accident, it was said that Gage was a well-mannered, soft-spoken man, but he began to behave in odd and inappropriate ways after the accident. Such changes in personality would be consistent with loss of impulse control—a frontal lobe function.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?